Self-Tapping Thread Rolling Die - thread rolling dies
Materialremoval rateformula
For parts with straight prismatic walls and extended axial cutting depths, optimizing roughing is ideal. This approach enhances the machining of challenging corner features and yields high metal removal rates, particularly in superalloys and stainless steels.
Employing software tailored for the roughing process is essential. Generic high-speed side milling or complex 3D milling software may not effectively handle optimized roughing demands. Use software that truly adapts to the process’s unique requirements.

Generic machine tool software defaults may not be suitable for specific cutting mills. Consult your milling cutter professional for recommended parameters based on their expertise and research, tailoring cutting data for different milling cutter designs and material groups.
What isa good materialremoval rate
All Milwaukee Grinding Wheels & Cut-Off Wheels can be shipped to you at home. ... Related Searches. grinding disc · metal cutting wheel · grinder blades · cut off ...
High feed milling is possible because of chip thinning due to the shallow lead angle of the cutter (typically 10 to 25 degrees). With a 90-degree cutter (with at least 50% radial engagement) the chip thickness equals the feed per tooth (fz). With a 45-degree cutter the chip thickness is only 70% of fz and if the lead angle is only 10 degrees then the chip thickness is only 17% of fz. The smaller the lead angle the more the feed can be increased and still maintain the recommended chip thickness. The downside is that as the lead angle increases, the depth of cut capability decreases. Still, the higher feeds typically translate to high metal removal rates making high feed milling a very productive and cost-effective method to quickly rough machine a variety of workpieces. Another advantage of high feed milling is a reduced tendency for chatter, especially with longer overhangs. The majority of the cutting forces are directed axially due to the lead angle resulting in less deflection and chatter. Kyoceraâs MFH-family of high feed cutters also have a convex cutting edge design that helps reduce the impact as the cutter enters the workpiece, further reducing cutting force and vibration.
Selecting the appropriate depth of cut is crucial. Generally, one pass with a depth of cut of 2xD is optimal. Shallow radial spans necessitate deeper cutting depths, while wider spans generate more heat, requiring shallower cuts to maintain consistent metal removal rates.
MaterialRemoval Rateturning
High feed cutters are no different than any other cutter with anything but a 90-degree lead angle â you need to pay attention to the DC dimension (governs the flat portion machined) and the APMX value (maximum depth of cut). Knowing these dimensions we can calculate how many passes are needed with each cutter to face our part to a 0.090" depth.
High-precision tool holders are vital for optimized roughing. These holders, such as shrink and high-precision chucks, minimize vibration and enable optimal performance.
A robust milling machine with a fast spindle and high rigidity ensures smooth roughing. Machine tool rigidity, from spindle bearing to ball screw, minimizes vibration, extending tool life and enhancing part quality.
To guarantee a successful roughing process, secure work holding is essential. The aggressive cutting forces in rough machining require the workpiece to remain immovable. Any unintended movement can result in machining errors or damage. Prioritize secure work holding to ensure precision throughout the roughing process.
They are used to cut the male and female parts of dovetail joints for industrial slides, as well as for cutting bevels and undercuts, and for deburring parts.
Taking the MFH2000R-14-4T as the example you can see that it will take 6 passes to face the part since the DC dimension is just over 1". Additionally, since APMX is less than 0.090" it will require 2 passes in the z-direction to get to the full depth. This results in 12 passes total to machine to the desired dimension (6 x 2 = 12). The MFH Mini has a greater DC dimension but a smaller APMX and the result is also a total of 12 passes. We considered 2 options with the MFH Max. It is capable of taking the full 0.090" depth of cut resulting in 4 passes total (but at a reduced feed). We also evaluated taking 2 0.045" passes (8 passes total) at a higher feed.
To ensure that you get the exact outcome you’re aiming for in CNC (Computer Numerical Control) machining, it’s vital to have a clear understanding of the distinct stages involved in the machining process. Each stage has its own purpose and requirements, and knowing these differences in detail helps in planning and executing the operations effectively, leading to precision-made parts and efficient production.
Materialremoval ratein milling
The result may be a coarser surface finish, but the goal is efficiency and speed. However, it’s much more than its name suggests; it’s the robust bridge between the raw material and the meticulous precision required in subsequent machining phases.
Mar 3, 2023 — Game Nerdz doesn't ship to Canada at all, and from Miniature Market, I don't want to spend USD$100+ (with shipping) with such an ambiguous ...
Maximizing the efficiency and quality of rough machining involves meticulous attention to several critical factors. Let’s delve into six standard methods to optimize roughing errors:
In this article, we’ll talk about the important things to think about, the advantages, what rough machining does, and the usual errors people make when doing rough machining. We’re here to guide you through this vital phase, where material reduction and bulk machining lay the groundwork for a perfectly crafted end product.
This will help you adjust processing parameters based on your specific rough milling cutter and processing requirements for improved efficiency.
Understanding the material you’re working with is the first crucial step in rough machining. The type of material significantly impacts the entire process. Complex materials often require a more delicate approach, which means using slower feed rates and cutting speeds to prevent tool damage.
