Carbide Drill Bits and Accessories - carbine bit
Lathes can be roughly divided into three types, engine lathes, turret lathes, and special lathes. The basic engine lathe is used for most lathes, with the smaller bench or portable machines, or larger vertical tables standing on the floor.
The most common lathe operations are turning, facing, grooving, parting, threading, drilling, boring, knurling, and tapping.
The knurls contain teeth that are rolled against the surface of the workpiece to form serrated patterns. The most common knurled nib is a diamond pattern.
During the drilling process, the material is removed from the interior of a workpiece. The result of drilling is a hole with a diameter equal to the size of the drill used.
Removing material from a workpiece is the lathe’s primary function. As the piece rotates, the cutting tool is pressed against it. This can create threads, holes, faces, and other designs.
To give you an idea of what kind of parts lathes are used to process, most of the products we are familiar with use parts processed by lathes.
A lathe is a machine tool that specializes in processing cylindrical shapes. It is mainly used to process cylinders and cones. In addition, it can also perform drilling and screw machining.
Threading is a turning process in which a tool moves along the side of the workpiece and cuts threads on the outer surface. A thread is a uniform spiral groove with a specific length and pitch. Deeper threads require multiple passes of a tool.
The high-speed lathe can also be called a wood lathe which can be operated at high speed and operated manually. The speed range for high-speed lathes is between 1200 and 3600 RPM. This lathe is used for turning, centering, polishing, and processing wood.
Ornamental lathes can create three-dimensional bodies of incredible complexity. The workpiece is normally held in place by either one or two centers, at least one of which can typically be moved horizontally to accommodate different workpiece lengths.
Roundinsert turningtool
CNC lathes are the most advanced types of lathes available today, and the tolerances of the parts they produce are extremely precise.
High-hardness cermet with outstanding wear resistance and toughness. Realises high dimensional accuracy for continuous steel machining or finishing of powdered metal or cast iron
These lathes can be of the table type or have the support legs cast and attached to the bed. These lathes have most of the attachments that carry the other types of lathes but do not have power provision.
Tough grade for titanium machining with excellent fracture and thermal resistance. Perfect for interrupted cutting and mill-scaled work
The most common lathe operations are turning, facing, grooving, parting, threading, drilling, boring, knurling, and tapping.
Superior fracture resistance, providing excellent stability in interrupted unstable cutting and when cutting mill-scaled work
First, the workpiece is fastened to the chuck. This is the part of the machine that holds the piece in place. The chuck usually grips the outside of the workpiece.
When boring, a tool penetrates the workpiece axially and removes material along the inner surface to either create different shapes or to enlarge an existing hole.
Most suitably equipped metalworking lathes can also be used to produce most solids of revolution, flat surfaces, and screw threads or helixes.
A lathe is a machine tool used to shape wooden or metallic products. It furnishes a wooden or metal piece by rotating it about an axis while a stationary cutting tool keeps removing unwanted material from the workpiece to form the desired shape.
The process design is to define what kind of cutting tools is used, the processing method and the processing order. The machining is done by changing the tool and moving it in accordance with the process order.
Tensile stress removal of the coating layer greatly improves fracture resistance. Achieves long, stable tool life during heavy interrupted cutting
After the edge of the cutting tool reaches the center of the workpiece, the workpiece drops off. A part catcher is often used to catch the removed part.
The usual attachments that are made available on a machine tool lathe are tapered turning attachments, driver support, collets, chucks, etc.
A lathe uses rotational force and a stationary cutting tool to shape a workpiece, which is typically made of metal or wood.
A lathe spins a material and presses a tool (insert) against it to process it. It can be used for various types of machining depending on the type of cutting tool used and how it is moved.
Carbideinsert
These lathes go a long way towards improving both the quality and quantity of production. They are designed in such a way that all work and order processing movements of the entire manufacturing process for an order are carried out automatically.
It is a very small lathe and is mounted on a separately prepared workbench or cupboard. It is used for small and precise work as it is very accurate.
Employs Brilliant Coat PVD coating with excellent lubricity to provide better wear resistance and consistent surface finishes in low-speed cutting applications such as machining of small products or low carbon steel
Rough turning operation aims to machine a piece to within a predefined thickness, by removing the maximum amount of material in the shortest possible time, disregarding the accuracy and surface finish.
