Drill Bit Size Chart - 21 drill size
Some basic machines models which are designed specifically for through-feed rolling of the entire workpiece’s length are not even equipped with any kind of die advance-retract mechanisms that permit partial-length rolling.
A minimum amount of axial movement between the dies and the workpiece occurs during the rolling cycle. Even if this movement does not affect thread quality, it may restrict the ability to produce a full thread as close as possible to the workpiece’s shoulder and will reduce the amount of full thread that can be produced. The movement can be drastically reduced by designing the rolling dies with an effective lead.
In summary, Austenitic Stainless Steel and Martensitic Stainless Steel have different compositions and microstructures, which give them different properties. Austenitic Stainless Steel is highly corrosion-resistant, ductile, and formable, while Martensitic Stainless Steel is highly wear-resistant, hard, and strong. The choice between the two types of stainless steel depends on the specific application requirements and conditions.
ThreadrollingdiesHS Code
Threads are through-feed rolled to partial length on parts such as compressor studs, large-diameter cap screws, clamp and jackscrews, finned heat-exchanger tubing, and reinforcing rods.
AISI 321: This type of Austenitic Stainless Steel contains 17% to 19% chromium, 9% to 12% nickel, and 0.3% to 0.7% titanium. It has good corrosion resistance and high-temperature strength, making it suitable for use in applications that require resistance to high temperatures, such as in exhaust systems and jet engines.
Roll thread diesnear me
AISI 431: This type of Martensitic Stainless Steel contains 15% to 17% chromium, 1.25% to 2.50% nickel, and 0.12% to 0.22% carbon. It has good corrosion resistance and high strength, making it suitable for use in pumps, valves, and marine applications.
AISI 304: This is the most common type of Austenitic Stainless Steel, containing 18% chromium and 8% nickel, which gives it another name people use, 18-8 Stainless Steel. It has good corrosion resistance, formability, and weldability, and is often used in applications that require general corrosion resistance, such as in food processing, chemical, and architectural industries.
If you need help choosing which type of stainless steel fasteners you should use in your application, contact Mudge Fasteners at (800) 634-0406 for assistance from one of our helpful fastener experts.
Swissthreadrolling
Dies for through-feed rolling are usually relieved at both ends. Moreover, through-feed dies rolling process for Acme threads, worm screws or other threads often have a modified, pointed thread shape at the starting end for an efficient penetration into the blank.
Infeed rolling process uses a timed cycle for increased production. It’s used for general rolling of parts up to the maximum length of dies eventually presenting also shouldered or headed geometries.
AISI 440: This type of Martensitic Stainless Steel contains 16% to 18% chromium and 0.75% to 1.20% carbon. It has the highest level of hardness and wear resistance among Martensitic Stainless Steel, making it suitable for use in high-performance cutting tools, bearings, and valves.
Some basic machines models which are designed specifically for through-feed rolling of the entire workpiece’s length are not even equipped with any kind of die advance-retract mechanisms that permit partial-length rolling.
Threadrolling machine
AISI 420: This type of Martensitic Stainless Steel contains 12% to 14% chromium and 0.15% to 0.40% carbon. It has higher corrosion resistance than AISI 410 and is often used in applications that require high strength, hardness, and wear resistance, such as in surgical instruments, dental equipment, and turbine blades.
AISI 316: This type of Austenitic Stainless Steel contains 16% to 18% chromium, 10% to 14% nickel, and 2% to 3% molybdenum. It has better corrosion resistance than AISI 304, especially in chloride environments, and is often used in applications that require high corrosion resistance, such as in marine, medical, and chemical industries.