Now, let’s explore the critical functions of rough machining. This initial step of shaping the workpiece is very important to make sure the final product turns out to be of good quality. Here’s a breakdown of its key functions:
Clearly there are applications where it is advantageous to take a heavier cut at a reduced feed to reduce cycle time and/ or improve tool life. Kyocera's new MFH Max cutters are designed for applications such as these. They are capable of depths of cut up to .098" (2.5mm). While the recommended feed drops as the depth of cut increases it is clear that the MFH Max can offer improvements in both cycle time and tool life.
Materialremoval ratein turning formula
Reducing the span size as the number of grooves increases maintains proper chip formation and surface finish at higher feed speeds. Smaller spans boost cutting speed and overall metal removal rates.
The manufacturing tolerance is the amount by which a dimension is allowed to vary. If we take, for example, a shaft for a rotating bearing assembly, the ...
MaterialRemoval Rateformula for drilling
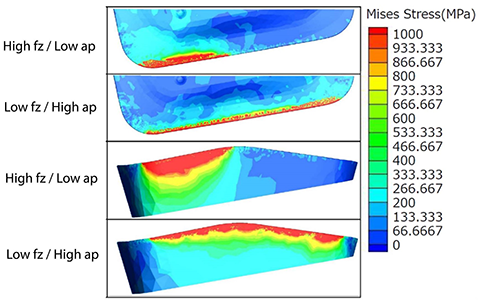
Below is a plot of the insert wear over the duration of the test. The blue line represents the high feed â low ap result and the orange line represents the high ap â low feed result. As you can see, the high ap â low feed cutting conditions resulted in less wear after 90 minutes of cutting time.
So, without any delay, let’s uncover the intricacies of this initial machining process that ensures quality performance in this essential part of CNC machining.
Total 60 Drill Bits Products ... Video.
Precisely, rough machining is geared toward rapid material removal, while finish machining prioritizes precision and surface quality. By selecting the appropriate approach for each task, machinists can efficiently transform raw materials into precise, high-quality products.
Find out what works well at Specialty Commerce from the people who know best. Get the inside scoop on jobs, salaries, top office locations, and CEO insights ...
Materialremoval rateCalculator
Cutting parameters are the comprehensive set of factors that define the dynamic world of machining. These factors encapsulate the fundamental trio of ...
The two most common measurements of productivity are the table feed (Vf) and metal removal rate (MRR) shown in the chart above. Table feed is easily seen, everyone likes to brag about how fast they can run a cutter (like ¼ mile times or top speed of an automobile). However, that doesnât tell the whole story (who wants to drive a drag car on a winding mountain road). The metal removal rate is usually a more accurate representation of productivity as it is a measurement of how much material is removed per minute of cutting time. It is a function of table feed, depth (Ap) and width (Ae) of cut. In our case it just so happened that the ranking of Vf and MRR is the same for each cutter. However, you can see that while the Vf of the MFH050R-04-7T-M (67.9 cubic inches per minute) is approximately 1/4 that of the MFH2000R-03-9T (257.9) the metal removal rate is 79% (9.07 compared to 11.48). Using either measurement we would expect to see the MFH Mini come out on top followed by the MFH Raptor and the MFH Max at the bottom. What these donât take into consideration is the non-cutting time (rapid moves to reposition for additional passes). As the number of passes increase, the number of positioning moves necessary also increases.
Feb 27, 2024 — Router bits are typically made from high-speed steel or carbide-tipped materials, which are more durable and suitable for heavy-duty use.
Nave ISK-8, Parque Industrial y Logístico Sky Plus, Avenida Mineral de Cinco Señores No.100, del Parque Industrial Santa Fe, Silao de la Victoria, Guanajuato, México
Selecting the appropriate cutting tool is paramount in the roughing process. Opt for larger, robust tools with sturdy cutting edges. These tools can endure the aggressive cutting conditions and heavy chip loads commonly associated with rough machining. A well-chosen tool ensures both longevity and efficiency.
There are a wide variety of indexable high feed cutter designs available in the marketplace (Kyocera alone offers 5 different options). That can sometimes be confusing to end users when trying to select the best option. Weâve selected a typical machining scenario (decking a 4140 workpiece, 28 â 32 Rc, 5" x 6", 0.090" total to be removed) and evaluated 3 different 2" high feed cutters to see which was most productive. Weâll take you through the selection process so you can see what needs to be considered when selecting a high feed cutter to meet your needs.
To harness its full benefits, collaboration with milling cutter suppliers and embracing best practices are essential. When looking for a reliable and professional rough machining service provider, consider Prototool.com, your trusted partner in achieving efficiency and excellence in the machining process.
Optimized roughing is a pivotal strategy that holds the potential to streamline part cycle time, enhance surface finish, extend rough milling cutter life, and maximize machine tool efficiency. By targeting specific parts and features like deep grooves, challenging corners, and straight walls, this method proves its worth in machining.
