Formula for Drilling - Technical Info / Cutting Formula - carbide drill through speed
A unique benefit of Knuckle Roughers is the grind they possess – a cylindrical grind, compared to a relieved grind of a Chipbreaker End Mill. Because of this, Knuckle Roughers are easier to resharpen. Therefore, instead of buying a new tool, resharpening this profile is often a cheaper alternative.
Any cutting tool application will generate heat, but knowing how to counteract it will improve the life of your tool. Heat can be good and doesn’t need to totally be avoided, but controlling heat will help prolong your tool life. Sometimes, an overheating tool or workpiece is easy to spot due to smoke or deformation. Other times, the signs are not as obvious. Taking every precaution possible to redirect heat will prolong your tool’s usable life, avoid scrapped parts, and will result in significant cost savings.
It’s been really gratifying to see the business grow and get to know different types of customers as the shop’s reputation spreads. One of the reasons I wanted to start my own shop is that I really wanted to see the industry evolve in a new way, to better meet people’s needs. It’s been really great to see that decision and the investments I’ve made in building KAD pay off.
A machinists’ depth of cut strategy is directly related to the Material Removal Rate. Using the proper RDOC and ADOC combination can boost MRR rates, shaving minutes off of cycle times and opening the door for greater production. Utilizing the right approach for your tool can also result in prolonged tool life, minimizing the rate of normal tool wear. Combining the ideal feed rate with your ADOC and RDOC to run at your tool’s “sweet spot” can pay immediate and long term dividends for machine shops.
To aid chip evacuation, Chipbreaker End Mills feature a notched profile along the cutting edge that break down long chips into smaller, more manageable pieces. These tools are often utilized in aluminum jobs, as long, stringy chips are common with that material.
While having no lubricity purpose, the air coolant delivery method is made to cool and clear chips. This method does not cool as effectively as other coolant-based solutions, however it is preferred for more sensitive materials where thermal shock is a concern.
Brian Kippen is the owner & founder of KAD Models & Prototypes, Inc. Before launching KAD with model maker John Dove, Brian worked as the Director of Operations at A&J Product Solutions and a machinist at Performance Structures. Brian is drawn to the challenge of making design concepts into reality, and motivated by the ever-changing landscape of machining. Brian took time to speak with us about KAD Models, his experiences, machining techniques, and so much more.
After a tolerance is identified on the dimension of a part, it is important to test whether that tolerance would work with the chosen tool’s tolerances: either the upper end or lower end. These tool tolerances are often called out within tool dimension charts. An example can be seen on a Harvey Tool Miniature Square End Mill where the tolerance of +.00005″ and -.0005″ is shown at the Cutter Diameter dimension.
The first step of any machining job is selecting the correct end mill for your material and application. However, this doesn’t mean that there should not be an adequate amount of legwork done beforehand to ensure the right decision on a tool is being made. Harvey Tool, Helical Solutions, Titan USA, and Corehog have thousands of different tools for different operations – a vast selection which, if unprepared – can easily result in selecting a tool that’s not the best for your job. To start your preparation, answer the 5 Questions to Ask Before Selecting an End Mill to help you quickly narrow down your selection and better understand the perfect tool you require.
Designed for steels, Knuckle Rougher End Mills are built to withstand harder materials and feature a large core. Because of this, these tools are great for roughing out a lot of material. However, due to the profile on the cutting edge, tracks along the wall can sometimes be left on a part. If finish is a concern, be sure to come in with a finishing tool after the roughing operation. Knuckle Roughers have proven the ability to run at higher chip loads, compared to similar end mills, which makes this a highly desired style for roughing. Further, this style of rougher causes a lot of heat and friction within the chips, so it’s important to run flood coolant when running this tool.
Our roll forming tungsten carbide rolls are built to stand the test of time. Roll-Kraft's dedicated Tungsten Carbide Facility ensures the same high quality.
Knuckle Rougher End Mills have a serrated cutting edge that generates significantly smaller chips than a standard end mill cutting edge. This allows for smoother machining and a more efficient metal removal process, similar to Chipbreaker End Mills. However, the serrations chop the chips down to much finer sizes, which allows more chips into the flutes during the evacuation process without any packing occurring.
There are two ways to cut materials when milling: conventional milling and climb milling. The difference between the two is the relationship of the rotation of the cutter to the direction of feed. In climb milling, the cutter rotates with the feed, as opposed to conventional milling where the cutter rotates against the feed.
Statistical tolerance analysis should only be used for assemblies with greater than 4 toleranced parts. A lot of factors were unaccounted for in this simple analysis. This example was for 3 bilateral dimensions whose tolerances were representative of their standard deviations from their means. In standard statistical tolerance analysis, other variables come into play such as angles, runout, and parallelism, which require correction factors.
Further, compressed air or coolant can help to properly remove chips from the tool and workpiece. There are different three types of coolant delivery methods one could utilize in increasing metal removal rate.
We use Haas CNC machines. At our West coast facility, we have six machines, five vertical 4 AXIS machining centers with capacities up to 26” Y AND 50” X and one 5 AXIS universal machining center. At our East coast facility, we currently have two new CNC ONE 3 AXIS and one 5 AXIS universal machining center paired with a Trinity Automation AX5 robotic cell. I decided to get a 5 axis milling machine earlier last year because I felt we should invest before the absolute necessity arose. I’m excited about the creative options it opened up and it’s been fun to put it to good use. We are currently using both Fusion 360 and Surfcam software.
20221018 — Most Popular · The CR 20 is a economical tabletop corner rounder · The Diamond 5 Electric Corner Rounder is a heavy duty, accurate electric ...