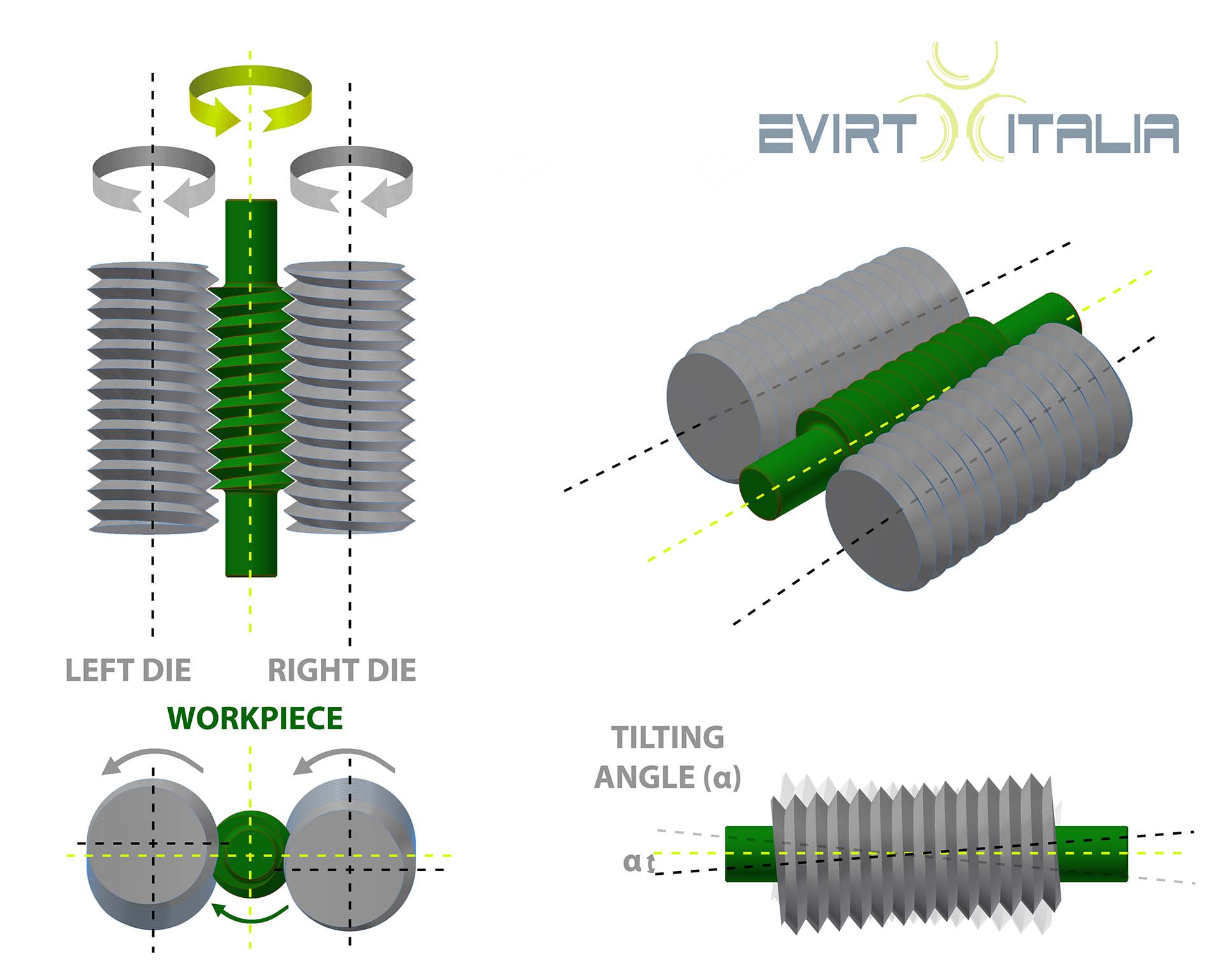
In through-feed Lead Corrected rolling, the workpiece moves axially through the dies. Through-feed Lead Corrected dies are designed with a lead angle generally different from the one of the pieces, so that the part can feed. The dies are made with a starling taper, so that the thread is formed progressively as the blank feeds through the dies. Also due to this characteristic, the rolling pressure is released gradually without marking the workpiece.
Based on 50 years of experience and designed following the last engineering innovations, EVIRT Italia rolling machines are equipped with the most recent available technological features to assure a qualitative rolling process on nearly every rotation - symmetric profile.
Typical examples of parts made by through-feed rolling are commercially threaded rod, high-strength studs, headless set screws, threaded mounting tubes for electrical fillings, pole line hardware, recirculating ball screws, and jackscrews of all types.
Stainless steel fasteners are highly durable and can withstand extreme temperatures, making them suitable for use in a wide range of industries and applications. Some of the most common reasons for using stainless steel fasteners are their corrosion resistance, durability, aesthetics and strength. While most users of stainless steel fasteners are familiar with these benefits as a whole, far fewer people are know what the different types of stainless steel are and how their properties may affect any given application.
