Spot and Centering Drill for CNC Machines - spotting drill vs center drill
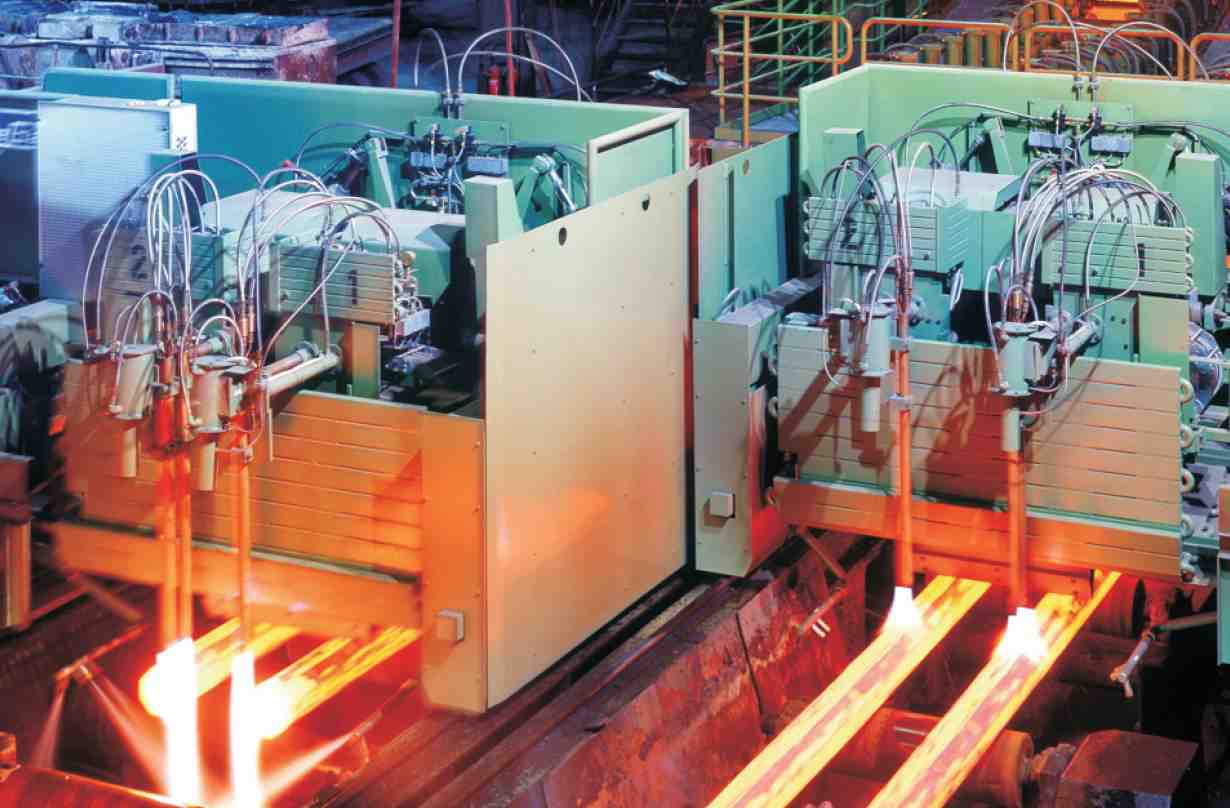
Hot rolling occurs when the slabs, blooms and billets are heated in a furnace until they are red hot (ca 1400 K) and then rolled until they have acquired the desired shape.
Steels are alloys of iron, carbon and other metals and non-metals. The composition of the steel is adjusted so that it has the precise properties needed.
Molten steel is poured into a cast iron mould to solidify as an ingot. This generally weighs less than 20 tonnes but rotor forgings can weigh up to 500 tonnes.
Chromium increases the corrosion resistance of steel, and a minimum of 12% chromium is necessary to produce a stainless steel. The best known of the stainless steels contains about 74% iron, 18% chromium and 8% nickel (known as 18-8 stainless). Stainless steel is perhaps most familiar as kitchenware (sinks, kettles and cutlery).
Molten steel from either process is transferred to a ladle where the alloying elements are added.The process provides precise control of harmful impurities (particularly sulfur, phosphorus and, in some cases, trace metals and hydrogen) by adding materials via ladle injection. For example, aluminium and silicon are added to reduce any oxidized material.
About 40% of the iron-containing materials used in steel production are now from recycled sources. It is estimated that recycling one tonne of steel saves 1.1 tonnes of iron ore, 0.6 tonnes of coal and 0.5 tonnes of limestone, with an overall energy saving of 60-75%.
