Countersink Drill Bits - 1 1/2 countersink bit
If you want to use a coating, e.g. to increase the tool life, it should be at least the TiAlN coating, because it has a high heat resistance. With TiAlN-coated drills, cooling is not necessarily required. In addition, they prevent cold welding on the drill.
Steel cobaltuses
Co becomes highly radioactive when exposed to the intense radiation of nuclear reactors, and as a result, any stainless steel that is in nuclear service will have a restriction in the Co content which is usually around 0.2 % maximum.
The point angle is located at the head of the twist drill. For hard materials such as stainless steel, the point angle should be large and e.g. 130° or 135°. For soft materials, point angles of e.g. 118° are used.
In stainless steel, it must be enriched with alloying elements such as titanium, niobium or chromium in addition to iron. Chromium (Cr) is the corrosion resistance of stainless steel and should have a minimum content of 12% and an extremely low carbon content. The chromium content creates a layer on the material surface which permanently protects against water and moisture.
Co is not a popular element which is commonly added to alloy steels. It does have some effects but these can also be achieved with other alloying elements such as molybdenum (Mo), and nickel (Ni) etc. at lower costs and mostly with better results. Due to this factor, Co does not find enough use in high tonnage low alloy steel production. However it does have some niche markets in steel.
Steel cobaltfor sale
What features does the twist drill have to have in order to cut stainless steel? The following criteria must be met in order to obtain a good drilling result.
Cobalt steelcomposition
Solubility of Co in the ? iron is up to 75 % while in the ? iron it is unlimited. Co is the only one alloying element that increases the critical cooling rate of steel and accelerates pearlitic transformation thus reducing hardenability.
In the application table you will find all our twist drills with which you can drill in stainless steel. If you click on the images of the twist drills in the PDF, you will be taken directly to the product page where you can find detailed information about the twist drill.
Nov 22, 2023 — Milling machines can machine materials such as metal, plastic, or wood. Mills use cutting tools including end mills, face mills, and drills.
Co has few, but highly specialized, uses in alloy steels. Its behavior is similar to Ni, in that it forms a complete series of solid solutions with iron at elevated temperatures and is also extremely soluble in ferrite. It is a potent ferrite strengthener; this solid solution strengthening persists to quite high temperatures, and hence Co is used in several grades of high speed tool steels, among others.
Co is a valuable alloying element for high speed tool steels. It has the effect of raising to softening temperature of ferrite so that tools made from Co bearing alloy steel can operate at high temperatures, maintaining their cutting capacity.
In order of decreasing tonnage usage, primary applications of Co are in non-ferrous (super)alloys, magnets, high speed tool steels, ultrahigh strength alloy steels, abrasion-resistant cemented carbides for cutting tools and stainless steels.
If you do not have a pillar drill available, use the pointed side of the punch and a hammer to make a small recess in your stainless steel workpiece. This gives you better guidance and prevents slippage when drilling. The center punching compresses the material a bit, but mainly the material is displaced to the side and over the top of the material. This does not pose any extreme challenges for the twist drill.
Kennametal's carbide boring bars for O.D. and I.D. turning increases productivity on the shop floor. Choose from several high-performance carbide boring ...
A CNC lathe machine can produce a range of products, from larger items such as automobile frames and airplane engines to smaller items, such as surgical ...
With a large point angle, more of the cutting edge engages in the workpiece when drilling. This also means that more force is applied to the workpiece and higher contact pressure (high feed) is required.
The addition of Co to cold work die steels (as in steels with 3 % Co) increases hardness and promotes greater wear resistance than grades where it is not used.
Co bearing high speed steels have a somewhat greater tendency to decarburization and are more sensitive to cracking when exposed to abrupt temperature changes. They are also somewhat more brittle than non Co grades. However, their increasing popularity is due to their excellent red hardness property.
You have chosen a suitable twist drill and now you finally want to drill your hole in stainless steel. When drilling, it is important that you
You want to drill a hole in stainless steel but don't know which twist drill to use? In this article we explain how to drill in stainless steel and which twist drills to use.
In each of our product groups you will find a Product finder. Under Products > Twist drills you can filter "stainless steel" in the field Applications. You will then be shown all twist drills that can be used for cutting stainless steel.
Cobalt steelproperties
Since stainless steel is a very hard material, you have to choose the right twist drill. The twist drill should belong to the application group Type H of the DIN 1386 division. Over time, however, mixed forms have been developed whose naming systems are not standardized in the DIN manual. So you will find at RUKO for the use in stainless steel the types VA, FO, UTL3000, UNI, TL3000, N and UTL.
