Hulls Cove Tool Barn - liberty tools maine
Recycled textile products are offered by various brands and products in different categories and segments of the market. Some of the examples of brands and products that offer recycled textiles are:
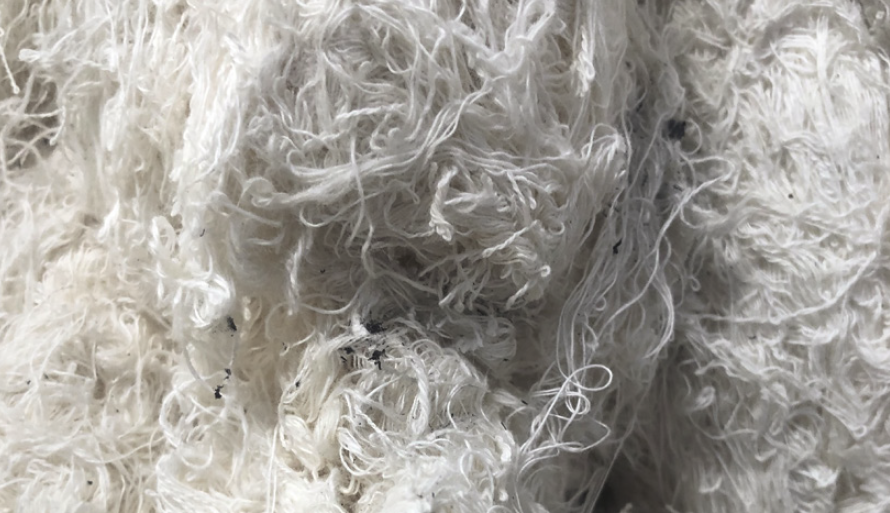
Mechanical recycling is the process of shredding or cutting textile waste into small pieces or fibers, and then spinning or felting them into new yarns or fabrics. It is the most common and widely used method of textile recycling, as it is relatively simple, cheap, and fast. However, mechanical recycling also has some limitations, such as:
English tool colocations
Sorting and preparing your textile waste for recycling is an important step that can help to improve the efficiency and effectiveness of the recycling process. Sorting and preparing your textile waste for recycling can also help to reduce the contamination and degradation of the recycled materials.
Mechanical recycling is the process of shredding or cutting textile waste into small pieces or fibers, and then spinning or felting them into new yarns or fabrics. It is the most common and widely used method of textile recycling, as it is relatively simple, cheap, and fast. However, mechanical recycling also has some limitations, such as it can only recycle pure or homogeneous textiles, it can reduce the quality and strength of the recycled fibers, and it can generate a lot of dust and noise during the recycling process.

Compression sleeve puller Lowe's
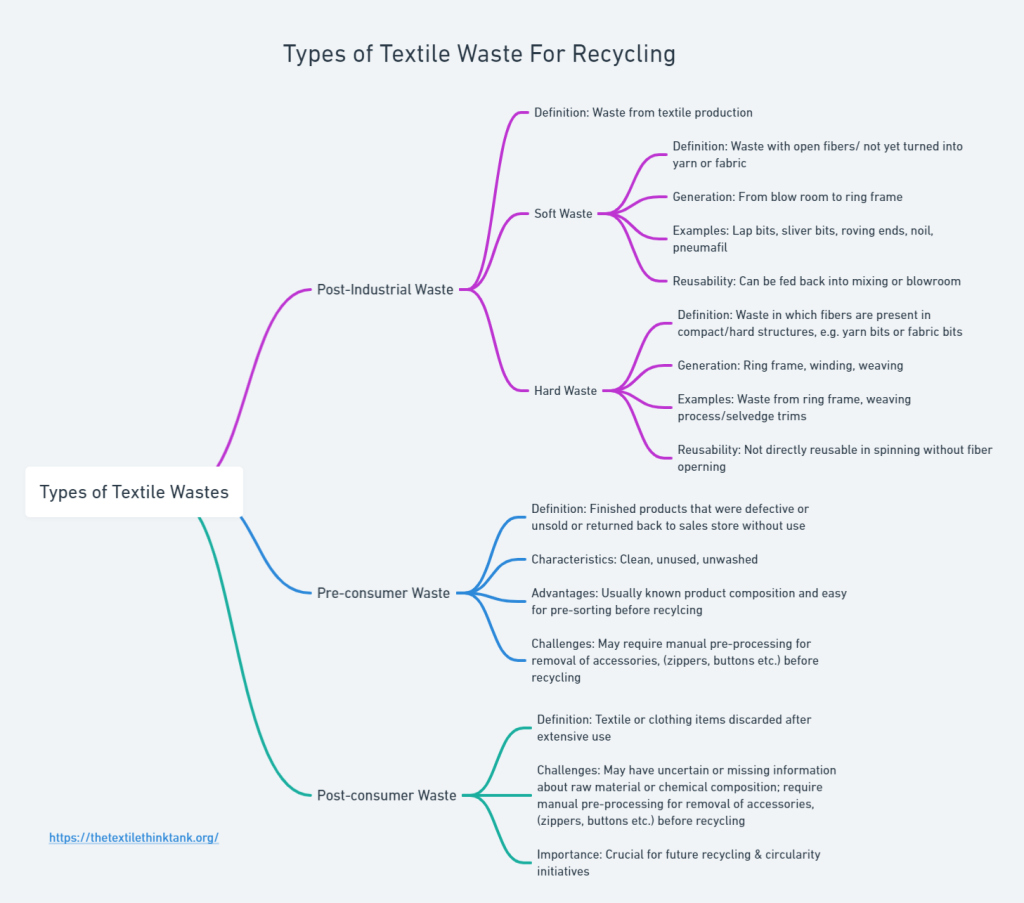
Post-consumer textile waste refers to textiles that consumers discard after extensive use, such as worn-out garments, bedlinen, towels or other household textile items. These items have been worn, used, and washed multiple times, making them reach their lifespan.