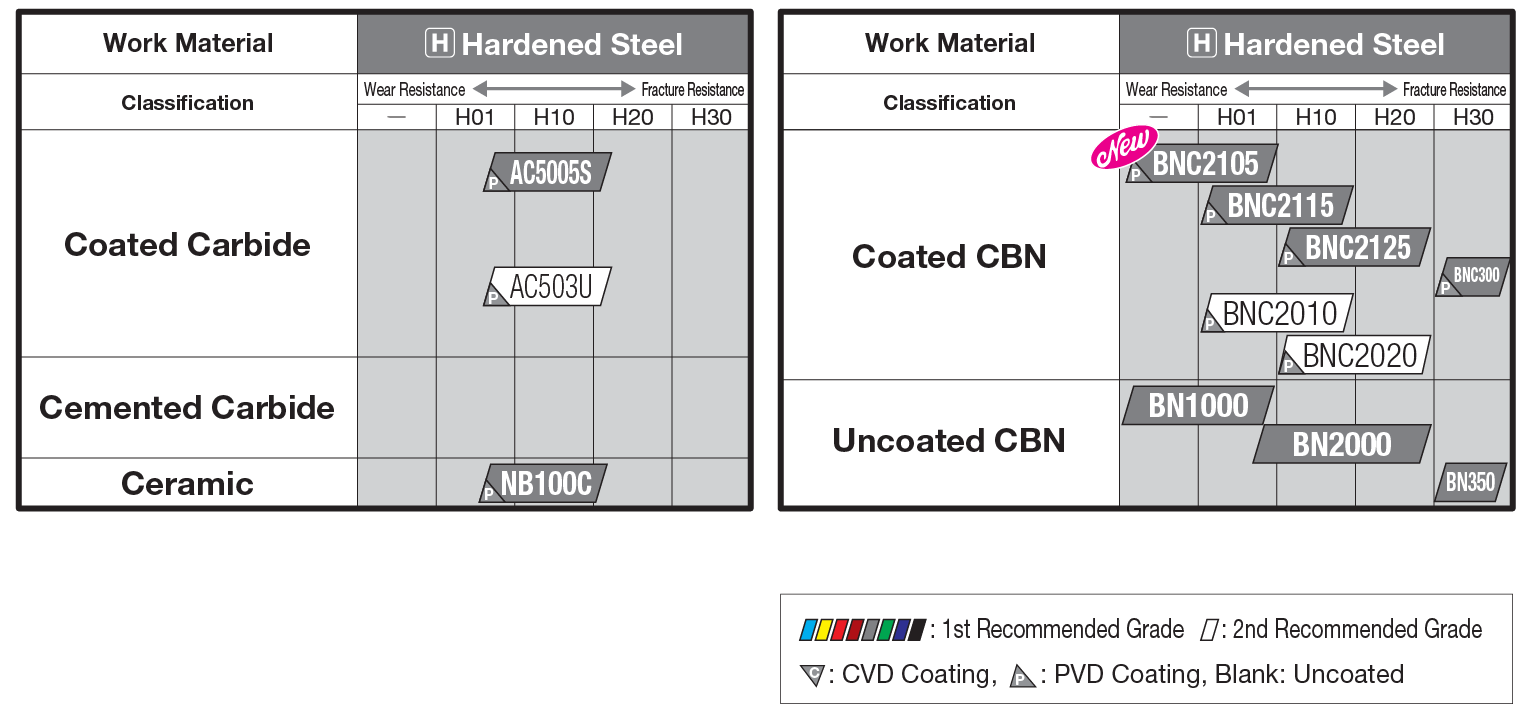
1st recommended grade, balancing excellent wear resistance and fracture resistance in hardened steel machining.Along with a tough CBN substrate, the coating combines wear resistance and toughness to achieve long, stable tool life even in high-efficiency and interrupted machining
Turning tools can cut material off of the workpiece. These flat blades are the most common kind of cutting tool used in lathe work.
Our 1st recommended grade for turning exotic alloys as it realises stable tool life with high-speed, high-efficiency machining
No operator involvement is required during operation. Another variant of this type of lathes is the semi-automatic lathes, in which the operator puts the work on and takes off, while all operations are carried out automatically by the machine.
This type of lathe is currently widely used and can perform operations such as turning, end face, grooving, knurling, and threading. The feed mechanism of the engine lathe can operate the cutting tool in both longitudinal and lateral directions.