Co is unique among alloying constituents in steel in that it is the only element that has negative effect on the hardenability of steel by accelerating the decomposition of austenite. It has a tendency to graphitization and is a very expensive component, hence it is not used as an alloying addition in normal steels. It is never used in the standard heat treatable steels. Co is, however, a constituent of maraging and 9Ni-4Co ultrahigh strength steels but here, its presence is overcome—from a hardenability standpoint—by the remaining alloying constituents.
Likewise, hot work die steels may contain about 0.5 % Co for better wear resistance and higher hot hardness. The chromium-bearing grades contains up to 4.25 % Co for this reason.
Through the ispatguru.com website I share my knowledge and experience gained through my association with the steel industry for over 54 years.
The twist drills made of HSSE-Co 5, HSSE-Co 8 or solid carbide do not neccesarily need coating . Coated drills are still ideally suited for industrial use. I.e. fast speeds (high cutting speeds), high feed rates and increased heat applications.
Cobalt is added to high speed steels to improve hot hardness. It is found in both Mo and tungsten (W) grades of tool steels.
If possible, use a pillar drilling machine as it allows you to better control the centering, speed and feed . High feed rate is required and your speed is rather low when drilling.
Under certain conditions (e.g. type of stainless steel, point angle, spiral angle etc.) you can also use a TiAlN-coated HSS drill. There are some stainless steels that are easy to cut and can also be drilled with coated HSS drills.
Oct 2, 2017 — The SFM calculation utilizes the industry standard of 3.82. Here, the cutter diameter of the chosen tool is multiplied by the speed or RPM. This ...
Scrap of super alloys normally contains high percentage of Ni and hence is not used for the production of tool steels. However this scrap can be used for the production of maraging and ultrahigh strength steels.
M42steelcomposition
Steel cobaltvssteel
The metallurgical behavior of Co is similar to that of Ni and hence oxide of Co is readily reduced in all but the most oxidizing steel baths and may be added to the electric arc furnace or the AOD(argon oxygen decarburization) furnace. More common practice in tool and alloy steel production, however, is to melt down a high scrap charge and then adjust the final Co content with the addition of Co metal. Vacuum melting is also employed for the production of steels with Co additions.
Co raises the A3 temperature in tool steels, thus calling for somewhat higher austenitizing temperatures. This is beneficial in that it forces a greater degree of dissolution of the complex carbides these materials contain. Co does form a carbide of the Fe3C type, but this compound does not contribute to secondary hardening.
Our flexible program provides exceptional training and equips you with the crucial skills to obtain your CDL in just eight weeks!
The effects of Co additions on the mechanical properties and strengthening mechanisms of martensitic precipitation strengthening stainless steels, whose composition is 0.005 % C/12 % Cr/5 % Mo/1.5 % Ni with Co levels of 9 %, 12 %, 15 %, 18 %, and 21 %, shows that hardness, yield strength and ultimate tensile strength increases as the Co content increases, while the charpy impact energy decreases as tempering temperature increases
Cobalt steelknife
With cooling you ensure that the surface quality is optimal, the temperature is lowered and the chips are swept away. This extends the life of the drill
The carbide and ceramic liner act a Bearing and guides the rod in & out as the Sliding head moves the Raw material while machining. The guide bush helps to ...
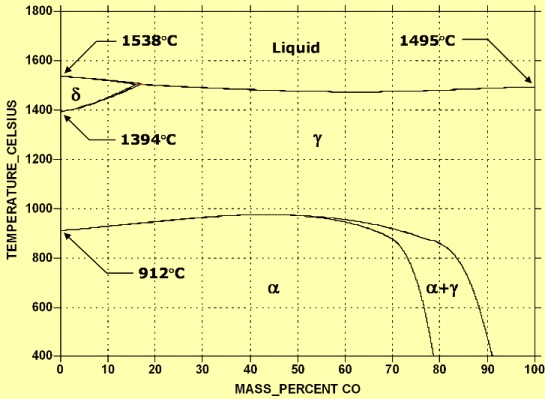
Cobalt (Co) (atomic number 27 and atomic weight 58.94) has density of 8.85 gm/cc. Melting point of Co is 1493 deg C and boiling point is 3100 deg C. At temperatures below 417 deg C cobalt exhibits a hexagonal close packed structure. Between 417 deg C and its melting point of 1493 deg C, Co has a face centered cubic (fcc) structure. Co is a magnetic metal with a curie temperature of 1121 deg C.