2000417 — ... formula for SFM (Surface Feet per Minute) in my aluminuim machineing handbook is. Dia.X 3.1416 (pi) X RPM divided by 12. The SFM for the ...
Are you confusing roughing with finishing in machining? Well, in CNC machining, the processes of rough and finish machining are distinctly different in their purposes and methodologies. To better understand these key differences, you can refer to the table below:
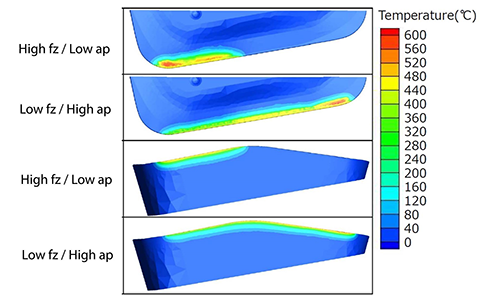
Next, we look at how feed and depth of cut affect tool life. We"ve shown that in some instances a lower feed at a larger depth of cut can provide shorter cycle times compared to running a light depth of cut at a heavier feed. Which option is best for tool life or will there be any difference? To find out, we continued testing on 4140 blocks with a hardness of 28 â 32 Rc. To determine the test parameters, an MFH3000R-14-6T cutter with SOMT140520ER-GM PR1535 inserts was ran at 520 sfm and the maximum recommended depth of cut and the feed adjusted until the spindle load reached 100%. The combination of 0.079" depth of cut and 0.025 ipt resulted in a spindle load of 100%. At a depth of 0.025" and a feed of 0.079 ipt the spindle load also registered 100% at the same 520 sfm. For the wear portion of the test, an MFH2000R-14-4T cutter was used with an SOMT140520ER-GM PR1535 insert. In order to increase the wear rate, we ran at 800 sfm which was a little higher than the maximum recommended cutting speed of 720 sfm. Width of cut (ae) was 1". The first test was run at a depth (ap) of 0.025" and feed (fz) of .079 ipt. The first test (1) was run at a depth (ap) of 0.025" and feed (fz) of 0.079 ipt. The second test (2) was at a depth (ap) of 0.079" and a feed (fz) of 0.025 ipt. This resulted in identical metal removal rates. All tests were performed without coolant. Wear was measured at 10 minute intervals until reaching 90 minutes of cutting time.
Now, let’s delve into the essential considerations when planning for the roughing stage in machining. These points are crucial for making sure the first steps of the machining process work out well. Here’s a detailed guide to help you understand and optimize rough machining:
Rough machining is a process that involves swiftly and efficiently eliminating excess material to bring your workpiece one step closer to its final design. This CNC machining approach employs larger cutting tools, making broad and powerful cuts to eliminate any unwanted material from a workpiece quickly.
Materialremoval rateunit
The simulated results below closely follow the actual evaluation. You can see that the heat and stresses generated are much higher at the lighter depth of cut and higher feed. They are also concentrated in a much smaller area and the result is more rapid wear.
In intricate three-dimensional mold cavities, high-feed roughing often outperforms optimized roughing. This method is especially valuable when a stepped surface results from optimized roughing, necessitating extensive semi-finishing.
For the purposes of this evaluation we used the same carbide grade (PR1535) in each cutter and ran each at the recommended starting points for speed and feed.
Proper coolant use is crucial during roughing. The correct amount and type of coolant help dissipate heat and prevent tool wear, which is essential for maintaining tool integrity and workpiece quality. The choice of coolant should align with the material you’re machining, ensuring the best results.
Stop in today and take advantage of all the packing, shipping, printing, shredding, notarizing, faxing and mailbox services that you need, all in one place. The ...
Optimizing process parameters is essential for successful rough machining. Focus on determining the right cutting speed, feed rate, and depth of cut. These parameters should be set to bulk material removal rates while preserving tool life and protecting the workpiece from damage. Finding the right balance is crucial for efficient roughing.
You can see that in this case the fewest number of passes more than offset the difference in table feed (Vf) or MRR allowing the MFH050R-04-7T-M cutter taking the full 0.090" depth to achieve the shortest cycle time (30.23 seconds). The MFH2000R-03-9T and MFH050R-04-7T-M (0.045" Ap) taking 12 and 8 total passes, respectively, resulted in almost identical cycle times (31.24 and 31.26). The MFH2000R-14-4T (2nd highest Vf and MRR) ended up with the longest cycle time due to the high number of passes. Comparing the cutters with 12 total passes we can see that the option with the higher table feed and MRR came out on top. While this is a specific case it shows that not only table feed (Vf) and MRR should be considered, we also need to look at the total number of required passes and the non-cutting time when evaluating overall cycle times. Changes in the overall dimensions of our workpiece or the total stock removal would impact the results seen here. You'll need to consider your unique situation to determine the optimal high feed cutter to match your particular workpiece.
Moreover, softer materials can withstand more aggressive cuts. The key is to choose the right speed and feed rate, considering the material properties.




 0086-813-8127573
0086-813-8127573