Counterbore Vs. Spotface Holes: Understanding the Differences - spotface tool
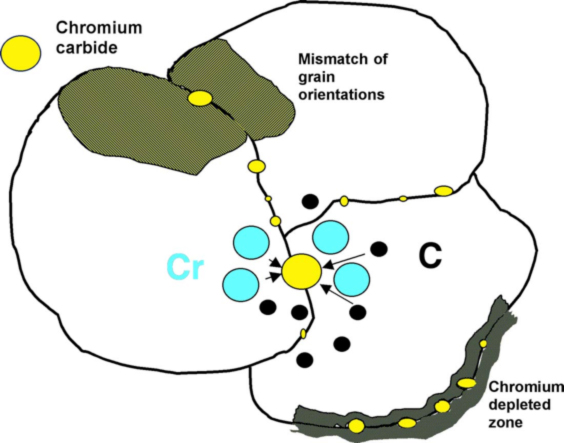
With austenitic stainless steels, intergranular attack is usually the result of chromium carbide precipitation (Cr23C6) at grain boundaries, which produces a narrow zone of chromium depletion at the grain boundary. This condition is termed sensitization and it is shown schematically Figure 2. Sensitization involves the precipitation of chromium carbides at grain boundaries, which results in a narrow zone of chromium depletion at the grain boundary.
Rapid attack at the grain boundaries can result in grains “dropping” or falling out of the metal surface resulting in the disintegration of the steel. Figure 1 shows the appearance of a surface where this is occurring. In practical application, the loss of cross section thickness and the introduction of cracks can have severe consequences for applications like pressure containment.
With the ferritic grades, sensitization occurs during cooling from higher temperatures (>1700 °F). At these high temperatures the carbides and nitrides are put into solution and during cooling they can precipitate at grain boundaries resulting in chromium depletion. The very high diffusion rates in the ferrite structure make it impossible to cool the steel fast enough to avoid precipitation of carbides and nitrides at grain boundaries. For this reason, most commercial ferritic grades avoid sensitization by restricting the level of C and N and requiring the addition of stabilizing elements such as Ti, Ta, or Nb.
Tamiya anime list
If sensitization has occurred in a ferritic stainless steel, the condition can be “healed” by back diffusing chromium into the depleted regions. “Healing” can be achieved by holding the material at 1100 – 1200 °F for several hours. The test methods outlined in ASTM A763 have been developed to detect susceptibility to intergranular attack in ferritic stainless steels.
noun a symmetrical sloping surface at an edge or corner. There are unfortunate chamfers on the back corners of the plan to allow for rights of light of ...
Common practices such as welding, stress relief, and hot forming can expose the steel to the sensitizing temperature range. The formation of chromium carbides is readily reversed by a solution anneal heat treatment. The test methods outlined in ASTM A262 have been developed to detect susceptibility to intergranular attack in austenitic stainless steels.
Vise INTRUDER
Like other common materials, metals have a visible grain structure when they are viewed under magnification. Rapid corrosive attack of immediately adjacent grain boundaries with little or no attack of the grains is called Intergranular Corrosion.
For example, drill bits made from high-speed steel (HSS) are fine for soft metals, while cobalt is the best drill bit for stainless steel. But solid carbide or ...
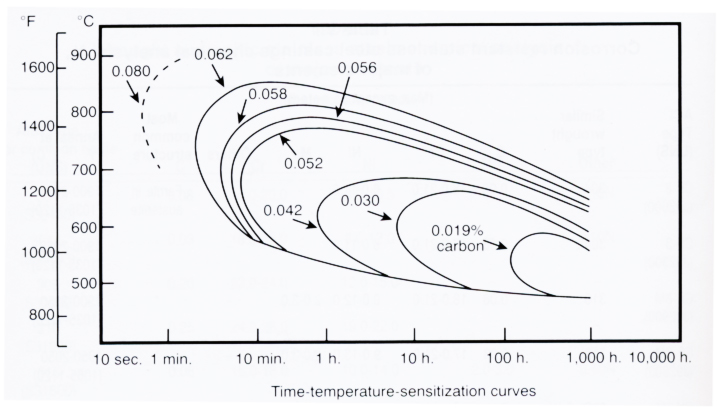
Resistance to IGA can also be achieved by reducing the carbon content to below 0.030% level. As shown in Figure 3, lower carbon contents move the nose of the time-temperature-sensitization curve to longer times. The low carbon grades such as Types 304L, 316L, and 317L have been designed to resist sensitization during typical welding operations, but they do not resist sensitization by long term exposure in the critical temperature range in service. The higher alloyed, more corrosion resistant stainless steels such as the 904L and 6Mo alloys have very low carbon contents and susceptibility to IGA is typically not a concern.
Because the chromium is the primary alloying element that makes stainless steel corrosion resistant, the chromium-depleted regions are susceptible to preferential corrosion attack. It is believed that this occurs because the chromium content immediately adjacent to the carbide may be below that required for the stainless steel alloy. If the carbides form a continuous network on the grain boundary, then corrosion can produce a separation or gap at the boundary and possible grain dropping or loss.
Rising Trigger
A great pattern for year round fishing. If you're fishing caddis rivers, you'll need these in your box. When wet, this fly looks exactly like a dislodged caddis pupa floating in the drift.
Pro ___ crossword clue? Find the answer to the crossword clue Pro ___ ... Pro ___ (for now) · Pro ___ (like some lawyer · Pro ___ (like some legal · Pro ___ ...
Boron carbide is used in a limited number of applications because of the high cost of fabricated parts. It is used as a thermal neutron absorber in fission ...