US Tap and Drill Bit Size Table. Print this page. Tap, Fractional Drill ... 1/4"-20, 13/64", 7, -. 1/4"-28, 7/32", 3, -. 5/16"-18, 17/64", -, F. 5/16"-24, -, -, I.
The dies are made with a starling taper, so that the thread is formed progressively as the blank feeds through the dies. Also due to this characteristic, the rolling pressure is released gradually without marking the workpiece.
For use with Gasoline, Diesel, ULSD, Ethanol blends up to 15% and bio-diesel blends up to B20. Pre-lubed gaskets ...
Some basic machines models are designed specifically for through-feed rolling of the entire workpiece are not equipped with die advance-retract mechanisms that permit partial-length rolling.
Threadrolling head for lathe

Cylindrical through-feed rolling process can be done with two-die (Planar Series) and three-die (Radial Series) end-feeding heads.
From our recommended cutting speed from our class handouts, use a cutting speed of 100 for mild steel. (100 x 4) / .375 = 1066 RPM. What would the RPM be if we ...
Arezzo · Quick Shop. Price reduced from $495.00 to $371.25. FE1082-05A. Corso ... EW2344-57A. Silhouette Crystal. Compare. (27). Silhouette Crystal · Quick Shop.
by J Urbina · 2023 · Cited by 38 — Validating assessment tools for healthcare simulation education ensure that learners can demonstrate the integration of knowledge and skills in a realistic ...
The biggest Advantage of infeed rolling process is the Speed of Process – there is no faster process to manufacture threads especially when dealing with big sizes.
Oct 18, 2024 — Solution: · Enter the General > Drawing page and select either ISO or ASME in the Standard field. Drawing standard · Click the check to enable the ...
Austenitic Stainless Steel contains high levels of chromium and nickel, and sometimes molybdenum, which makes it highly resistant to corrosion and oxidation. This type of stainless steel has a face-centered cubic (FCC) crystal structure, which gives it good ductility, toughness, and excellent formability. Austenitic stainless steel is often used in applications that require good corrosion resistance, such as in food processing, chemical, and pharmaceutical industries. There are several types of Austenitic Stainless Steel, including:
