By manually impacting and cooling drill bit in water may ... - best drill bits for brick
Most commonmachining steel

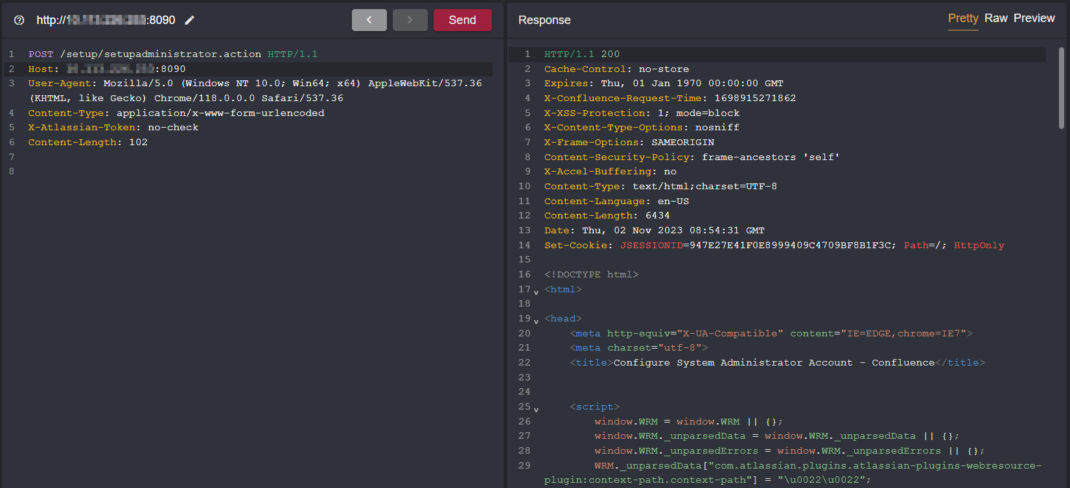
After the setupComplete attribute has been updated, the expected behavior would allow us to access the setup/setup administrator.action endpoint and create an Administrator account.
Steelmachinability chart
Unifying components from classes such as ConfluenceActionSupport, BootstrapStatusProviderImpl, and ApplicationConfig, we can chain method calls, including getBootstrapStatusProvider(), getApplicationConfig(), and setSetupComplete(), which we’ve explored thus far.
Machinability is the ease with which a metal can be cut (machined) permitting the removal of the material with a satisfactory finish at low cost.[1] Materials with good machinability (free machining materials) require little power to cut, can be cut quickly, easily obtain a good finish, and do not cause significant wear on the tooling. Factors that typically improve a material's performance often degrade its machinability, presenting a significant engineering challenge.
Once the vulnerability is successfully detected, users shall see similar results in the vulnerability scan report for both the QIDs:
Machinability can be difficult to predict due to the large number of variables involved in the machining process. Two sets of factors are the condition of work materials and the physical properties of work materials.[2] The condition of the work material includes at least eight factors: microstructure, grain size, heat treatment, chemical composition, fabrication, hardness, yield strength, and tensile strength.[3] Physical properties are those of the individual material groups, such as the modulus of elasticity, thermal conductivity, thermal expansion, and work hardening.[3] Other important factors are operating conditions, cutting tool material and geometry, and the parameters of the specific machining process being performed.[3]
That worked! We have now gained unrestricted access to the endpoint, receiving a 200 status for the Configure System Administrator Account – Confluence page. All that’s left is to include the POST request body with the necessary parameters for the Administrator account.
However, Later Atlassian Security Advisory updated the vulnerability to a Broken Access Control Vulnerability. Thereafter, Qualys WAS has also updated the QID title.
Steel machining propertieschart
The ‘success’ response confirms that the server is operational and doesn’t expose sensitive or detailed information directly through this endpoint.
There are a variety of chemicals, both metal and non-metal, that can be added to steel to make it easier to cut. These additives may work by lubricating the tool-chip interface, decreasing the shear strength of the material, or increasing the brittleness of the chip. Historically, sulfur and lead have been the most common additives, but bismuth and tin are increasingly popular for environmental reasons.
By chaining method calls, we efficiently set the setupComplete value to false using getBootstrapStatusProvider().getApplicationConfig().setSetupComplete(false);
The machinability rating of a material attempts to quantify the machinability of various materials. It is expressed as a percentage or a normalized value. The American Iron and Steel Institute (AISI) determined machinability ratings for a wide variety of materials by running turning tests at 180 surface feet per minute (sfpm).[9] It then arbitrarily assigned 160 Brinell B1112 steel a machinability rating of 100%.[9] The machinability rating is determined by measuring the weighted averages of the normal cutting speed, surface finish, and tool life for each material.[9] Note that a material with a machinability rating less than 100% would be more difficult to machine than B1112 and material with a value more than 100% would be easier.