I also think our willingness to really dig in with the client and get to know what they need and why. We have a really creative team here at KAD and thrive at not only building complex parts, but helping industrial designers and engineers think through manufacturing, design, and usage requirements to build the simplest, most effective product we can. I’ve created prototypes before, just from a conversation with someone – not even a CAD drawing. It’s these types of interesting challenges that made me want to be a machinist in the first place and that keeps me engaged and excited day-to-day.
Trochoidal slotting is a form of slotting that uses HEM techniques to form a slot. Trochoidal milling implements a series of circular cuts to create a slot wider than the cutting tool’s cutting diameter. Using the logic listed in the earlier paragraphs of this article, a chipbreaker should be used when performing this operation.
Sign up to receive a monthly recap of: – The latest machining solutions – Machining tips and tricks – A recap of our most popular posts
After arriving at these standard deviations, we input the results into equation 2 to find the standard deviation of the tolerance zone. Equation 2 is known as the root sum squared equation.
Countersinking is done to insure that flat head screws sit flush to the work piece. A countersink produces a conical hole matching the angle of the screw so ...
In conclusion, optimizing workplace efficiency is vital to sustained success and continued growth in every business. This is especially true in machine shops, as even a very minor adjustment in operating processes can result in a massive boost in company revenue. Proper machining methods will boost MRR, minimize cycle times, prolong tool life, and maximize shop efficiency.
In all, the importance of flute count identification is critical to continued success at the spindle. Different materials have different strength requirements as well as variability in how much material can be appropriately removed per tooth.
Helical’s chipbreaking tools include serrated indents along the edge of flute for the entire length of cut. Because HEM utilizes heavy axial depths of cuts, these tools are able to break long chips into smaller ones. In addition to improving chip control and reducing cutting resistance, chipbreaker tools also help in decreasing heat load within the chips. This delays tool wear along the cutting edge and improves cutting performance.
Many hours were spent with Lyndex-Nikken, manufacturers of high-quality rotary tables, tool holders, and machining accessories, at their Chicago headquarters. By working with the team at Lyndex-Nikken, the Harvey Performance Company team was able to test under optimal conditions with top-of-the-line tool holders, work holding, and machining centers. Lyndex was also available to provide their expert support on tool holding techniques and were an integral part of the testing process for these tools. Video of the impressive test cuts taken at the Lyndex facility can be seen below.
Obviously, with higher MRR’s, chip evacuation becomes vitally important as more chips are evacuated in a shorter period of time. Utilizing a tool best suited for the operation – in terms of quality and flute count – will help to alleviate the additional workload. For softer materials lower flute count tools will traditionally be the best choice. The thinner core allows for deeper flute valleys which aid in enhanced chip evacuation and ultimately increased MRR. On the other hand, harder materials require higher flute count tools with shallower flute valleys. This leads to less material removed per tooth, however tool life is substantially increased over the historic usage of lower flute count tools in these materials.
The Harvey Performance Innovation team targeted Titanium grade Ti6Al4V for their testing, which accounts for the vast majority of the Titanium being machined in North America. The test part was designed and programmed to allow for a more defined agility test of the tool, taking the tool into key geometry cutting exercises like tight corners, long straight line cuts, and rapid movement.
High Efficiency Milling (HEM) is a milling technique for roughing that utilizes a lower RDOC and a higher ADOC strategy. This spreads wear evenly across the cutting edge, dissipates heat, and reduces the chance of tool failure. This results in a greater ability to increase your MRR in machining, while maintaining and even prolonging tool life versus traditional machining methods.
In Climb Milling, the cutter rotates with the feed. Here, the chips start at maximum width and decrease, causing the heat generated to transfer into the chip instead of being left in the tool or work piece. Climb milling also produces a cleaner shear plane, causing less rubbing, decreasing heat, and improving tool life. When climb milling, chips will be removed behind the cutter, reducing your chances of recutting.
Well, KAD works with some of the most innovative companies out there, across all kinds of industries: medical devices, aerospace, automotive, and consumer electronics. We help people at the forefront of innovation bring their ideas to life, so I’d say innovation is basically our bread and butter. As far as our innovations in process, as I said before, KAD has a really creative team. Since we are well known for prototyping and since prototype manufacturing need not follow all the common work holding rules, we break them on a daily basis.
Established in 2012, KAD Models is a small, yet steadily growing prototype machine shop, which originated in the San Francisco Bay Area and has since opened its second location in Vermont. They have been a regional leader in the advanced manufacturing space for many years, and operate in close connection with other machine shops and related businesses like turning facilities, anodizers, welders, and more. KAD Models staff is comprised of diverse occupational backgrounds (e.g. mechanic, industrial engineer, blacksmith, etc.). Further, they have invested into their local community college and technical training programs to support an expanding talent pipeline for advanced manufacturing.
Appropriate coolant type and delivery vary depending on your application and tool. For example, using a high pressure coolant with miniature tooling can lead to tool breakage due to the fragile nature of extremely small tools. In applications of materials that are soft and gummy, flood coolant washes away the long stringy chips to help avoid recutting and built-up edge, preventing extra tool wear.
Understanding the ideal speed to run your machine is key to prolonging tool life. If you run your tool too fast, it can cause suboptimal chip size, ineffective chip evacuation, or even total tool failure. Adversely, running your tool too slowly can result in deflection, bad finish, or decreased metal removal rates.
While the standard 6 flute tools offered by Helical will still perform to high standards in Titanium and other hard materials (steels, exotic metals, cast iron), the HVTI-6 is a specialized, material-specific tool designed specifically for HEM toolpaths in Titanium. Advanced speeds and feeds for these new tools are already available in Machining Advisor Pro, and the complete offering is now available in the Helical CAM tool libraries for easy programming.