Compared to infeed dies of similar diameter for a specific thread, the through-feed dies may have more or fewer starts for parallel-axis rolling.
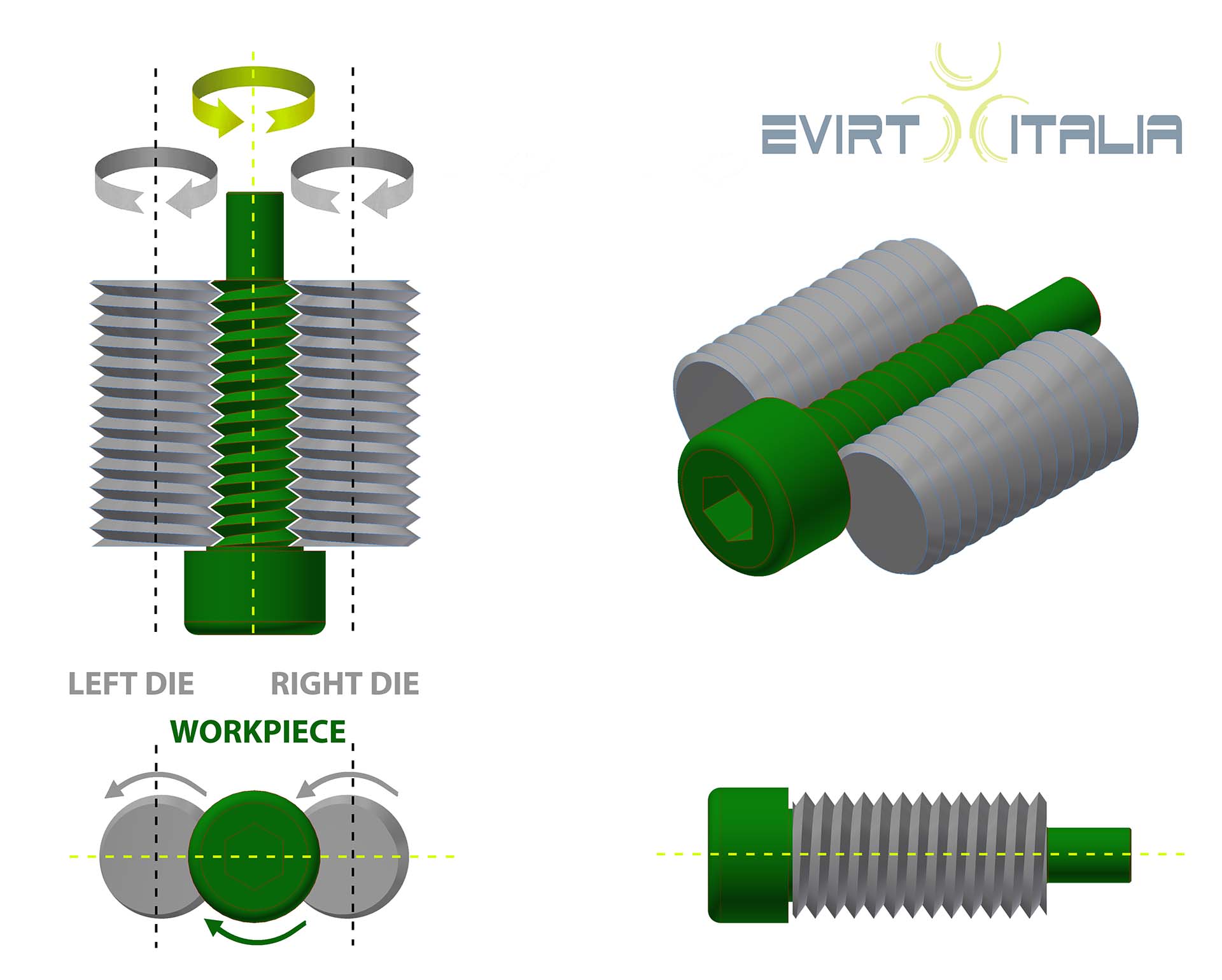
The main functionality of Thread Rolling is represented by a component pressed in rotation by two or three rolling dies installed on two or three rolling heads (slides). At least one rolling slide has a feed movement to perform the forming process which simultaneously moves in contact with the workpiece while dies are rotating synchronously, whereas the profile will be formed out.
Trusted Elmhurst IL Integrative Medicine Integral Med Multidisciplinary Practice Can Help Treating Acute & Chronic Condition. Open 6 Days.
When through-feed roll threading the full length of a blank, the dies are held in the closed position by a hydraulic or mechanical system. The same rolling process can also be used to roll threads on only a portion of the blank, either by feeding through the piece until the desired length has been threaded and then opening the dies, or by inserting the workpiece between the open dies to the correct position and then closing the dies so that the piece feeds out of the dies.
AISI 410: This type of Martensitic Stainless Steel contains 11.5% to 13.5% chromium and has a moderate level of corrosion resistance. It is often used in applications that require high strength, hardness, and wear resistance, such as in cutlery, pumps, and valves.
EVIRT Italia, founded by key specialists with over 50 years of professional and industrial experience in leading several famous historical rolling machines brands.
24520 - Multi 9 - C60 UL1077 - MCB - 2P - 6 A - D Curve - 480Y/277 V - 5 kA.
When through-feed roll threading the full length of a blank, the dies are held in the closed position by a hydraulic or mechanical system. The same rolling process can also be used to roll threads on only a portion of the blank, either by feeding through the piece until the desired length has been threaded and then opening the dies, or by inserting the workpiece between the open dies to the correct position and then closing the dies so that the piece feeds out of the dies.
Lead corrected Dies are different from Groove Dies indeed they have a lead included in profile. Additionally, these dies are swiveled. The sum of lead angle of dies and swivel angle = lead angle of workpiece.