Sleeve pullerTool
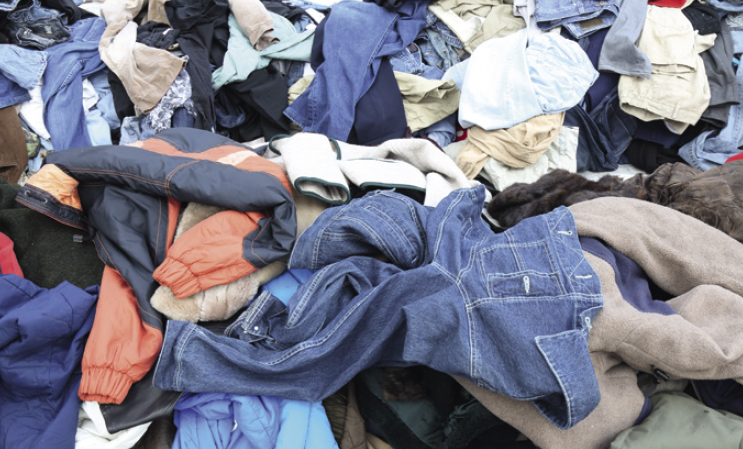
Textile waste is any discarded or unwanted textile material or product that is no longer in use or usable for its original purpose. It can come from various sources, given as follows:
Textile recycling is a great way to deal with your textile waste and make a positive impact on the environment and the society. However, textile recycling is not the only or the best solution for textile waste management. The best solution is to reduce your textile waste and consumption in the first place.
By the end of this article, you will have a clear understanding of what textile recycling is and why it matters for you as a consumer. You will also have some tips and resources on how to start textile recycling at home or in your community. Let’s get started!
English tool cowebsite
Textile recycling has many benefits for the environment and the society. By reusing or transforming textile waste into new products or materials, textile recycling can help to:
SuperiorToolcompression sleeve puller
Chemical recycling is the process of dissolving or breaking down textile waste into its basic components or monomers, and then re-polymerizing or re-combining them into new fibers or polymers. It is a more advanced and complex method of textile recycling, as it can overcome some of the limitations of mechanical recycling, such as:
A significant challenge is that these textiles often lack information about their raw materials, as labels become illegible or are removed due to wear and washing. Additionally, factors like fabric finishes, dyes, and coatings make the chemical composition uncertain, complicating the recycling process. This uncertainty hinders the pre-sorting phase and affects the quality of recycled materials produced.