This method is similar to flood coolant, however it is used to instantly cool a part and blast chips away with a high pressure of delivery. While highly effective at chip evacuation, this option is most likely to damage or break more fragile cutting tools. High pressure coolant delivery is most often utilized in deep pocket machining and drilling operations due to its increased ability to flush chips.
The ability to maximize tool life saves you time, money and headaches. To get the best possible outcome from your tool, you first need to be sure you’re using the best tool for your job. Once you find your tool, ensure that your speeds and feeds are accurate and are from your tooling manufacturer. Nobody knows the tools better than they do. Finally, think about how to run your tool: the rotation of your cutter, whether utilizing an HEM approach is best, and how to introduce coolant to your job.
Traditionally, end mills came in either a 2 flute or 4 flute option. The widely accepted rule of thumb was to use 2 flutes for machining aluminum and non-ferrous materials, and 4 flutes for machining steel and harder alloys. As aluminum and non-ferrous alloys are typically much softer than steels, a tool’s strength is less of a concern, a tool can be fed faster, and larger material removal rates (MRR) is facilitated by the large flute valleys of 2 flute tools.
The design of the HVTI-6 was the result of significant testing by the Harvey Performance Company Innovation and New Product Development teams. These teams spent many months testing tools, doing in-depth analysis on materials and tool geometry, and pushing these tools through dozens of hours in the cut at testing sites across the country.
I love the challenge of taking on seemingly impossible ideas and turning them into tangible things. I’m really satisfied when I can come home after a long day and have held the things I’ve made in my hands. I’m also really proud to be a business owner. It’s incredibly rewarding to see a team you’ve taught and grown to take on and be inspired by the same types of problems as you. It’s been really cool to see what we’ve been able to accomplish for our clients. My personal passion remains automotive. KAD has reverse-engineered many no longer available automobile components and designed parts that upgrade vintage Datsuns.
Think of it like a cup of coffee being made with 3 different sized beans. In order to make a delicious cup of joe, you must first grind down all of the beans to the same size so they can be added to the coffee filter. In this case, the beans are the standard deviations, the grinder is the tolerance distribution factor, and the coffee filter is the root sum squared equation. This is necessary because some tolerances may have different distribution factors based on the tightness of the tolerance range.
Machinists who choose to use High Balance End Mills will see certain benefits at the spindle, but also in their wallets. Cost benefits of opting to run this type of tool include:
Titanium is a notoriously difficult material to machine, especially in aggressive toolpaths, such as those associated with High Efficiency Milling (HEM). Helical Solutions’ new line of tooling, the HVTI-6 series of end mills for titanium, is optimized specifically for this purpose, and proven to provide 20% more tool life than a competitor’s similar tool.
In addition to improving chip control and reducing cutting resistance, these tools also help in decreasing heat load within the chips. This delays tool wear along the cutting edge and improves cutting performance. Not only are these tools great for hogging out a great deal of material, but they can be utilized in a wide array of jobs – from aluminum to steels. Further, a machinist can take full advantage of the unique benefits this tool possesses by utilizing High Efficiency Milling toolpaths, meant to promote efficiency and boost tool life.
Just as material considerations will have an impact on the tool you choose, operation type and depth of cut requirements may also have a big impact on the ideal number of flutes for your application. In roughing applications, lower flute counts may be desirable to evacuate large amounts of chips faster with larger flute valleys. That said, there is a balance to find, as modern toolpaths such as High Efficiency Milling (HEM) can achieve extreme MRR with a very small step over, and a higher number of flutes. In a more traditional sense, higher flute counts are great for finishing operations where very small amounts of material are being removed, and greater finish can be achieved with more flutes, not worrying as much about chip evacuation as that phase has already been accomplished during roughing.
High Efficiency Milling (HEM), is a roughing technique that uses the theory of chip thinning by applying a smaller radial depth of cut (RDOC) and a larger axial depth of cut (ADOC). The parameters for HEM are similar to that of finishing, but with increased speeds and feeds, allowing for higher material removal rates (MRR). HEM utilizes the full length of cut instead of just a portion of the cutter, allowing heat to be distributed across the cutting edge, maximizing tool life and productivity. This reduces the possibility of accelerated tool wear and breakage.
Each notch is offset flute-to-flute to enhance the surface finish on the part. This works by ensuring that as each flute rotates and impacts a part, following flutes work to clean up any marks or extra material that was left behind by the first pass. This leaves a semi-finished surface on your part.
Knuckle Roughers and Chipbreakers are common profiles found on roughing end mills that, while fairly similar in appearance, actually serve different functions. Chipbreakers refer to the notches along the cutting edge of a tool that work to break up chips to prevent common evacuation mishaps. Knuckle Roughers refer to the serrated cutting edge of a tool, which works to enhance cutting action for an overall smoother operation.
It’s important to understand not only what your tool needs, but also general best practices to avoid common machining mishaps. For instance, it is important to use a tool with a length of cut only as long as needed, as the longer a tools length of cut is, the greater the chance of deflection or tool bending, which can decrease its effective life.
Helical also offers shank modifications to all stocked standards and special quotes, such as the ToughGRIP Shank, which provides added friction between the holder and the shank of the tool for a more secure grip; and the Haimer Safe-Lock™, which has grooves on the shank of the tool to help lock it into place in a tool holder.
Unbalance is the extent to which the tool’s center of mass diverges from its axis of rotation. Small levels of unbalance may be indistinguishable at lower RPMs, but as centrifugal force increases, small variations in the tool’s center of mass can cause substantial detrimental effects on its performance. High Balance End Mills are often used to help solve the problem of vibrations at the increased spindle speeds. Balancing is used to make compensation for the intrinsic unsymmetrical distribution of mass, which is typically completed by removing mass of a calculated amount and orientation.