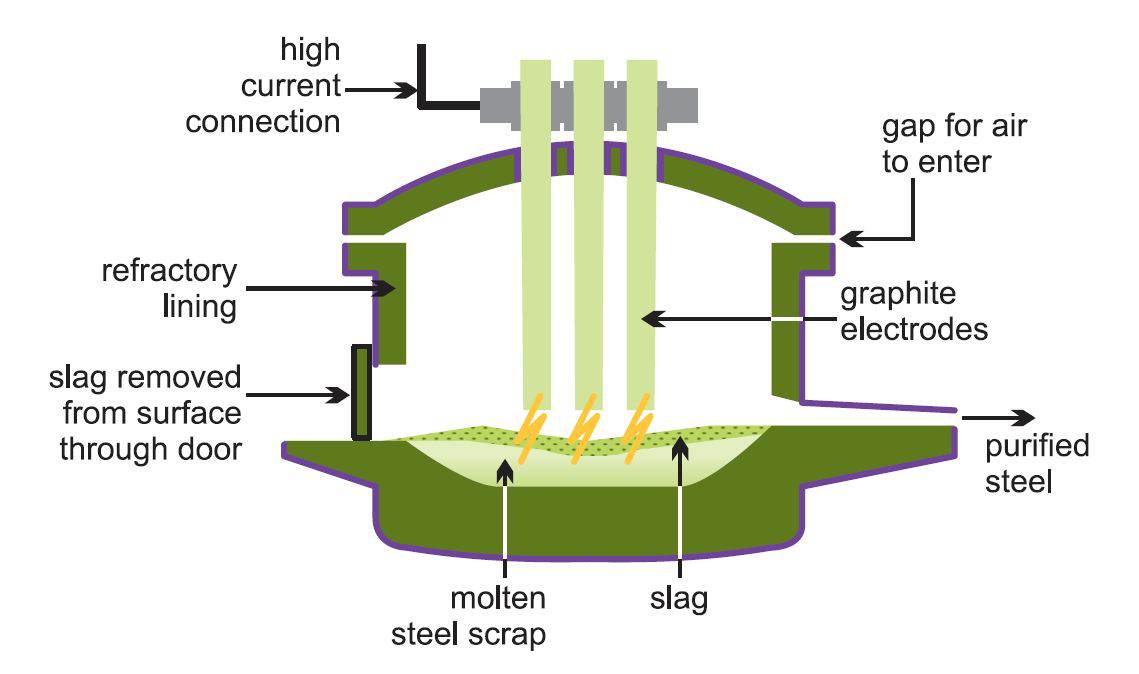
The furnace is a circular bath with a movable roof through which three graphite electrodes are raised or lowered. These electrodes are massive, often 6 m high and 4 m wide, and the furnace can hold over 100 tonnes of liquid steel.
Most steel is continuously cast to the desired shape, but a small quantity (ca 10-20%) is first cast into ingots which are cooled and then worked on to produce the shape required.
The term alloy steel is confined to steels containing some combination of one or more of the following elements: nickel, chromium, tungsten, molybdenum, vanadium, manganese, cobalt, copper, niobium, zirconium, selenium and lead.
There are two main processes used to make steel. The Basic Oxygen Steelmaking Process, which is used for the majority of steel production, uses iron freshly produced from the blast furnace together with some scrap steel. The Electric Arc Furnace Process uses scrap steel only.
Steel is one of the most widely used materials, particularly in construction and engineering and in the manufacture of cars. It is estimated that there are over 20 billion tonnes of steel in use, equivalent to well over 2 tonnes for every person on Earth.
After the steel scrap is placed in the furnace, the roof is put into position and the electrodes lowered into the furnace. An arc is struck by passing an electric current through the metal. The heat generated melts the scrap metal. Lime (as calcium oxide or calcium carbonate), fluorspar (which helps to keep the hot slag as a fluid) and iron ore are added and these combine with impurities to form a slag. When the steel has reached the correct composition the slag is poured off and the steel tapped from the furnace.
The term secondary production is often used when referring to recycling. However, in steelmaking the term secondary steelmaking refers to the production of steels which are needed for specific purposes and which require the addition of very carefully controlled quantities of other elements.
Figure 3 is the interwoven structure of the Olympic Stadium in Beijing made of steel plate. Unwrapped, the I strands of the 'Bird's Nest' would stretch for 36 km.By kind permission of World Steel Association.
Steels containing molybdenum, vanadium, chromium and tungsten in various combinations produce very hard, if brittle, steels. These are used, for example, in drill bits which need to retain a cutting edge. Steels are used widely in the manufacture of electrical motors, power generators (nuclear, conventional fuels and wind), gears and engines, which have to be very tough and withstand high temperatures.
Other techniques used to help to improve the quality of the steel include stirring (ladle stirring) and applying a vacuum to the steel to remove gases (vacuum degassing).