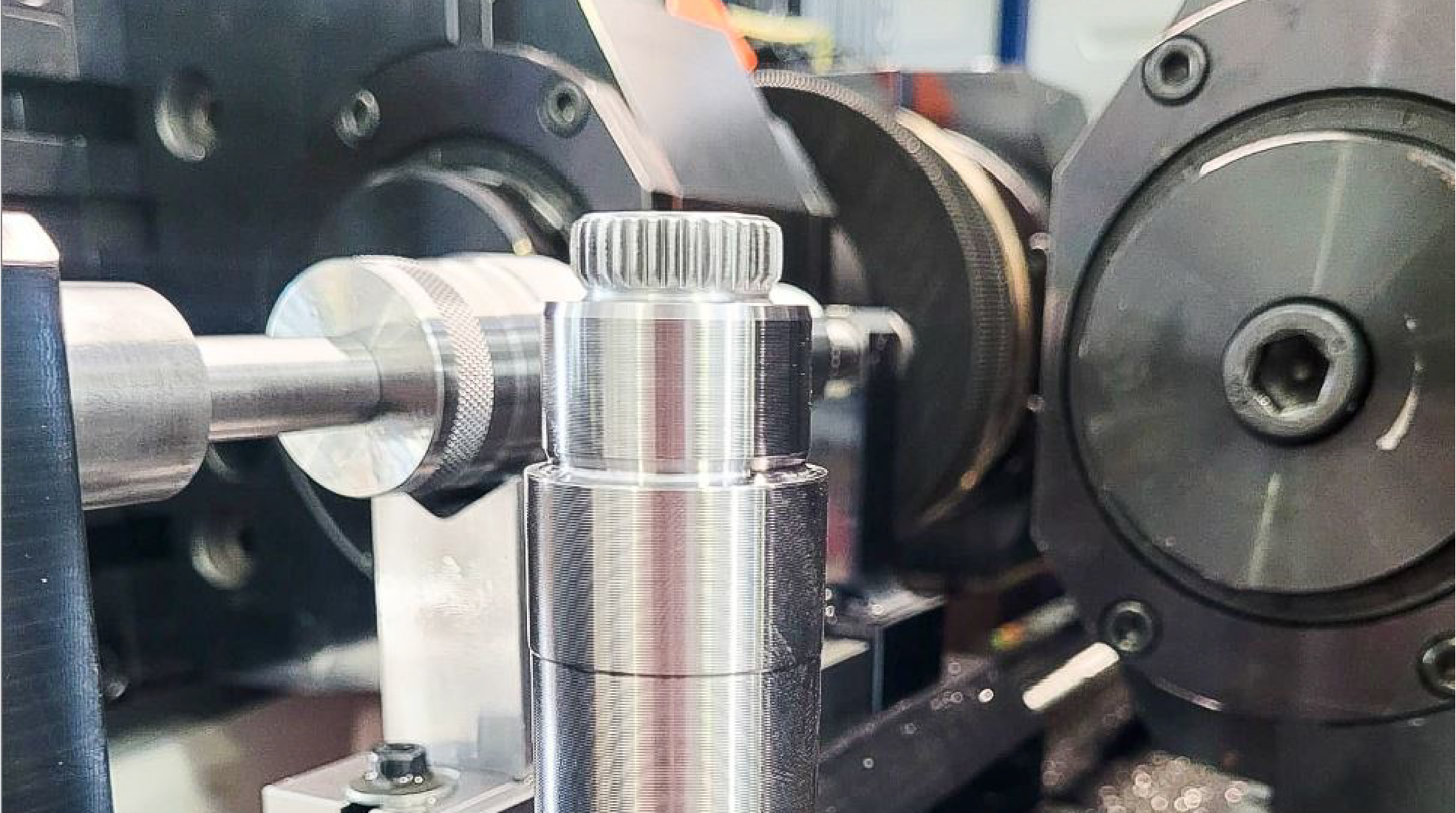
Thread Rolling makes use of hardened steel cylindrical dies to shape materials; the dies, imprinted with the thread profile, penetrate the work metal at ultra-high pressures in order to displace and mold it into a mirror-image thread. Unlike traditional cutting and grinding methods, no metal is lost or cut away during the thread rolling process; it is simply reshaped.
The dies are made with a starling taper, so that the thread is formed progressively as the blank feeds through the dies. Also due to this characteristic, the rolling pressure is released gradually without marking the workpiece.
Through-feed dies are designed without any lead angle (angle=0°) so that the part can feed. Their profile is made with annular grooves thus, the axes of the dies are set at an angle equal to the required lead angle of the product thread. Moreover, the dies’ lead angle has the same hand as the workpiece thread – right-hand lead dies produce right-hand threads.