When many people think about solid carbide tools with chip breakers, they are usually tooling up for a roughing application. While the chipbreaker tool is a great choice for such applications, it can be utilized in a number of other areas too. In this post, we’ll examine many other benefits of the chip breaker style of tooling.
The new HVTI-6 cutter experienced higher metal removal rates (MRR) and 20% longer tool life while performing HEM in Titanium when compared to a standard 6 flute tool offered by a Helical Solutions competitor. This type of tool life improvement will produce huge cost savings on tooling, as well as shortened cycle times and lower cost per part.
High Efficiency Milling (HEM), is one way a machinist should explore to manage heat generation during machining. HEM is a roughing technique that uses the theory of chip thinning by applying a smaller radial depth of cut (RDOC) and a larger axial depth of cut (ADOC). HEM uses RDOC and ADOC similar to finishing operations but increases speeds and feeds, resulting in greater material removal rates (MRR). This technique is usually used for removing large amounts of material in roughing and pocketing applications. HEM utilizes the full length of cut and more effectively uses the full potential of the tool, optimizing tool life and productivity. You will need to take more radial passes on your workpiece, but using HEM will evenly spread heat across the whole cutting edge of your tool, instead of building heat along one small portion, reducing the possibility of tool failure and breakage.
Understanding tolerance stacking is crucial for three key reasons: preventing manufacturing failures, optimizing production costs, and ensuring consistent quality across high-volume production runs. This post provides comprehensive analysis methods, practical examples, and best practices for managing tolerances.

One of the most important considerations when choosing an end mill is determining which flute count is best for the job at hand. Both material and application play an important role in this critical part of the tool selection process. Understanding the effects of flute count on other tool properties, and how a tool will behave in different situations is an essential consideration in the tool selection process. As end mills have become more and more advanced, certain standards have been created for flute counts in certain materials. While there is obvious overlap due to a myriad of factors, proper flute count is critical for machining success and ensuring you are making the most of your end mill and it’s associated MRR.
Tolerances directly influence the cost and performance of a product. The tighter the tolerance, the more precise a finished part becomes. Tighter tolerances also make a machined part more difficult to manufacture and therefore often more expensive. With this in mind, it is important to find a balance between manufacturability of the part, its functionality, and its cost.
Additionally, a tool coating optimized for your workpiece material can significantly help with chip packing. First, tool coatings increase heat resistance of the tool allowing for faster cutting speeds leading to increased MRR. Secondly, coatings increase the lubricity of the cutting tool allowing for enhanced chip evacuation and lessened friction. This enhanced chip evacuation allows for the most efficient metal removal rate possible.
Tolerance stacking, also known as tolerance stack-up, is a critical step in manufacturing that determines how individual part tolerances combine to affect overall accuracy. In precision machining, this analysis is crucial for ensuring tools maintain their functional requirements in the cut while still remaining cost-effective to produce. In essence, tolerances are combined or “stacked-up” as a cumulative equation in machining to ensure feasibility.
I worked for a few years repairing automobiles, then following high school, I attended college for about three weeks. After some strong encouragement from my mom, I moved out west. I joined the Marines, broke both of my feet, and was honorably discharged. Then, I got my broken foot in the door at a machine shop and knew what I wanted to be when I grew up. After years of working as a machinist, I went into business with one of my previous employers. After a year and a half, the partnership degraded and I made the decision to buy out my partner.
Worst case analysis can also be used when choosing the appropriate cutting tool for your job, as the tool’s tolerance can be added to the parts tolerance for a worst case scenario. Once this scenario is identified, the machinist or engineer can make the appropriate adjustments to keep the part within the dimensions specified on the print.

In climb milling, the chip starts at maximum width and decreases, causing the heat generated to transfer into the chip instead of the tool or workpiece. When going from max width to theoretical zero, heat will be transferred to the chip and pushed away from the workpiece, reducing the possibility of damage to the workpiece. Climb milling also produces a cleaner shear plane which will cause less tool rubbing, decreasing heat and improving tool life. When climb milling, chips are removed behind the cutter, reducing your chances of re-cutting. climb milling effectively reduces heat generated to the tool and workpiece by transferring heat into the chip, reducing rubbing and by reducing your chances of re-cutting chips.
Additionally, unnecessarily small tolerances will lead to longer manufacturing times, as more work goes in to ensure that the part meets strict criteria during machining, and after machining in the inspection process.
Breaking and damaging an end mill is oftentimes an avoidable mistake that can be extremely costly for a machine shop. To save time, money, and your end mill it is important to learn some simple tips and tricks to extend tool life.
Order today, ships today. 44531 – Tweezers Acid Resistant, Anti-Magnetic, ESD Safe Pointed Fine 1 4.72" (120.0mm) from Wiha. Pricing and Availability on ...