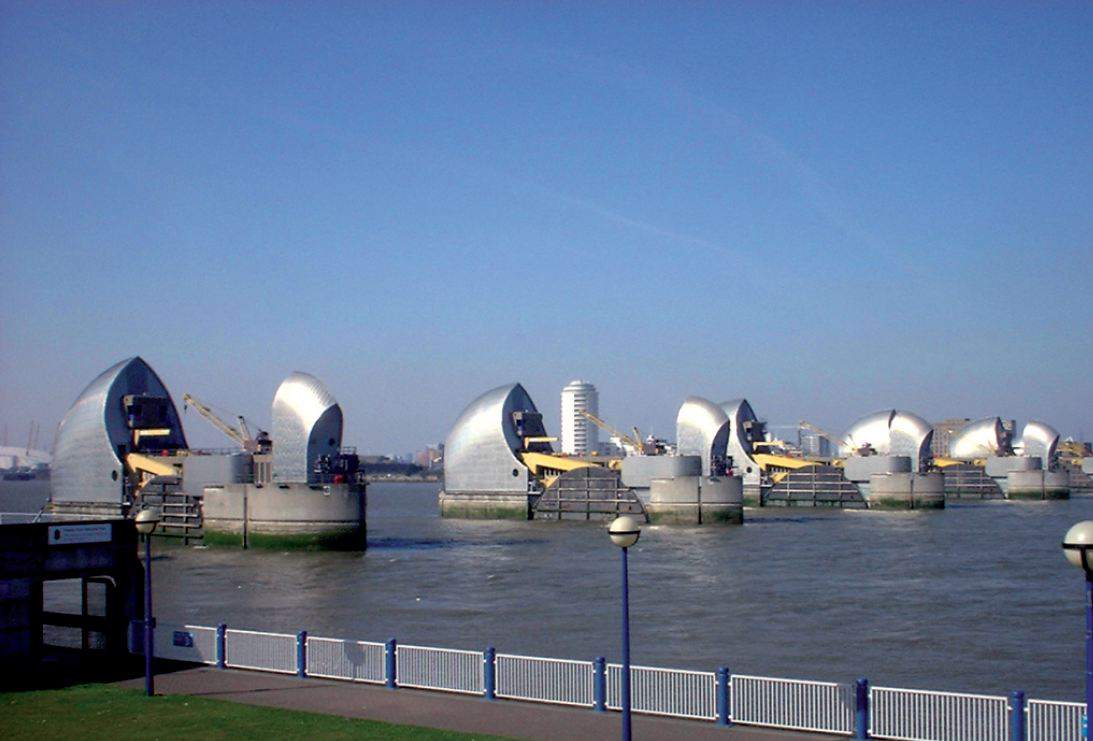
Figure 2 is the barrier across the River Thames, to protect London I from flooding. It is a system of stainless steel plated hollow flood gates.By kind permission of Peter Trimming.
Steels with a thin coating of tin are used to make cans for beverages and food. Steels coated in various ways with zinc are used in roofing, for example, and in cars as the zinc gives protection against rusting.
The stripping process is known as pickling. The steel is passed through several baths of hydrochloric acid (sometimes sulfuric acid) which dissolves the oxide without attacking the metal. The spent acid is recycled.
The speed at which the hot steel is subsequently cooled is a crucial factor, affecting the strength and other properties of the steel. Cooling is done by spraying water as the steel passes through the rollers.
Steels used in such large constructions are often produced from iron which has been treated with molten magnesium to remove sulfur.
In continuous casting, the steel, still molten from the furnace, is poured into a water-cooled mould (teeming) from which it emerges as a strand which is solidifying at the surface. The strand passes through a series of rollers which are water sprayed to produce a solid (a slab, bloom or billet) which is then sent to be hot rolled.
The 'pickled' steel is then subjected to cold rolling. As the name implies, the steel, following hot rolling, is rolled cold and gradually compressed to the required thickness. This improves the quality of the surface and also hardens the steel. On annealing (heating the strip very carefully), it can be pressed into shapes without cracking. Such sheet is used, for example, to press out car bodies. Steel cans are pressed out with sides and bottoms as a single entity, needing only the top to be fitted after filling.
The furnace (also known as a converter or vessel) is charged with steel scrap (up to about 30%) and molten iron from a ladle. An oxygen lance, cooled by circulating water, is lowered into the furnace and high purity oxygen is injected into the vessel at twice the speed of sound which ensures that all the impurities are converted into their oxides. The main chemical reactions are:
There is a group of steels known as Advanced High Strength Steels, AHSS, which are specially treated steels that can be rolled very thin without losing the element of strength needed for the specific purpose. They are particularly useful in the manufacture of cars, helping to reduce the overall mass and thus decrease fuel consumption.
The construction industry is a main user of steel, from small buildings to huge bridges, and uses it in multiple ways, even within a single construction. A bridge, for example, might use steel in the huge suspension ropes, the steel plate flooring for the road, the beams for the columns, and for the safety barriers and lighting columns.
The recovery of scrap steel probably constitutes the world's largest scale recycling process. The scrap is either part of the charge for the Basic Oxygen Process or is the complete charge for the Electric Arc Furnace Process.
Steel products are classified into flat products and long products. Slabs of steel are rolled to produce flat products, for example steel sheet for the construction of ships. The sheet is rolled further to produce thinner sheet, used for example in the manufacture of cars.
During this rolling, oxygen in the air has reacted with the hot iron to form a very thin layer of iron(III) oxide on the surface. It is blue/grey in colour (only when it is thicker does it appear red). This must be stripped from the surface prior to the next stage, otherwise the final product will be susceptible to rusting and unsuitable for galvanizing with zinc and other surface treatments.
When the ingot has solidified, the mould is removed. Each ingot is of carefully pre-arranged dimensions and mass from which articles of the required size can be rolled.
The above reactions are all exothermic and controlled quantities of scrap are added as a coolant to maintain the desired temperature.






 0086-813-8127573
0086-813-8127573