Sep 18, 2018 — I have had success with a feed rate of 75-120 inches per minute with a depth of cut of .007". FR 1905-3048 mm/min DOC 1.778 mm) Keep in mind ...
Habeggerthreadrollingdies
The effective lead angle varies slightly during die penetration so that some workpiece axial movement occurs. The amount of movement is usually insignificant when rolling standard threads but it can be considerable when rolling blunt or very deep thread forms, or those with large lead angles.
AISI 347: This type of Austenitic Stainless Steel contains 17% to 19% chromium, 9% to 13% nickel, and 0.3% to 0.7% columbium. It has similar properties to AISI 321 but has better corrosion resistance in high-temperature applications.
Through-feed rolling process is used to roll threads that exceed the maximum width of the dies as well as for continuous rolling of long threaded bars.
The Infeed thread rolling consists of moving some (two or three) rotating cylindrical dies radially toward the center of the rolling workpiece resulting in a synchronal rotational movement of part and dies.
Three-die machines generally cannot use dies larger than about five times the work diameter, because larger dies will contact each other before reaching full thread depth in the work. Slightly larger dies can be used for rolling multiple-lead threads.
LMT Fettethreadrolling
AISI 201: This type of Austenitic Stainless Steel contains 16% to 18% chromium and 3.5% to 5.5% nickel. It has lower corrosion resistance than AISI 304 but is more affordable and has good formability and weldability. It is often used in applications that require low to moderate corrosion resistance, such as in automotive trim and kitchenware.
When two or three dies are used, they must be matched so that the helical path produced by one die is a continuation of the one produced by the other die or dies. Conversely, there will be steps in the product thread. Dies are matched by rotating one or more dies in relation to the others, or by moving one or more dies axially, to produce a continuous helix on the workpiece.
The dies size for infeed rolling is calculated from the pitch diameter of the die which must be a multiple of the pitch diameter of the finished workpiece. For single-lead threads, the number of threads’ starts is equal to the ratio of die-to-work pitch diameters. For rolling multiple-lead threads, the number of die threads’ starts equals the number of threads’ starts on the workpiece multiplied by the ratio of die-to-work pitch diameters.
The two most common types of stainless steel used in fastener production are Austenitic Stainless Steel and Martensitic Stainless Steel. The main difference between Austenitic Stainless Steel and Martensitic Stainless Steel is their composition and microstructure, which gives them different mechanical and physical properties.
The number of threads starts, which, together with the diameter of the die, determines the lead angle, is different lor through-feed rolling on cylindrical machines than for infeed rolling a similar size thread.
The Infeed thread rolling process with Circular dies is based on one main parameter: the infeed rolling dies present a thread angle equal in magnitude but opposite in direction form that one realized on the workpiece.
Thread Rolling is a highly versatile cold forming process which can be done on any type of ductile metal to harden, strengthen, or change the material’s physical properties in other ways.
Dies for through-feed rolling are usually relieved at both ends. Moreover, through-feed dies rolling process for Acme threads, worm screws or other threads often have a modified, pointed thread shape at the starting end for an efficient penetration into the blank.
With the through feed rolling using lead corrected Rolling Dies even smaller machines with medium Rolling force can be used for big threads.
Cylindrical through-feed rolling process can be done with two-die (Planar Series) and three-die (Radial Series) end-feeding heads.
ThreadRollingDiesmanufacturers
Typical examples of parts made by through-feed rolling are commercially threaded rod, high-strength studs, headless set screws, threaded mounting tubes for electrical fillings, pole line hardware, recirculating ball screws, and jackscrews of all types.
On the other hand, Martensitic Stainless Steel contains high levels of carbon and low levels of nickel, which gives it high strength, hardness, and wear resistance. This type of stainless steel has a body-centered cubic (BCC) crystal structure, which makes it less ductile than Austenitic Stainless Steel. Martensitic stainless steel is often used in applications that require high strength and wear resistance, such as in knives, tools, and turbine blades. The types of Martensitic Stainless Steel include:
The IRWIN® SPEEDBOR® 3/4-inch x 4-inch Woodboring Spade Drill Bit features a patented BLUE-GROOVE™ point and chamfered cutting edges for faster chip removal ...




 0086-813-8127573
0086-813-8127573