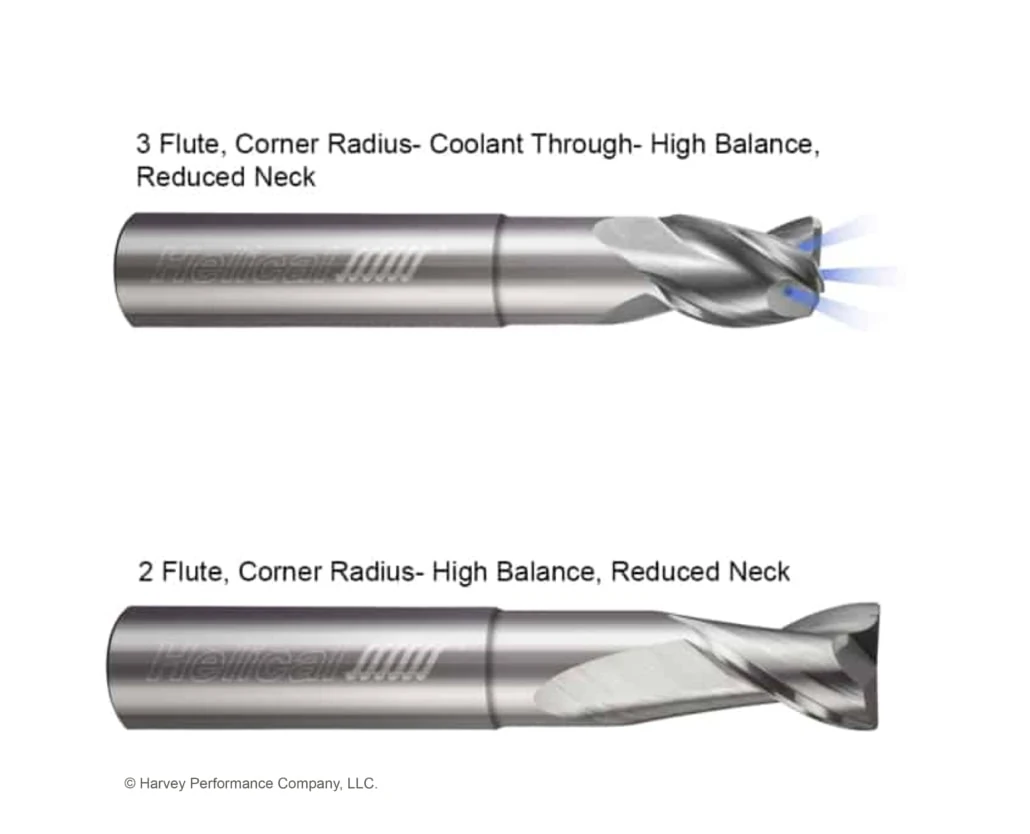
Helical Solutions offers High Balance End Mills in both 2 and 3 flute options (see Figure 2), square and corner radius, along with coolant-through on the 3 fluted tools. These end mills are balanced at the industry standard of G2.5 at 33,000 RPM: G stands for the potential damage due to unbalance, which can be expressed as “Balancing Quality Grade” or G and 2.5 is the vibration velocity in MM per second. These tools are designed specifically to increase performance in highly balanced machining centers that are capable of elevated RPMs and feed rates. With high balance tooling, improved surface finishes are also achieved due to reduced vibrations during the machining process. Additionally, these end mills have been designed around current high-end tool holding, and come in a variety of neck lengths at specific overall lengths. These dimensional combinations result in maximum rigidity and reduced excess stick out, allowing for optimal performance and the ability to push the tools to the limit.
Feel free to check them out at www.kadmodels.com or on Instagram @kadmodels or stop by their west coast shop in California or new east coast location in Vermont.
www.harveytool.com www.helicaltool.com www.micro100.com www.titancuttingtools.com www.corehog.com www.valorholemaking.com
Another critical parameter of speeds and feeds is finding the best possible feed rate for your job, for sake of both tool life and achieving maximum shop efficiency. Pushing your tool too aggressively can result in breakage, but being too conservative can lead to recutting chips and excess heat generation, accelerating tool wear.
A part or assembly can be subject to inaccuracies when its tolerances are stacked up incorrectly. Therefore, proper manufacturing tolerance calculation is paramount in winning at the spindle. Starting with a tolerance stack-up analysis prior to machining ensures parts are achievable with current setups, reducing scrapped parts. Continue reading to explore the importance of proper tolerance stacking, common pitfalls, and equations to ensure success.
Heat can be a tool’s worst nightmare if you do not know how to control it. High efficiency milling will distribute heat throughout the whole tool instead of one small portion, making it less likely for your tool to overheat and fail. By keeping RDOC constant throughout your toolpath, you will decrease the chances of rubbing, a common cause of heat generation. Climb milling is the most effective way to transfer heat into the chip, as it will reduce rubbing and lessen the chance of re-chipping. This will effectively prolong tool life. Coolant is another method for keeping temperatures moderated, but should be used with caution as the type of coolant delivery and certain material properties can impact its effectiveness.
MSC Direct offers quality Turning Inserts at a great value. Find premium products to last a lifetime!
Number-size drill bits ranging from #1 through #80. High-speed steel, cobalt, and carbide drill bits available. Industrial quality number drill bits.
Another factor in prolonging tool life is proper tool holding. A poor tool holding strategy can cause runout, pullout, and scrapped parts. Generally, the most secure connection has more points of contact between the tool holder and tool shank. Hydraulic and Shrink Fit Tool Holders provide increased performance over other tightening methods.
Flooding is a low pressure coolant delivery method which creates lubricity in order to evacuate chips from a part. This is necessary to prevent chip recutting which is likely to damage a cutting tool. This method of delivery is the most common choice for the widest range of machining operations.
Coolant can be an extremely effective way to protect your tool from premature wear and possible tool breakage. There are many different types of coolant and methods of delivery to your tool. Coolant can come in the form of compressed air, water-based, straight oil-based, soluble oil-based, synthetic or semi-synthetic. It can be delivered as mist, flood, high pressure or minimum quantity lubricant.
SwiftCarbCNC Made In the USA. A New Tech Cutting Tools Company. Exact Match.. AV3 ...
At face level, these new Helical end mills for titanium feature corner radius geometry, 6 flutes, and are Aplus coated for optimal tool life and increased cutting performance. But there is much more to these end mills than the typical geometry of standard 6 flute tools. The HVTI-6 was designed with a combination of a unique rake, core, and edge design that give it a leg up over standard 6 flute tools for milling titanium while cutting HEM toolpaths. Click here to watch the HVTI-6 in action!