Machinability can be based on the measure of how long a tool lasts. This can be useful when comparing materials that have similar properties and power consumptions, but one is more abrasive and thus decreases the tool life. The major downfall with this approach is that tool life is dependent on more than just the material it is machining; other factors include cutting tool material, cutting tool geometry, machine condition, cutting tool clamping, cutting speed, feed, and depth of cut. Also, the machinability for one tool type cannot be compared to another tool type (i.e. HSS tool to a carbide tool).[6]
The advantage of this method is that it is easily measured with the appropriate equipment. The disadvantage of this criterion is that it is often irrelevant. For instance when making a rough cut, the surface finish is of no importance. Also, finish cuts often require a certain accuracy that naturally achieves a good surface finish. This rating method also doesn't always agree with other methods. For instance titanium alloys would rate well by the surface finish method, low by the tool life method, and intermediate by the power consumption method.[7][8]
QID 150745 is an intrusive detection that exploits vulnerable servers by sending requests to the vulnerable endpoint. Vulnerable and unpatched servers are flagged when application configuration alteration is confirmed. Subsequently, it verifies the accessibility of Administrator endpoints and finally leverages the same vulnerability to restore the application configuration.
Machinability ratings can be used in conjunction with the Taylor tool life equation, V T n = C {\displaystyle VT^{n}=C} , in order to determine cutting speeds or tool life. It is known that B1112 has a tool life of 60 minutes at a cutting speed of 100 sfpm. If a material has a machinability rating of 70%, it can be determined, with the above knowns, that in order to maintain the same tool life (60 minutes) the cutting speed must be 70 sfpm (assuming the same tooling is used).[1]
There are many factors affecting machinability, but no widely accepted way to quantify it. Instead, machinability is often assessed on a case-by-case basis, and tests are tailored to the needs of a specific manufacturing process. Common metrics for comparison include tool life, surface finish quality, cutting temperature, tool forces, and power consumption.[5][6]
However, when we send a POST request to this endpoint, we receive a 403 Forbidden response status code and a response body containing the following message: ‘Your request could not be processed because a required security token was not present in the request. You may need to re-submit the form or reload the page.’
Best mildsteelformachining
Using the payload against the server-info.action endpoint would adjust the setupComplete value to false, signifying that the setup process remains incomplete.
The machinability of rubber and other soft materials improves by using a very low temperature coolant, such as liquid carbon dioxide. The low temperatures chill the material prior to cutting so that it cannot deform or stick to the cutting edge. This means less wear on the tools and easier machining.
The forces required for a tool to cut through a material is directly related to the power consumed. Therefore, tool forces are often given in units of specific energy. This leads to a rating method where higher specific energies equal lower machinability. The advantage of this method is that outside factors have little effect on the rating.[6]
Confluence uses the XWork2 framework, which manages actions, interceptors, and parameter binding, among other things. In XWork2, HTTP parameters are used to set properties in action classes, and the framework automatically maps these parameters to setter methods based on naming conventions.
Machining steelgrades
Chromium, molybdenum and other alloying metals are often added to steel to improve its strength. However, most of these metals also decrease machinability.
Freemachining steel
Inside the Java class ConfluenceActionSupport, we see a public method named getBootstrapStatusProvider returning an object bootstrapStatusProvider. If the bootstrapStatusProvider is null, it initializes by calling BootstrapStatusProviderImpl.getInstance(), where the getInstance() method appears to get an instance of the bootstrap status provider. Once the object bootstrapStatusProvider is created or already exists, the method returns it.
Thermoplastics are difficult to machine because they have poor thermal conductivity.[10] This creates heat that builds up in the cutting zone, which degrades the tool life and locally melts the plastic. Once the plastic melts, it just flows around the cutting edge instead of being removed by it. Machinability can be improved by using high lubricity coolant and keeping the cutting area free of chip build up.
Aluminium is a much softer metal than steel, and the techniques to improve its machinability usually rely on making it more brittle. Alloys 2007, 2011 and 6020 have very good machinability.[11]
Inside the getApplicationConfig method, the method call to this.delegate.getApplicationConfig(); is using delegation where getApplicationConfig() is delegating the task of fetching application configuration on another object referred to as delegate.
ApplicationConfig class implements the ApplicationConfiguration interface, and we do find a synchronized method called setSetupComplete:
Machiningmaterials chart
The carbon content of steel greatly affects its machinability. High-carbon steels are difficult to machine because they are strong and because they may contain carbides that abrade the cutting tool. On the other end of the spectrum, low-carbon steels are troublesome because they are too soft. Low-carbon steels are "gummy" and stick to the cutting tool, resulting in a built up edge that shortens tool life. Therefore, steel has the best machinability with medium amounts of carbon, about 0.20%.[5]
Stainless steels have poor machinability compared to regular carbon steel because they are tougher, gummier and tend to work harden very rapidly.[5] Slightly hardening the steel may decrease its gumminess and make it easier to cut. AISI grades 303 and 416 are easier to machine because of the addition of sulfur and phosphorus.[11]
Due to the Vulnerability marked as Critical Severity and highlighted as CISA’s Known Exploited Vulnerabilities, organizations using the confluence application are strongly advised to upgrade to version 8.3.3, 8.4.3, 8.5.2, or later releases to remediate CVE-2023-22515 vulnerability. For more patching and threat detection-related details, please refer to Atlassian Security Advisory.