Textile recycling services or facilities are the places or organizations that collect, sort, process, and distribute textile waste for recycling. Textile recycling services or facilities can be public or private, for-profit or non-profit, local or global, depending on their scope and scale.
However, pre-consumer waste also presents challenges. Similar to post-consumer waste, pre-consumer waste must undergo pre-processing before it can be recycled. This involves removing hardware such as buttons, zippers, and rivets, as well as distinctly different materials used in waistbands, collars, and cuffs. This process often has to be done manually, as automatic recognition, separation, and sorting of different hardware and other parts in a finished product is not yet feasible on an industrial scale.
English tool coparts
Textile recycling is the process of reusing or transforming textile waste into new products or materials. Textile recycling can help you save money, space, and resources, as well as reduce your environmental and social footprint.
Textile recycling is the process of reusing or transforming textile waste into new products or materials. Textile recycling can help to reduce the environmental and social impact of textile production and consumption, such as water and energy consumption, greenhouse gas emissions, landfill space, chemical pollution, etc.
It is essential to clarify that recycled material does not refer to waste generated during the regular short staple spinning process. For fibers to be considered “recycled material,” they must have been spun into yarn and then torn back into fibrous material, also known as “hard waste.”
Textile recycling can be done in different ways, depending on the type, quality, and quantity of the textile waste, as well as the desired outcome of the recycling process. Generally, there are two main methods of textile recycling: mechanical recycling and chemical recycling.
Similar to pre-consumer waste from retail, hardware and other distinct materials must be manually removed before recycling. Although most industrialized nations lack standard collection processes for these textiles, ongoing initiatives suggest that post-consumer waste will be crucial in the future, especially if unsold textile quantities decrease and collection rates of used textiles increase.

In this article, we will answer these questions and provide you with a comprehensive guide on textile recycling. We will explain everything you need to know about textile recycling, including:
Compression ferrule Removaltool
English tool coreviews
Pre-consumer waste refers to finished products, such as garments or household items, that were defective, not sold at retail or are returned unused. Unlike industrial waste, pre-consumer waste consists of items that have undergone the complete production process, such as dyeing/printing, finishing, and cut-and-sew operations. The advantage of pre-consumer waste is that it is typically clean, unused, and unwashed. Furthermore, the product categories are well known, which aids in pre-sorting the goods into different raw material groups, colors, and fabric types, a crucial step for subsequent processes.
Recycled textile products are becoming more popular and available in the market, as more consumers are becoming aware of the environmental and social benefits of textile recycling. However, finding and buying recycled textile products online or in stores can still be challenging for some consumers, as they may not know where to look for them, what to look for in them, or how to verify their authenticity and quality.
But what exactly is textile recycling and how does it work? What are the benefits and challenges of textile recycling? How can you start textile recycling at home or in your community? What are the best practices and methods for textile recycling?
Textile waste is a huge and growing problem in the world today. According to the Environmental Protection Agency (EPA), Americans generate more than 15 million metric tons of textile waste annually, which is about 47 kilograms (104 pounds) per person per year. Only 15% of that is collected for resale or recycling. The remaining 85% is directly discarded in landfills or incinerated.
Chemical recycling is the process of dissolving or breaking down textile waste into its basic components or monomers, and then re-polymerizing or re-combining them into new fibers or polymers. It is a more advanced and complex method of textile recycling, as it can overcome some of the limitations of mechanical recycling, such as it can recycle mixed or heterogeneous textiles. It can maintain or improve the quality and strength of the recycled fibers, and it can reduce the dust and noise generation during the recycling process. However, chemical recycling also has some challenges and barriers, such as it requires more energy and resources than mechanical recycling, it generates more waste and emissions than mechanical recycling, and it faces more technical and regulatory hurdles than mechanical recycling.




 0086-813-8127573
0086-813-8127573