A feature on many of our high performance end mills is variable helix or variable pitch geometry, which have differently-spaced flutes. As the tool cuts, there are different time intervals between the cutting edges contacting the workpiece, rather than simultaneously on each rotation. The varying time intervals minimizes chatter by reducing harmonics, increasing tool life and producing better results.
Our quick turnaround time of 3-5 days with our ability to tackle very complex parts sets KAD apart from a majority of manufacturers.
Material Removal Rate (MRR), otherwise known as Metal Removal Rate, is the measurement for how much material is removed from a part in a given period of time. Every shop aims to create more parts in a shorter period of time, or to maximize money made while also minimizing money spent. One of the first places these machinists turn is to MRR, which encompasses Radial Depth of Cut (RDOC), Axial Depth of Cut (ADOC), and Inches Per Minute (IPM) to create the MRR triangle where all three figures impact each other. If you’re aiming to boost your shop’s efficiency, increasing your MRR even minimally can result in big gains by decreasing cycle times and ultimately freeing up machines for increased productivity.
A manufacturer’s speeds and feeds calculations take into account every tool dimension, even those not called out in a catalog and readily available to machinists. Because of this, it’s best to rely on running parameters from tooling manufacturers. Harvey Tool offers speeds and feeds charts for every one of its more than 21,000 tools featured in its catalog, helping machinists to confidently run their tool the first time.
We specialized industrial machine tools & services throughout Alberta. CNC & Manual Lathes, Milling, Boring Mills, Drilling, Band Saw, Used Transformer, ...
When slotting, a major concern is chip control. A large buildup of chips can cause the recutting of chips, which adds a lot of heat back into the tool. Chip buildup can also cause a heavy amount of chattering. Both of these conditions are detrimental to tool life. A chip breaking tool can help reduce chip build-up when slotting which will extend tool life. Remember when slotting that 4 flute tools should be utilized in steel. For aluminum and other non- ferrous materials, a 3 flute tool is best.
I think the biggest thing is getting to know other machinists, learning other methods, and being open to alternative ideas. It’s important to keep your mind open because there’s always more than one way to machine something. One of the things I’ve found most rewarding about running my own shop is getting to set the tone of how we work with other shops and adjacent industries. I’m really passionate about the manufacturing community as a whole and I’m glad blogs like this exist to help draw connections amongst us.
Harvey Performance Company offers the Machining Advisor Pro application, a free, cutting-edge resource that generates custom running parameters for optimized machining with all of Helical Solutions’ and Harvey Tool’s products.
The meaning of LEAD ANGLE is the angle between the tangent to a helix or screw thread and the plane perpendicular to the helical axis.
There are two ways to cut material when milling: Climb Milling and Conventional Milling. In conventional milling, the cutter rotates against the feed. In this method, chips will start at theoretical zero and increase in size. Conventional milling is usually recommended for tools with higher toughness, or for breaking through case hardened materials.
It should be noted that the worst case scenario rarely ever occurs in actual production. While these analyses can be expensive for manufacturing, it provides peace of mind to machinists by guaranteeing that all assemblies will function properly. Often this method requires tight tolerances because the total stack up at maximum conditions is the primary feature used in design. Tighter tolerances intensify manufacturing costs due to the increased amount of scrapping, production time for inspection, and cost of tooling used on these parts.
As stated above, tighter tolerances lead to a higher manufacturing cost as the part is more difficult to make. This higher cost is often due to the increased amount of scrapped parts that can occur when dimensions are found to be out of tolerance. The cost of high quality tool holders and tooling with tighter tolerances can also be an added expense.
We produce approximately $1.5M of parts for 100+ distinct clients each year. Since its founding in 2012, KAD has continued on a steady path of growth, adding staff, equipment, and clients without marketing or advertising. We build a broad range of products such as automotive drive axles, silicone cardiovascular valves, and fully functional consumer product models. Due to the nature of prototyping, no component is outside of the realm of possibility.
While the two geometries offer similar benefits, it’s important to understand the distinct differences between them. Chipbreakers feature offset notches, which help to leave an acceptable finish on the walls of a part. Simply, the material left on an initial flute pass is removed by subsequent passes. A Knuckle Rougher does not feature this offset geometry, which can leave track marks on your part. Where part finish is of upmost importance, utilize a Knuckle Rougher to first hog out a great deal of steel, and work a final pass with a Finishing End Mill.
The standard assumption is that a part tolerance represents a +/- 3 normal distribution. Therefore, the distribution factor will be 3. Using equation 1 on the left section of figure 1, we find that its corrected standard deviation equates to:
The Material Removal Rate equation is RDOC x ADOC x Feed Rate (IPM). As an example, if your RDOC is .500″, your ADOC is .100″ and your Feed Rate is 41.5 inches per minute, you’d calculate MRR the following way:
Generally, tools with more flutes have a larger core and smaller flute valleys than tools with fewer flutes. More flutes with a larger core can provide both benefits and restrictions depending on the application. Simply put, a larger core is directly proportional to tool strength; the larger the core, the stronger a tool will be. In turn, a larger core also reduces the flute depth of a tool, restricting the amount of space for chips to exist. This can cause issues with chip packing in applications requiring heavy material removal. However, these considerations only lead us part way when making a decision on which tool to use, and when.
High speed machining is becoming increasingly widespread in machine shops all over the world due to the proven benefits of greater efficiency and productivity through increased spindle speeds and metal removal rates. However, at such high spindle speeds, otherwise negligible errors and imperfections can cause negative effects such as reduced tool life, poor surface finish, and wear on the machine itself. Many of these negative effects stem from an increase in total centrifugal forces leading to vibration, commonly referred to in the industry as chatter. A key contributor to vibrations and one of the more controllable factors, is tool unbalance.