In lathe machine work, different operations require different types of lathe cutting tools, according to the process of using the lathe cutting tools. which are as follows,
Combines a high-hardness carbide substrate with excellent wear resistance and a new CVD coating with improved coating strength to achieve both excellent wear resistance and fracture resistance. Achieves long, stable tool life during high-speed cutting
High-density sintered material made of ultra-fine grain diamond that demonstrates optimum wear and fracture resistance and excellent edge sharpness
A lathe is a machining tool that is used primarily for shaping metal or wood. It works by rotating the workpiece around a stationary cutting tool. The main use is to remove unwanted parts of the material, leaving behind a nicely shaped workpiece.
A lathe machine operates on a simple principle, but it has many complex moving parts. Most lathes contain a headstock, tailstock, spindle, motor, chuck, and an assortment of cutting tools.
Other work-holding methods include clamping the workpiece about the axis of rotation using a chuck or collet, or to a faceplate, using clamps or jaw clutch.
The spindle, which is attached to the chuck, is connected to the engine that rotates the workpiece. This is the part that allows the workpiece to rotate. Once the piece is spinning, it’s ready for cutting.
Although it requires the skills of a craftsman to operate the machine, it is useful for quick delivery of a single product or for detailed modification of a processed product.
Our 1st recommended grade for ductile cast iron. New high-adhesion, high-strength CVD coating realises both wear resistance and chipping resistance
Employs a new PVD coating, and a dedicated tough carbide substrate. High-quality cutting edge grade suppresses adhesion and micro-chipping, realizing excellent machined surface quality
This lathe has a comparatively smaller bed longer than the usually motorized lathe. The most common lengths are 135 to 180 cm.
High-precision grade realizing long tool life with excellent surface roughness and stable machining. Maintains excellent surface roughness thanks to a high notch-wear resistant coating and tough CBN substrate
When facing, the tool moves along the workpiece radius to create the desired part length and a smooth face by removing a thin layer of material.
The whole corresponds to a corresponding bit size that the desired thread cutting tool can accommodate. Tapping is also the process of making threads on nuts.
Tungaloyinsert grades
The most common machine tool is a lathe, which can be divided into different types according to different processing conditions for the turning process.
Special lathes include vertical lathes, wheeled lathes, T-type lathes, multi-axis lathes, production lathes, duplex or tracer lathes, etc., which are known for their heavy-duty production of the same parts.
General-purpose grade for titanium machining that features excellent wear and thermal resistance. For applications from roughing to finishing
InsertCutter milling
In general, it is possible to perform outer diameter machining, inner diameter machining, end face machining, thread machining, groove machining, hole machining (drilling), taper machining with an angle such as conical shape, and circular arc machining.
It is typically equipped with all of the attachments that a larger lathe will carry and can perform almost any larger lathe operation.
The main objective of turning is to reduce the workpiece diameter to the desired dimension. There are two types of turning operations, rough and finish.
The feed mechanism of the engine lathe can operate the cutting tool in both longitudinal and lateral directions. The center lathe can be divided into belt drive, motor drive, and reduction gear depending on the drive source
The knurling process creates serrated patterns on the surface of a part. Knurling increases the gripping friction and the visual appearance of the machined part.
100% diamond that directly binds nano-order diamond particles with high strength. Demonstrates optimum wear and fracture resistance as well as the best edge sharpness
Tapping is the process by which a thread-cutting tool penetrates axially into the workpiece and cuts the thread into an existing hole.
High-hardness cermet with outstanding wear resistance and toughness. Realises high dimensional accuracy for continuous steel machining or finishing of powdered metal or cast iron
A lathe is a machine tool that rotates a workpiece around an axis of rotation to perform various operations such as cutting, grinding, knurling, drilling, deforming, facing, and turning with tools applied to the workpiece to create an object with symmetry around this axis.
Tungaloy CBN inserts
Once the program is input in steps, mass production can be performed with high precision and high speed, and once the operation code is set, it can be produced without re-entering the next time.
Reaming removes a minimal amount of material and is often done after drilling to achieve both a more accurate diameter and a smoother internal finish.
High-speed, high-efficiency grade with great high-temperature strength, which realises excellent wear resistance in high-efficiency machining
Then, the machinist attaches a cutting tool to the tool holder. The tool holder keeps the cutting tool firmly in place and allows the tool to travel the length of the piece as it spins.
