25010 THERMO RETRACTABLE - 25010
Sign up for free and stay up to date on research advancements, health tips, current health topics, and expertise on managing health. Click here for an email preview.
Your healthcare team is likely to ask you many questions. Being ready to answer them may save time to go over any details you want to spend more time on. Your care team may ask:
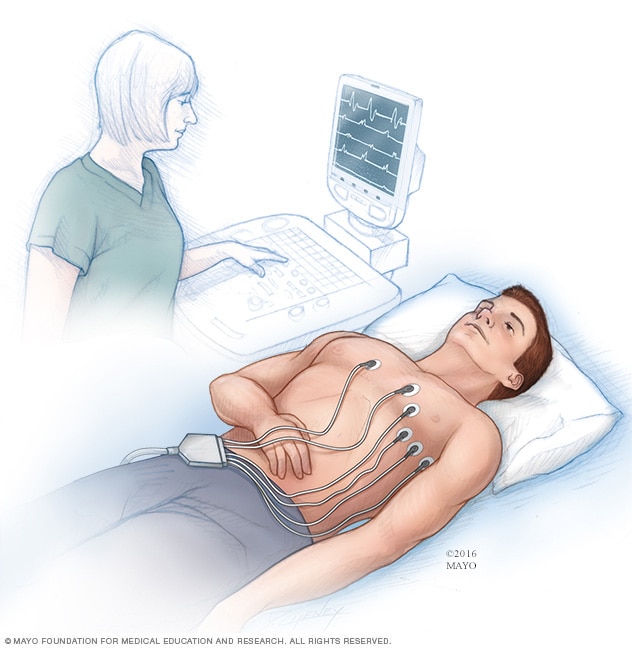
An electrocardiogram (ECG or EKG) is a simple test to determine how the heart is beating. Sensors, called electrodes, are placed on the chest to record the heart's electrical signals. The signals are shown as waves on an attached computer monitor or printer.
If you have tachycardia, you may see a doctor trained in heart conditions. This type of healthcare professional is called a cardiologist. You also might see a doctor trained in heart rhythm disorders, called an electrophysiologist.
Connect with others like you for support and answers to your questions in the Heart Rhythm Conditions support group on Mayo Clinic Connect, a patient community.
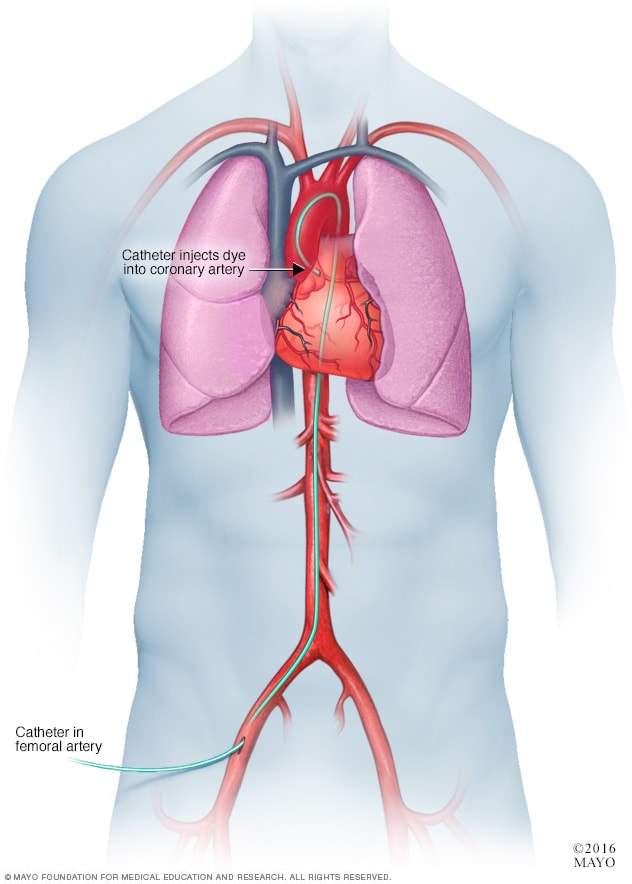
In a coronary angiogram, a flexible tube called a catheter is inserted into an artery, usually in the groin, arm or neck. It's guided to the heart. A coronary angiogram can show blocked or narrowed blood vessels in the heart.