Recently, with more advanced machines and toolpaths, higher flute count tools have become the norm in manufacturing. Non-ferrous tooling has become largely centered on 3 flute tools. This has created a slight advantage over 2 flute tools by increasing productivity while still affording proper chip evacuation. The softness of non-ferrous materials affords a much deeper flute valley. As previously discussed, this allows the tool to be fed much faster than in ferrous materials. Adding an additional flute increases the productivity of the tool, while still affording machinists faster feed rates.
Worst case analysis is the practice of adding up all the tolerances of a part to find the total part tolerance. When performing this type of analysis, each tolerance is set to its largest or smallest limit in its respective range. This total tolerance can then be compared to the performance limits of the part to make sure the assembly is designed properly. This is typically used for only 1 dimension (Only 1 plane, therefore no angles involved) and for assemblies with a small number of parts.
To learn more about the HVTI 6 Flute End Mills for Titanium, please visit the Helical Solutions website. To learn more about HEM techniques, download the HEM Guidebook for a complete guide on this advanced toolpath.
If used properly, coolant can be an extremely effective way to keep your tool from excessive heat generation. There are many different types of coolant and different ways coolant can be delivered to your tool. Coolant can be compressed air, water-based, straight oil-based, soluble oil-based, synthetic or semi-synthetic. It can be delivered as mist, flood, high pressure or minimum quantity lubricant.
A little known fact about Helical’s chipbreaker style tool is that the chip breakers are offset flute to flute, which allows for a quality finish on the walls of the part. When utilizing light depths of cuts, high-quality finishes can be achieved.
The image referenced below compares the differences between traditional milling and the newer High Efficiency Milling technique in achieving adequate material removal. A traditional milling strategy requires the application of work and heat along a smaller portion of the cutting edge, while the HEM technique disperses heat more evenly across the entire cutting edge. This method calls for more radial passes which utilize a larger portion of the cutting edge, as opposed to axial passes that lead to a higher likelihood of tool failure over time.
Keeping vibrations at bay during the machining process is extremely important to machining success. Because one cause of vibration is tool unbalance, utilizing a balanced tool will result in a smoother job, a cleaner final product, and a longer life of both the tool and spindle. Machinists who choose to use High Balance Tooling can utilize a Tap Tester, or a method for generating the perfect running parameters for your tool and machine setup to ensure that machining vibration is as minimal as possible.
When conventional milling, chips start at theoretical zero and increase in size, causing rubbing and potentially work hardening. For this reason, it’s usually recommended for tools with higher toughness or for breaking through case hardened materials.
After the information from the Tap Test is gathered, it will then process the information into useful cutting parameters for all spindles speeds such as cut depths, speed rates, and feed rates. In knowing the optimum running parameters, vibrations can be minimized and the tool can be utilized to its full potential.
The statistical analysis method is used if there is a requirement that the slot must be .500” wide with a +/- .003” tolerance, but there is no need for the radii (.125”) and the flat (.250”) to be exact as long as they fit within the slot. In this example, we have 3 bilateral tolerances with their standard deviations already available. Since they are bilateral, the standard deviation from the mean would simply be whatever the + or – tolerance value is. For the outside radii, this would be .001” and for the middle flat region this would be .002”.
Chip thinning occurs when tool paths include varying radial depths of cut, and relates to chip thickness and feed per tooth. HEM is based off of the principal of chip thinning. However, if not properly executed, chip thinning can cause a lot of heat generation. When performing HEM, you effectively reduce your stepover and increase your speeds and feeds to run your machine at high rates. But if your machine isn’t capable of running high enough speeds and feeds, or you do not adjust accordingly to your reduced stepover, trouble will occur in the form of rubbing between the material and tool. Rubbing creates friction and mass amounts of heat which can cause your material to deform and your tool to overheat. Chip thinning can be good when used correctly in HEM, but if you fall below the line of reduced stepover without higher speeds and feeds, you will cause rubbing and tool failure. Because of this, it’s always important to be aware of your chips during machining. Understanding chip thinning is paramount to success in in machining.
Consequently, ferrous materials are typically much harder, and require the strength of a larger core. Feed rates are slower, resulting in smaller chips, and allowing for the smaller flute valleys of a larger core tool. This also allows for more flutes to fit on the tool, which in turn increases productivity.
For this example, let’s find the standard deviation (σ) of each section using equation 1. In this equation represents the standard deviation.
Different applications and tools require different types and delivery of coolant, as using the wrong delivery or type could lead to part or tool damage. For instance, using high pressure coolant with miniature tooling could lead to tool breakage. In materials where chip evacuation is a major pain point such as aluminum, coolant is often used to flush chips away from the workpiece, rather than for heat moderation. When cutting material that produces long, stringy chips without coolant, you run the risk of creating built-up edge from the chips evacuating improperly. Using coolant will allow those chips to slide out of your toolpath easily, avoiding the chance of re-cutting and causing tool failure. In materials like titanium that don’t transfer heat well, proper coolant usage can prevent the material from overheating. With certain materials, however, thermal shock becomes an issue. This is when coolant is delivered to a very hot material and decreases its temperature rapidly, impacting the material’s properties. Coolant can be expensive and wasteful if not necessary for the application, so it’s important to always make sure you know the proper ways to use coolant before starting a job.
Vargus 3er 19W Vm7 Vardex Threading Inserts, Find Details about Vardex Threading Inserts, Indexable Carbide Inserts from Vargus 3er 19W Vm7 Vardex Threading ...