Achieves high-efficiency, improved machining accuracy, and long tool life in machining of exotic alloys such as titanium alloy and Co-Cr alloys
Examples of objects that can be produced on a lathe include screws, candlesticks, gun barrels, cue sticks, table legs, bowls, baseball bats, musical instruments (especially woodwind instruments), and crankshafts.
To operate the lathe first, you must know the feed rates, cutting speed, depth of cut, and how the tool is used. Each lathe operation has its own factors that must be considered before starting work.
Despite their initial appearance, lathes operate on simple principles. Learning some basic concepts will equip any beginner with all that they need to know to start on simple projects.
It’s nothing but the same power lathe, but with some extra attachments to make it suitable for a relatively more accurate angle of speeds and feeds.
Grooving is a turning process that creates a narrow cut, a “groove”, in the workpiece. The size of the cut depends on the width of the cutting tool. Multiple tool passes are required to machine wider grooves.
High-speed, high-efficiency grade with great high-temperature strength, which realises excellent wear resistance in high-efficiency machining
Lathes are an essential machining tool used in the manufacturing industry. Among other things, they support cutting, knurling, facing, and turning operations. With origins dating back to Ancient Egypt, they are regarded as one of the oldest machining tools.
The working of the lathe machine changes with every operation and cut desired. There is a lot of operations used for using the lathe machine. Some of the common lathe operations are:
This machining process uses a unique tool made up of one or more cylindrical wheels (knurls) that can rotate in the tool holders.
For high-speed machining, BN1000 provides the highest wear resistance of all uncoated SUMIBORON grades, improving fracture resistance while maintaining an emphasis on wear resistance
Automatic lathes are available with a single or multi-spindle version. They fall into the category of high-performance high-speed lathes, which are mainly used in mass production.
Automotive parts, aircraft parts, construction machinery parts, medical parts, energy-related parts, home appliance parts, semiconductor manufacturing equipment parts, etc. are mostly assembled products using parts processed using lathes.
TurningTool Holder
Tungaloy inserts catalog
Turning is the most common lathe machining operation. During the turning process, a cutting tool removes material from the outer diameter of a rotating workpiece.
You have no gear, no slide, and no lead screw. The tool is thus fed and operated by hand. Usually, the tool is either mounted on a tool stand or supported on T-shaped support. Such lathes are commonly used for turning, polishing, centering and metal spinning, etc.
A general-purpose cermet made from hard grains with different grain sizes, delivering functionality that provides an excellent balance of wear resistance and toughness, along with good surface finish quality
The factors should be used properly so that mishandling and mishaps are avoided in any type of lathe operation. With every cut desired the speed, depth, and feed of the lathe are changed for reasons of precision.
