Solve Edge Cracking Problems in Coated MDF Boards - edge cracking
Surface feet per minuteformula
Due to added elements, hardness, and durability, high-speed tool steel is often a bit more expensive than standard carbon tool steel. However, that extra cost is well worth it if your application requires it.
Because of these features, TiAlN has amazing wear resistance on cutting edges and is ideal for high-heat applications and high-stressed components. It can also be used with minimal lubrication.

Although PM-grade steels are more expensive on the front end, they’re worth the investment if you need their strength and versatility.
Chromium nitride (CRN) is the best tool coating choice when hard chrome is preferred, but you need something a little harder and with better coating adhesion. It has these features:
SFM to RPM Drilling calculator
These characteristics give TiCN great wear resistance, excellent toughness in high-pressure conditions, and great lubricity.
Surface speedformulaRPM
You can learn more about M2 material in our Inch and Metric catalogs, and you can learn more about PM-M4 material in our Advanced Stamping catalog.
As mentioned above, DLC is excellent for piercing and forming aluminum, as its resistance to abrasive wear and galling is unmatched. It also has an incredible coefficient of friction.
As an example of how strong PM-grade materials are over standard ones, let’s take a quick look at the differences between M2 (the tried-and-true material for standard punching applications) and PM4 (its stronger alternative).
As a superior substitute to hard chrome, CRN is a great choice for forming low-strength steels and copper. It’s also resistant to corrosion and harsh chemicals.
Precision tools can be made of hundreds of different materials. Most of them are not “better” or “worse” than any of the others — the right choice depends on what your particular application requires. As examples, here are three of the most common materials we work with at Moeller Precision Tool.
Titanium aluminum nitride (TiAlN) offers improved wear resistance and heat resistance. Its specifications are as follows:
SFM to RPMformula

Surface Feet per minute Chart
Inches per minuteformula
At Moeller Precision Tool, we offer a wide variety of tool materials and coatings. Even if you need one we don’t have listed we can lead you to our coating partner, Oerlikon Balzers, that can help you.
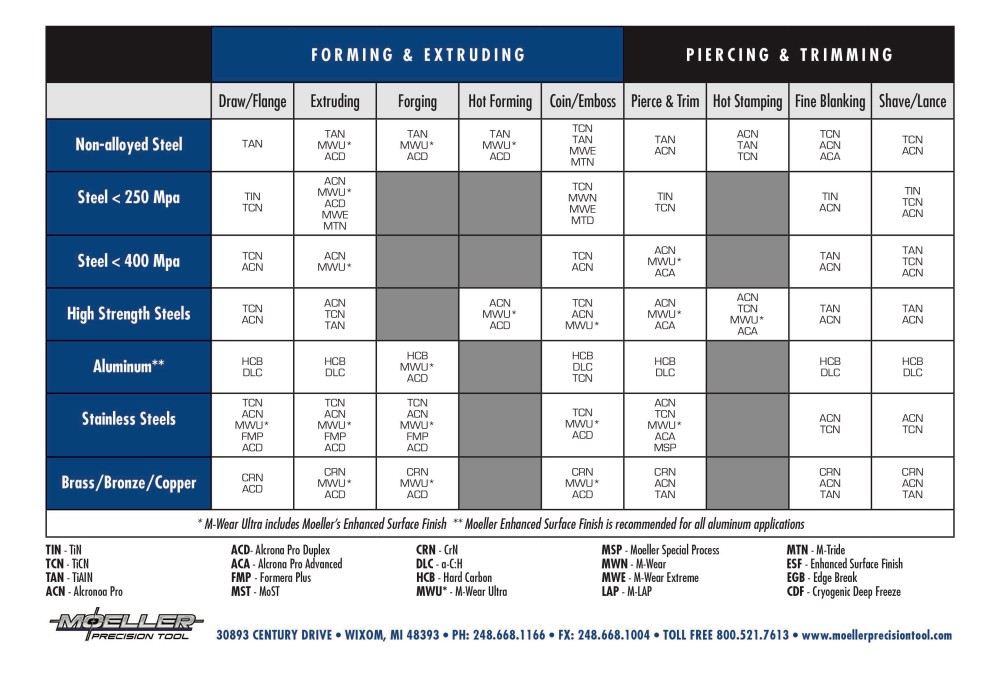
View our full list of coatings in our Performance Enhancement Coatings catalog, or check out our Performance Enhancement Coatings Selection Chart below.
PM-grade (short for “powder metal grade”) steels are the most versatile of all material options listed here. Wrought tool steels are manufactured using ingot metallurgy. PM-Grade steel is made using particle metallurgy processing. This includes hot isostatic pressing (HIP), which compresses the materials at high temperatures and high pressures to forge. The end result is an improved microstructure that offers incredible wear resistance and toughness (or both), as well as improved tool life.
Titanium CarboNitride (TiCN) is becoming incredibly popular due to its broad range of stamping applications. It’s great for piercing and forming carbon steel, stainless steel, nickel, and copper.
SFM to IPM
Often, the right tool material is just one aspect of improving tool life. If you want the greatest longevity and performance from your tools, you may want to apply a performance enhancement coating. While there are many good surface treatments to choose from, physical vapor deposition (PVD) coatings are typically the best suited for precision slip and press-fit punch components.
SFM Calculator turning
High-speed tool steel is similar to carbon tool steel, except it’s modified to be more durable and perform better in stamping applications that standard carbon tool steel just can’t handle. Alloying elements like tungsten, chromium, and more are added to carbon tool steel for increased hardness (up to HRC 67), abrasion resistance, and durability.
Diamond-like carbon (DLC) is your go-to tool coating for applications that incur the most extreme wear and galling. It’s commonly used for aluminum applications and has the following specifications:
Although carbon tool steel works great for low-speed stamping applications, it should be kept to that. It’s not a good material choice for higher-speed operations.
All metals have unique properties related to toughness, wear resistance, compressive strength, and more. If you understand those properties well, you can use them to your advantage and create the most suitable tool for your application.
If you need help finding the right tool material or coating for your application, contact Moeller Precision Tool. Our engineers are happy to guide you in the right direction or refer you to one of our industry partners that specializes in material and coating selection.
To get optimal performance out of your precision tools, they must be made of the right materials. Here’s a look at why tool materials and coatings are so important, as well as some types you may choose from.
Carbon tool steel is one of the most popular precision tool materials, mostly because it’s affordable and works great for low-speed stamping applications. It’s composed of 0.6-1.5% carbon and less than 0.5% manganese and silicon. It can reach hardness ratings up to 65 on the Hardness Rockwell C (HRC) scale.




 0086-813-8127573
0086-813-8127573