ApplicationConfiguration is an interface specifying multiple methods that any class can implement. Whichever class implements this interface will define the behavior of the methods.
Machinability index ( % ) = cutting speed of material for 20 minute tool life cutting speed of free-cutting steel for 20 minute tool life ∗ 100 {\displaystyle {\text{Machinability index (}}\%{)}={\frac {\text{cutting speed of material for 20 minute tool life}}{\text{cutting speed of free-cutting steel for 20 minute tool life}}}*100}
Beststeelformachiningand welding
Atlassian Security Advisory: https://confluence.atlassian.com/security/cve-2023-22515-privilege-escalation-vulnerability-in-confluence-data-center-and-server-1295682276.html
When this vulnerability was disclosed, Atlassian Security Advisory mentioned this as a Privilege Escalation Vulnerability. Following that, Qualys WAS had released the following QID:
QID 150725 was released with detection logic that detects the vulnerable version of the Confluence application based on the response to requests sent to the server.
Steels are among the most important and commonly used materials in engineering. Free machining steels are alloys that include elements like sulfur and lead that reduce the size of chips produced by the machining process.[4] Free machining steels are more expensive than standard steels, but their cost is offset by savings on manufacturing costs.
The surface finish is sometimes used to measure the machinability of a material. Soft, ductile materials tend to form a built up edge. Stainless steel and other materials with a high strain hardening ability also want to form a built up edge. Aluminium alloys, cold worked steels, and free machining steels, as well as materials with a high shear zone don't tend to form built up edges, so these materials would rank as more machinable.[7]
Lead can improve the machinability of steel because it acts as an internal lubricant in the cutting zone.[10] Since lead has poor shear strength, it allows the chip to slide more freely past the cutting edge. When it is added in small quantities to steel, it can greatly improve its machinability while not significantly affecting the steel's strength.
setSetupComplete method accepts a boolean parameter named setupComplete used to set the setup completion status.The setupComplete variable of the class is assigned a value supplied as the parameter. The purpose of this parameter is to define or update the setup completion status of the Confluence application. The setup process is complete when we pass true as the setupComplete parameter. When we pass false, it indicates that the setup process is incomplete.
Machinability Rating= (Speed of Machining the workpiece giving 60min tool life)/( Speed of machining the standard metal)
In the final step, we proceed with another POST request to the /setup/finishsetup.action endpoint, effectively exiting the setup wizard.
The class ServerInfoAction extends the ConfluenceActionSupport class, which likely handles specific functionalities. Within this class, there’s a method named execute(). It’s designed to be invoked using any HTTP method, exempt from XSRF protection, and accessible to the public without requiring authentication. When the execute method is called, it returns the string “success” once the action was executed successfully.
The initial request is sent to server-info action with bootstrapStatusProvider.applicationConfig.setupComplete=false as the payload parameter. When we access server-info.action endpoint without authentication returns a simple response with a “success” status message.
Concerning the above guide, including X-Atlassian-Token: no-check in the HTTP Request Headers, we trigger the same request:
Atlassian issued an Advisory on October 4, 2023, for CVE-2023-22515, a critical severity vulnerability affecting Confluence Server and Data Center. According to the advisory, the vulnerability was initially published as a Privilege Escalation vulnerability but was later updated to a Broken Access Control Vulnerability, Atlassian has also rated the vulnerability with 10 CVSS score. On October 5, 2023, the vulnerability was included in “CISA’s Known Exploited Vulnerabilities Catalog”.
CVE-2023-22515 is an unauthenticated critical severity vulnerability allowing remote attackers to create unauthorized Confluence Administrator accounts and access Confluence instances. Although the vulnerability is categorized as a Broken Access Control, the initial exploitation stage requires Injection which modifies the application’s configuration, granting unrestricted access to Administrator setup endpoints. The vulnerability affects Confluence versions 8.0.0, 8.0.1, 8.0.2, 8.0.3, 8.0.4, 8.1.0, 8.1.1, 8.1.3, 8.1.4, 8.2.0, 8.2.1, 8.2.2, 8.2.3, 8.3.0, 8.3.1, 8.3.2, 8.4.0, 8.4.1, 8.4.2, 8.5.0, 8.5.1 and is fixed in versions 8.3.3, 8.4.3 and 8.5.2 or later.
Scripts that access Confluence remotely may have trouble acquiring or returning a security token or maintaining an HTTP session with the server. To opt out of token checking, include the following HTTP header in the request: X-Atlassian-Token: no-check
Composites often have the worst machinability because they combine the poor thermal conductivity of a plastic resin with the tough or abrasive qualities of the fiber (glass, carbon etc.) material.

Sulfur improves the machinability of steel by forming low shear strength inclusions in the cutting zone. These inclusions are stress risers that weaken the steel, allowing it to deform more easily.
Following that, BootstrapStatusProviderImpl class at com.atlassian.confluence.impl.setup, comprises a public method named getApplicationConfig which returns the ApplicationConfiguration object.




 0086-813-8127573
0086-813-8127573