You should not wear gloves, because they can get caught in the twist drill. In contrast to the gloves, you should unconditionally put on protective goggles.
Cobalt steelhardness
Stainless steel is a very hard material and therefore difficult to cut. Therefore, the tool steel of the twist drill should be made of HSSE-Co 5 (5% cobalt content), HSSE-Co 8 (8% cobalt content) or solid carbide.
Rolling and hot working High speed tool steels containing Co are treated in a similar way as Co free alloy steels. Since the composition of these highly alloyed steels is quite complex, these steels are susceptible to heavy segregation. Hence these steels ordinarily require massive amounts of hot reduction to break up the cast structures. These days with the development of powder processes in combination with hot isostatic pressing (HIP process) techniques, these processes have become more preferred route for the production of high speed tool steel containing Co.
Magnetic steels containing from 9 % to 40 % Co have been used for compass needles, hysteresis motors and electrical instrumentation.
3/16" x 1 1/4" Concrete Screws / Phillips / Flat Head / Blue Perma-Seal Case Hardened Steel | 1 Drill Bit Per Box 100 $10.73
If you have found the right twist drill and follow these instructions, you will get a good drilling result in stainless steel.
We invest in cool, dynamic spaces that make it easier for you to connect to customers and your team members. Watch Video.
You should not have used the twist drill on other steels before. The metal particles on the twist drill can attack the stainless steel and make it susceptible to corrosion.
The spiral angle determines the process of chip formation. Small spiral angles are used for hard short-chipping materials.
a cutting tool's ability to perform properly. MSC is not responsible for ... Important Disclaimer: The Accupro speed and feed rates are suggested by the ...
The break sensitivity in comparison to HSS is higher in HSSE-Co or carbide tool steels. Basically you can negate this with the correct application (correct speed, feed and cooling). In general, the more cobalt, the harder and therefore more brittle the drill.
Oct 14, 2005 — I believe it was at Bass Pro recently, my son pointed out a Bur Remover they had on the end of a rack in the hunting section or near the cashier ...
The presence of Co in the steel improves its durability and hardness at higher temperatures, reduces the fall in hardness of austenite and ferrite under the influence of temperature increase, and therefore is used as a supplement to some grades of high speed steels and tool steels. It is also a component of creep resistant steels.
Co is used in a series of magnetic steels, It is an important constituent of the 18 % Ni maraging steels and several other ultrahigh strength steels and is added to one grade of austenitic stainless steel.
With cooling you ensure that the surface quality is optimal, the temperature is lowered and the chips are swept away. This extends the life of the drill
Co increases hardness and allows for higher quenching temperatures during heat treatment. It intensifies the individual effects of other elements in steels with complex compositions.
See the table below for information on the speed and feed settings and the type of cooling. You can download the speed table as a PDF file. Click on the image.
Stainless steel is a metallic material which is characterized by its special purity . There are alloyed and unalloyed steel, but only the alloyed variant is also stainless.
Co is not a carbide former. However addition of Co to alloy steels allows for higher attainable hardness and higher red hot hardness.
A tool steel that is too soft would immediately overheat. So since stainless steel is a hard material, you need a twist drill type H. In the course of time, the features of twist drills have been combined differently in order to optimize them for special applications. Thus, mixtures have formed whose naming system is not standardized in the DIN manual. So you will find at RUKO for use in stainless steel types VA, FO, UTL3000, UNI, TL3000, N and UTL.
In the production of co bearing alloy steels, additions of Co during the steel making is made in the form of Co metal which is supplied to steel producers in the form of briquettes, granules, and broken electrolytic cathodes. Content of Co in these additive agents is usually in the range of 98 % to 99.9 %.
Maraging steels containing Co have found many uses where their strength coupled with workability have got them the application over possibly stronger materials. These ultrahigh strength alloy steels are commonly heat treated to yield strengths approaching 2070 MPa and have excellent toughness as well. Their primary application is in aircraft and aerospace and military industries. Typical applications are landing gears, arrestor hooks, torque shafts, rocket motor casings, gun barrels, bolts, fasteners, extrusion arms etc.
The Co matrix has a high-work hardening sensitivity, which combines with the carbide fraction and allows to achieve excellent wear resistance associated with a high degree of corrosion resistance.
In our detailed article "8 features of a twist drill and its functions" you will learn all the important features of twist drills and which functions they have when drilling.




 0086-813-8127573
0086-813-8127573