Asheville Tool Library - tool library
Medium carbon steel microstructurepdf
This work is licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution International License (CC BY). http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/
Medium carbon steelproperties
Correspondence to: Md Israr Equbal, Department of Mechanical Engineering, Cambridge Institute of Technology, Tatisilwai, Ranchi, India.Email:
Cite this paper: Md Israr Equbal, Parwez Alam, Rajkumar Ohdar, Kumar Aniket Anand, Md. Serfraj Alam, Effect of Cooling Rate on the Microstructure and Mechanical Properties of Medium Carbon Steel, International Journal of Metallurgical Engineering, Vol. 5 No. 2, 2016, pp. 21-24. doi: 10.5923/j.ijmee.20160502.01.
Medium carbon steel microstructurediagram
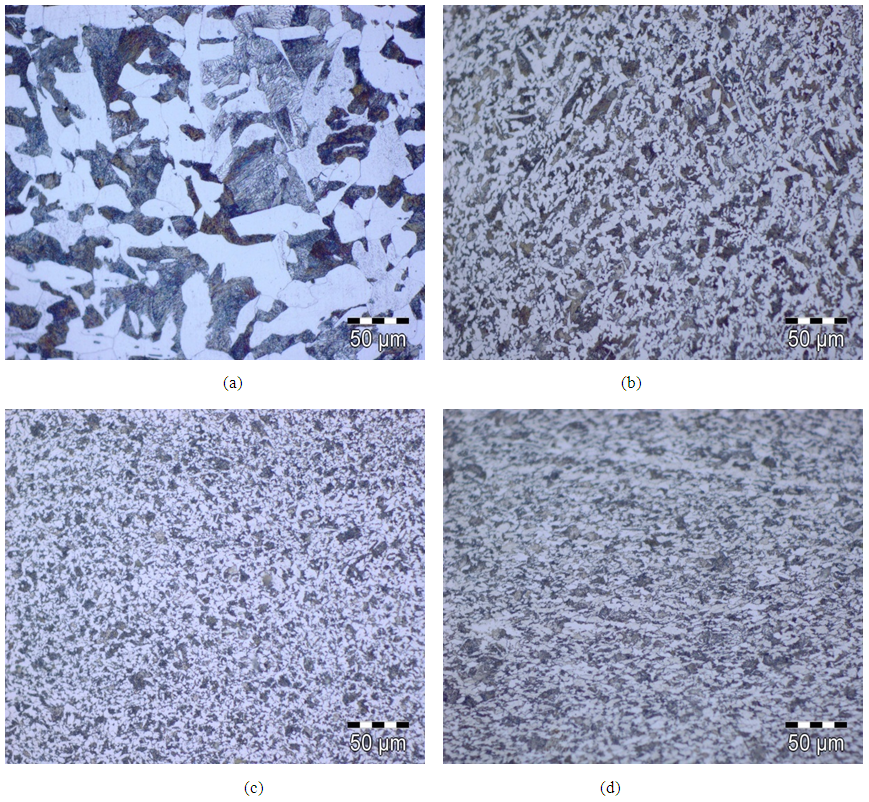
Medium carbon steel is being widely used for machinery structural parts. The microstructure, tensile and impact behaviour of a commercial medium carbon forging steel (AISI 1035) have been determined before and after forging with respect to different cooling conditions in a hydraulic press at 950°C. Final microstructures and mechanical properties were evaluated by optical microscopy, hardness, tensile and impact tests. The results indicated that the microstructures of all forging and cooling conditions are dominated by ferrite and pearlite phases with different morphologies and grain sizes according to various cooling rate. Oil quenching leads to a formation of relatively fine ferrite and pearlite grains in comparison to normal air and forced air cooling. Relatively fine ferrite, pearlite increase strength but decrease ductility. The cooling rate has a remarkable effect on the microstructure and mechanical properties at room temperature.
1Department of Mechanical Engineering, Cambridge Institute of Technology, Tatisilwai, Ranchi, India2Department of Forge Technology, National Institute of Foundry and Forge Technology, Ranchi, India3R&D Centre for Iron and Steel, Steel Authority of India Limited, Ranchi, India




 0086-813-8127573
0086-813-8127573