With the stabilized grades, standard solution annealing treatments generally do not tie up all the available carbon. So when the stabilized grades in the solution-annealed condition have long time exposures to the sensitizing temperature range (1450 to 950 °F), chromium carbide precipitation and sensitization can occur. Stabilizing heat treatments can be used to more effectively tie up carbon by completing the precipitation reactions. These treatments consist of holding the alloy for several hours in the 1500 to 1600°F temperature range.
2024312 — Intravaginal boric acid during treatment and continuing for 3-4 weeks ... Avoid tight-fitting clothing in the evening/during sleep. Dr.
Beat Magnum
Three approaches have been used with the austenitic stainless steels to minimize to the effects of IGA. Material that has been sensitized can be solution annealed by heating to a temperature where the carbides dissolved and the chromium-depleted regions are eliminated. The carbon is then kept in solution by rapid cooling through the sensitizing temperature range. The recommended solution anneal temperature depends on the alloy and is typically done in the range of 1900 to 2150°F followed by rapid cooling.
Although intergranular attack of ferritic stainless steels is similar to that found in austenitic stainless steels, there are some important differences. Because the solubility of nitrogen is low in the ferritic crystal structure, the precipitates that cause sensitization in ferritic grades include both chromium carbides (Cr23C6) and chromium nitrides (Cr2N).
The chromium carbides tend to precipitate at the grain boundaries of austenitic stainless steels in the 950 to 1450°F temperature range. Any exposure or thermal excursion into this temperature range during metal manufacture, fabrication, or service could potentially sensitize the steel.
Dec 7, 2019 — Did you also already try one of these types of inserts then let us know your experience down in the comments! For the last test I also used M5 ...
The time and temperature required to produce susceptibility to intergranular attack (IGA) is dependent on alloy composition, particularly the carbon content. Figure 3 shows the time-temperature-sensitization curves for Type 304 alloys with varying amounts of carbon content.
Hilti has power tools, grinders, drills, and saws as well as fasteners, anchors, design and layout software and services for construction professionals.
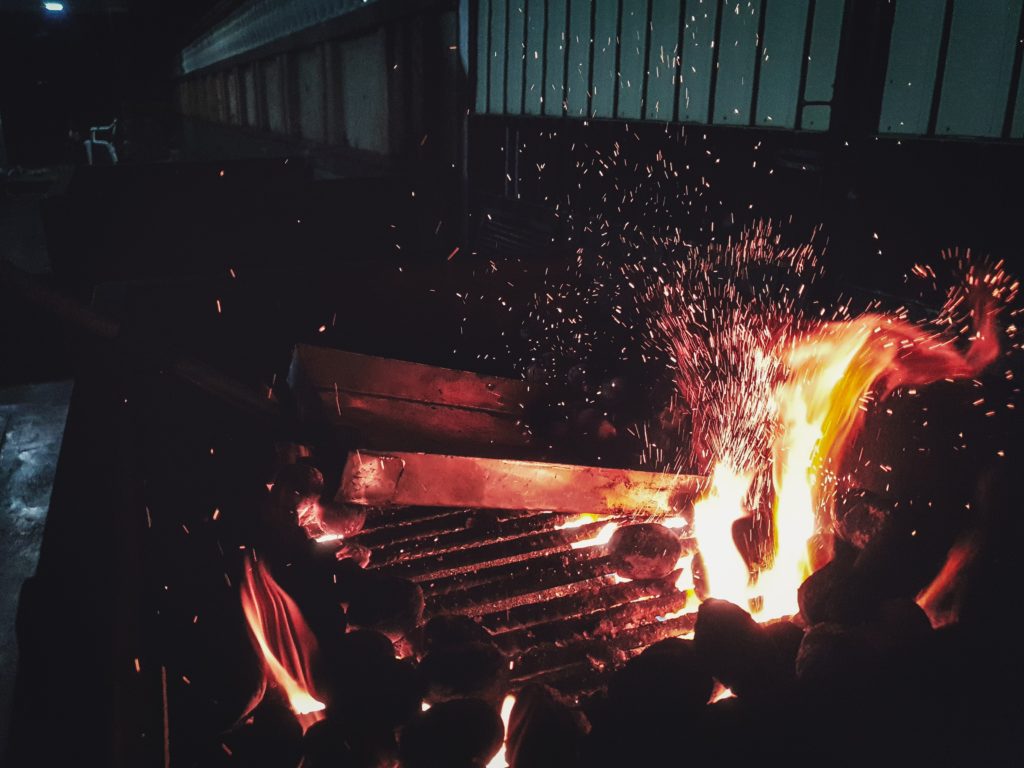

In practical application, the loss of cross section thickness and the introduction of cracks can have severe consequences for applications like pressure containment.
Tamiya Mini 4WD list
intransitive verb To cut into or join by means of dovetails. ... a saw used in dovetailing ... I agree with John the dovetail is a perfect joint the way it works is ...
... corner roller, 5" corner roller, adjustable corner trowel, marshalltown corner trowel, kraft corner trowel, bullnose tool, Corner Pro Flexible Rubber Drywall.
The addition of stabilizing elements such as Ti, Nb (Cb), and Ta can also provide increased resistance to sensitization, especially for long-term exposures in the critical range in service. These stabilizing elements tend to form carbides that are more stable than chromium carbide in the temperature range of 2250 to 1450°F. So as the alloy cools from high temperatures, the carbon combines with the stabilizing elements and is unavailable for chromium carbide precipitation at the lower sensitizing temperature range of 950 to 1450 °F. Common stabilized austenitic grades include Type 321, 347, 20-Cb3, and 316Ti. Figure 4 summarizes the carbide precipitation reactions that occur in type 304 and 347 stainless steels.
With a cutting tap, the tap cuts the material, and chips are generated. Forming taps. Advantages compared to cutting taps: Forming is usually faster than ...




 0086-813-8127573
0086-813-8127573