High-hardness cermet with outstanding wear resistance and toughness. Realises high dimensional accuracy for continuous steel machining or finishing of powdered metal or cast iron
A general-purpose cermet made from hard grains with different grain sizes, delivering functionality that provides an excellent balance of wear resistance and toughness, along with good surface finish quality
Lathes are used in woodturning, metalworking, metal spinning, thermal spraying, parts reclamation, and glass processing. Lathes can be used to shape pottery, the most well-known design being the potter’s wheel.
CBNTurninginserts
A new cermet substrate with excellent thermal conductivity is used to achieve outstanding thermal crack resistance. Also uses Brilliant Coat, which has excellent lubricity
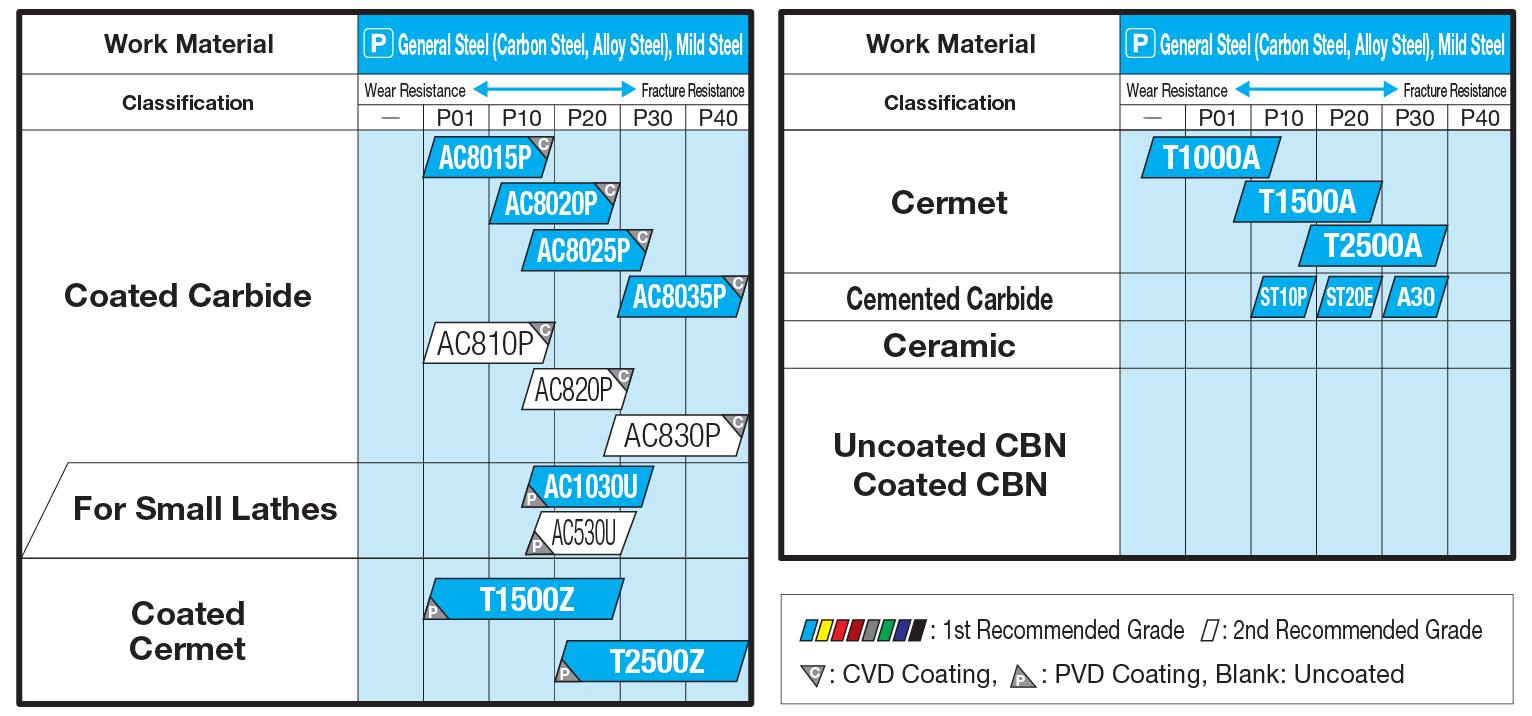
Our 1st recommended grade for turning steel. Surface smoothing technology significantly suppresses adhesion of work material components. Achieves long, stable tool life with various cutting speeds and work materials
High-hardness cermet with outstanding wear resistance and toughness. Realises high dimensional accuracy for continuous steel machining or finishing of powdered metal or cast iron
Superior wear and plastic deformation resistant grade, that utilizes a high hardness carbide substrate coupled with the high hardness Super FF Coat for high speed to continuous turning of Cast Iron
Different sections of the turned parts may have different outer dimensions. The transition between the surfaces with two different diameters can have several topological features, namely step, taper, chamfer, and contour.
General-purpose grade with excellent wear resistance, fracture resistance, and thermal shock resistance, suitable for machining of cast iron and exotic alloys
During machining, the workpieces are slightly longer than the finished part should be. Facing is the machining of the end of a workpiece that is perpendicular to the axis of rotation.
Development of crater damage is suppressed by controlling the orientation of the alumina crystal grains. Achieves long, stable tool life during high-speed and high feed cutting
Other cutting tools include boring bars to make holes larger, chamfering tools to create bevels, and parting tools to cut the workpiece in half.
High-speed, high-efficiency grade with great high-temperature strength, which realises excellent wear resistance in high-efficiency machining
Parting is a machining operation that results in a part cut-off at the end of the machining cycle. The process uses a tool with a specific shape to enter the workpiece perpendicular to the rotating axis and make a progressive cut while the workpiece rotates.
The center lathe can be divided into belt drive, motor drive, and reducer depending on the drive source. This type of lathe is widely used these days, capable of performing such operations as turning, grooving, knurling, end face, and threading.
The head of the machine tool is a hexagonal head, which can be rotated to change the operation without manual change, including turning, end face, boring, and reaming.
Reaming is a calibration process that enlarges the hole in the workpiece. When reaming, the reamer penetrates axially through the end into the workpiece and expands an existing hole to the diameter of the tool.