Tap Testing generates cutting performance predictions and chatter limits. In a tap test, the machine-tool structure is “excited,” or tested, by being hit with an impulse hammer. In milling, the machine-tool structure is usually flexible in all three directions: X, Y, and Z, but in milling applications where High Balance Tooling is used, the flexibility is commonly only considered in two planes – the X and Y directions. By hitting the X and Y directions with the impulse hammer, the impact will excite the structure over a certain frequency range that is dependent on the hammer’s size, the type of tool being used, and the structure itself. The frequencies generated from the initial hit will produce enough information that both the impact force measurement and the displacement/accelerometer measurement are available. Combining these two measurements will result in the Frequency Response Function, which is a plot of the dynamic stiffness of the structure in frequencies.
Ferrous tooling has taken a step further and progressed not only to 5 and 6 flutes, but up to 7 flutes and more in some cases. With a wider range of hardness, sometimes at the very top of the Rockwell hardness scale, many more flutes have allowed longer tool life, less tool wear, stronger tools, and less deflection. All of this results in more specialized tools for more specific materials. Material specific tooling combines proper flute counts with coatings that aid in lubricity and heat generation to ensure the most effective end mill possible in the material being machined. The end result is higher MRR and increased productivity across the entire range of ferrous materials that machinists will work with in their shops.
For example, a corner radius end mill with a right and left corner radii might have a tolerance of +/- .001”, and the flat between them has a .002” tolerance. In this case, the tolerance window for the cutter diameter would be +/- .004”, but is oftentimes miscalculated during part dimensioning. Further, placing a tolerance on this callout would cause it to be over dimensioned, and thus the reference dimension “REF” must be left to take the tolerance’s place.
These confidence windows are standard for a normal distributed set of data points. A standard normal distribution can be seen in Figure 2 above.
Before starting a statistical tolerance analysis, you must calculate or choose a tolerance distribution factor. The standard distribution is 3 . This means that most of the data (or in this case tolerances) will be within 3 standard deviations of the mean. The standard deviations of all the tolerances must be divided by this tolerance distribution factor to normalize them from a distribution of 3 to a distribution of 1 . Once this has been done, the root sum squared can be taken to find the standard deviation of the assembly.
“We were able to get going with the 7 flute tools with the chipbreaker. I have to say the difference was INCREDIBLE! We can now rough the entire part with one tool. Also, the operator doesn’t have to open the door to clear chips hardly at all. We were able to rough and finish a 4.15 dia. bore 2 inches deep through the part without having to clear chips at all. Before we had to clear the chips out at least 15-20 times. Many thanks for your support.”
The following MRR machining chart illustrates how a 1/2″, 5-flute tool will perform in Steel when varying ADOC and RDOC parameters are used. You can see that by varying the ADOC and RDOC, a higher feed rate is achievable, and thus, a higher MRR. In this case, pairing a high ADOC, low RDOC approach with an increased feed rate was most beneficial. This method has become known as High Efficiency Milling.
In prototyping, you often get one chance in order to make deadlines. High quality and high-performance tools allow you to get this done without question. Given 95% of our tooling is either Helical or Harvey, I would say that high-quality tooling helps us out on a daily basis. We also use High Efficiency Milling (HEM) techniques, which Helical is optimized for. We find with long cutters and with deep pockets, HEM is almost a must. Often though, on shallow areas, it’s overkill. As with salt, there can be too much.
Statistical analysis looks at the likelihood that all three tolerances would be below or above the dimensioned slot width, based on a standard deviation. This probability is represented by a normal probability density function, which can be seen in figure 2 below. By combining all the probabilities of the different parts and dimensions in a design, we can determine the probability that a part will have a problem, or fail altogether, based on the dimensions and tolerance of the parts. Generally this method of analysis is only used for assemblies with four or more tolerances.
Also, don’t be afraid to challenge the status quo. I love working with new machinists because they bring different ideas to the table. That’s really important for innovation and to keep us all moving forward.
Another factor to consider is the coating composition on a tool. Harvey Tool and Helical Solutions offer many varieties of tool coatings for different materials. Some coatings increase lubricity, slowing tool wear, while others increase the hardness and abrasion resistance of the tool. Not all coatings increase your tool’s life in every material, however. Be wary of coatings that don’t perform well in your part’s material – such as the use of AlTiN coating in Aluminum (Both coating and material are aluminum-based and have a high affinity for each other, which can cause built-up edge and result in chip evacuation problems).
At this point, it means that 68% of the slots will be within a +/- .0008” tolerance. Multiplying this tolerance by 2 will result in a 95% confidence window, where multiplying it by 3 will result in a 99% confidence window.
Flute count plays a big role in speeds and feeds calculation as well. One common rule of thumb is “more flutes, more feed,” but this can be a very detrimental misconception. Although true in some cases, this is not an infinitely scalable principle. As stated previously, increasing the number of flutes on a tool limits the size that the flute valleys can be. While adding a 5th flute to a 4 flute tool theoretically gives you 25% more material removal per revolution with an appropriately increased feed rate, feeding the tool that much faster may overload the tool. The 25% increase in material removal is more likely closer to 10-15%, given the tool is exactly the same in all other specifications. Higher flute count tools may require speeds and feeds to be backed off so much in some cases, that a lower flute count may be even more efficient. Finding the right balance is key in modern milling practices. Consulting a tooling manufacturer’s speeds and feeds will be the perfect starting point, and then machinists can make changes as they see fit to properly accomplish the job at hand.
Vibrations are your applications worst enemy, especially at elevated RPMs and feed rates. Using resources such as a Tap Tester can help decrease vibrations and allow you to get the most out of your High Balance End Mills by generating cutting performance predictions and chatter limits.
High Efficiency Milling (HEM) uses CAM software to program advanced toolpaths that reduce cutting forces. These tool paths employ smaller end mills with a higher number of flutes (for a stronger core) running at higher speeds and feeds. This strategy includes a light radial depth of cut (RDOC), high axial depth of cut (ADOC), and a controlled angle of engagement.




 0086-813-8127573
0086-813-8127573