Catheter ablation doesn't require surgery to reach the heart, but it may be done at the same time as other heart surgeries.
There is a problem with information submitted for this request. Review/update the information highlighted below and resubmit the form.
Electrocardiogram (ECG or EKG). This quick test checks the heartbeat. Sticky patches, called electrodes, are attached to the chest and sometimes to the arms or legs. An ECG shows how fast or how slow the heart is beating.
There's often a lot to discuss at a health checkup. It's a good idea to be prepared for your appointment. Here's some information to help you get ready.
If you have tachycardia or any type of heart disease, it's important to take steps to keep your heart healthy. Steps include lifestyle changes such as eating a heart-healthy diet, getting regular exercise, and not smoking or using tobacco. Your care team also may suggest that you limit or avoid caffeine.
Stress-relief techniques, such as meditation and yoga, might help slow the heartbeat. This can reduce tachycardia symptoms.
In a coronary angiogram, a flexible tube called a catheter is inserted into an artery, usually in the groin, arm or neck. It's guided to the heart. A coronary angiogram can show blocked or narrowed blood vessels in the heart.
A Holter monitor is a small, wearable device that continuously checks the heartbeat. It uses one or more sensors called electrodes and a recording device to measure the heart's activity. The device is typically worn for a day or more during daily activities.
To provide you with the most relevant and helpful information, and understand which information is beneficial, we may combine your email and website usage information with other information we have about you. If you are a Mayo Clinic patient, this could include protected health information. If we combine this information with your protected health information, we will treat all of that information as protected health information and will only use or disclose that information as set forth in our notice of privacy practices. You may opt-out of email communications at any time by clicking on the unsubscribe link in the e-mail.
Explore Mayo Clinic studies testing new treatments, interventions and tests as a means to prevent, detect, treat or manage this condition.
To diagnose tachycardia, a healthcare professional examines you and asks questions about your symptoms, health habits and medical history.
Tachycardia treatment involves taking steps to prevent the heart from beating too fast. This may involve medicines, implanted devices, or heart surgeries or procedures.
If another health condition is causing tachycardia, treating the underlying problem may reduce or prevent episodes of a fast heartbeat.
An implantable device, such as a pacemaker or implantable cardioverter-defibrillator (ICD), may be used to treat some types of tachycardia.
Catheter ablation. In this procedure, the doctor inserts thin, flexible tubes called catheters through a blood vessel, usually in the groin. Sensors on the tip of the catheters use heat or cold energy to create tiny scars in the heart. The scars block irregular electrical signals. This helps restore a typical heartbeat.
If you have a plan to manage an episode of a fast heartbeat, you may feel calmer and more in control when one occurs. Ask your care team:
Tests may be done to confirm an unusually fast heartbeat and to look for the cause. Tests to diagnose tachycardia may include:
Electrophysiological (EP) study. This test may be done to confirm a diagnosis of tachycardia. It can help find where in the heart the incorrect signaling occurs. An EP study is mostly used to diagnose some specific types of tachycardias and irregular heartbeats.

A Holter monitor is a small, wearable device that continuously checks the heartbeat. It uses one or more sensors called electrodes and a recording device to measure the heart's activity. The device is typically worn for a day or more during daily activities.
An electrocardiogram (ECG or EKG) is a simple test to determine how the heart is beating. Sensors, called electrodes, are placed on the chest to record the heart's electrical signals. The signals are shown as waves on an attached computer monitor or printer.
During this test, one or more flexible tubes are guided through a blood vessel, usually in the groin, to various areas in the heart. Sensors on the tips of the tubes record the heart's electrical signals.




 0086-813-8127573
0086-813-8127573