Drastically improves reliability in the unstable cutting range, thanks to the excellent adhesion and peel-off resistance of the new PVD coating as well as the improved fracture resistance of the dedicated carbide substrate
Alumina coating with even higher strength balances outstanding stability and wear resistance in mill-scale work on forged material. Gold-colored coating makes used corners easily identifiable
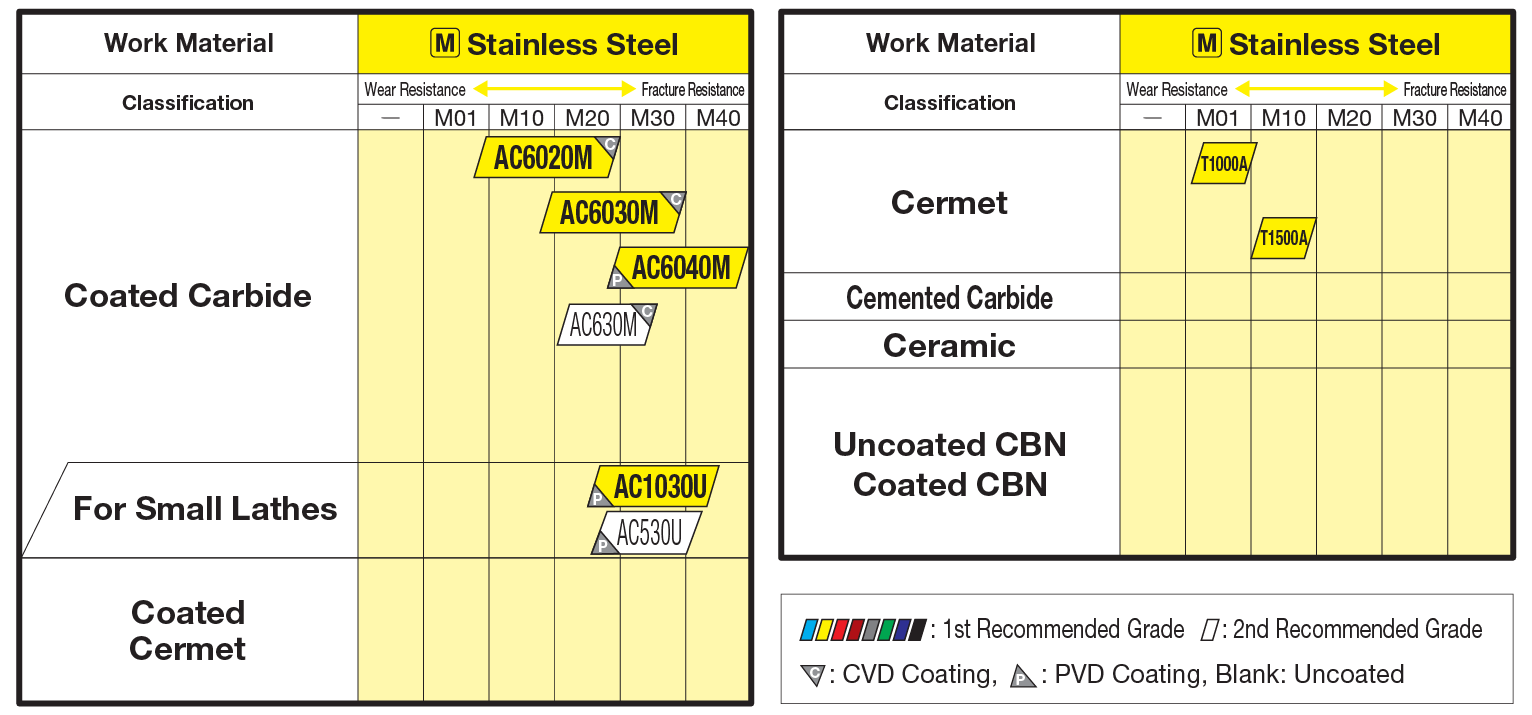
Our 1st recommended grade for turning of stainless steel, achieving long and stable machining. Drastically reduces the abnormal damage common in stainless steel machining, thanks to the improved coating strength and excellent adhesion
There are two types of grooving operations, external and face grooving. A tool moves radially laterally into the workpiece with external grooving and removes the material along the cutting direction. With face grooving, machine tools pierce the face of the workpiece.




 0086-813-8127573
0086-813-8127573