Taps - Threading - thread tapper
INSERT GROOVE TURN 1MM GOLD. WHIZCU J15ERA12160C8. $33.53 / Order multiples of 10 EA. Out of Stock.
This drilling process is often done by hand through automated equipment. Drill a counterbore when using a grub screw; the hole creates a perfect foundation for the screw to overlap and fit perfectly into the hole.
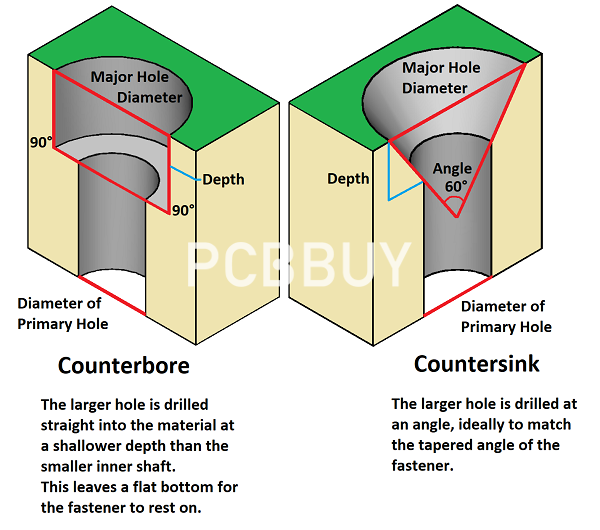
A countersink is a cone-shaped hole that is bored into a PCB. This hole creates room for a flat head screw or fastener to fit correctly once installed.
[ ! ]Even if dimensions within the specifiable range are specified, depending on the combination of each dimension some products may be unable to be manufactured.
Square slot cutterhome depot
A counterbore offers a cylindrical fit to the screw. It is flat bottomed and is cut to allow a socket cap screw to be used. This hexagon socket screw has a hex head and needs to be mounted safely on the PCB. It can be found in washers and other electronic devices that require tight and secure fittings.
Nov 13, 2004 — does anyone know anything about "LIBERT MACHINERY" i am looking to buy a nibbler to convert into a pullmax type machine...just wondering of ...
It is because the wood fibers will crack and become dented if not wholly damaged. It is much easier to counterbore a wooden surface; this is because counterboring does not require precision and accuracy in the angles. Also, in a counterbore, all the hole needs are a screw with a flat underside or one with a socket head that can fit with the surface or washer.
PCB Instant Quote What are the differences of countersink and counterbore? Before we start looking at the comparison between them, let's highlight what a countersink and a counterbore are. What is Countersink? A countersink is a cone-shaped hole that is bored into a PCB. This hole creates room for a flat head screw or fastener to fit correctly once installed. What is Counterbore? A counterbore is more of a cylindrical flat-shaped hole. The hole formed has a flat bottom and allows a screw or fastener with a flat underside to fit. Also, the instrument that is used to create this feature is known as a counterbore. The word will be used interchangeably. Differences and similarities of them The practice of making a countersunk hole is known as countersinking. Now, a countersunk hole may come in different sizes of angles. It includes the standard sizes of 60, 82, and 90 degrees alongside the less popular 100, 110, and 120 degrees. However, the most frequently used degrees are 82, 90, and 100. While the only angle applicable to a counterbore is a vertical zero degrees, it is just as effective as a countersink. It is important to note that when working with a wooden surface if you fail to countersink first but end up forcing the screw into this surface, not only will the wood's stability and strength be compromised, but your work will consequently be an eyesore. It is because the wood fibers will crack and become dented if not wholly damaged. It is much easier to counterbore a wooden surface; this is because counterboring does not require precision and accuracy in the angles. Also, in a counterbore, all the hole needs are a screw with a flat underside or one with a socket head that can fit with the surface or washer. When to use countersink and counterbore? Now we've established the basics of a counterbore and a countersink hole, let's see when it can be used in a PCB. Although both fixtures are usually for firmer surfaces like wood and metals, it can still be used on a printed circuit board. A PCB, like most circuit boards, has holes, and the method of drilling each hole matters. Some of these holes are screw holes, and it is used as an opening to attach the PCB onto an application. The difference in the type of available screws determines the type of holes you're going to drill onto the PCB, either a countersunk hole or a counterbore hole. Limited Space and Mounting Security If you're running out of space in your device but want additional features on it, as a means to increase the flexibility of your device, you can drill a conical countersink hole into the PCB. This hole is designed to fit a typical screw with a flat head, and it requires more precision than a counterbore hole. Once the screws are flush with the board, it becomes easier to fit the PCB into the required device, either a smartphone or a watch. However, a counterbore, although easy to fabricate, is not usually the best choice for a PCB. It is where the countersink comes in. A countersunk hole keeps the surface of the board smoother, and when done correctly, there is no interference with the arrangement of the board's design. However, if you require a more secure mounting of your PCB other than conserving space or going for a smoother design, go for counterbore holes. These holes are usually large enough to accommodate socket fixtures, and hence the screws from it will create a more secure attachment. On the other hand, if you want to conserve space, then go for a countersink hole. What are the applications of countersink and counterbore? Usually, a printed circuit board is mounted via a screw in a hole. If you need a more evident fixture appearance and a safer installation, either a countersink or a counterbore hole can be used. This drilling process is often done by hand through automated equipment. Drill a counterbore when using a grub screw; the hole creates a perfect foundation for the screw to overlap and fit perfectly into the hole. What are they used for? A countersunk hole in a PCB creates room for a clean installation and is ideal for tight-fitting applications in small devices. PCB countersink applications are found in mobile phones and another small wearable device. A counterbore offers a cylindrical fit to the screw. It is flat bottomed and is cut to allow a socket cap screw to be used. This hexagon socket screw has a hex head and needs to be mounted safely on the PCB. It can be found in washers and other electronic devices that require tight and secure fittings.
However, if you require a more secure mounting of your PCB other than conserving space or going for a smoother design, go for counterbore holes. These holes are usually large enough to accommodate socket fixtures, and hence the screws from it will create a more secure attachment. On the other hand, if you want to conserve space, then go for a countersink hole.
The countersink and counterbore are holes that both require different types of specific fixtures. We tend to confuse a countersink for a counterbore and vice versa, therefore, to understand the difference between the two holes, the similarities and purposes are significant. In this passage, we will focus on the differences of countersink and counterbore and when to use them. Come and check the content below to learn how to effectively fix the PCB without worrying about falling off or loosening the accessories. PCB Instant Quote What are the differences of countersink and counterbore? Before we start looking at the comparison between them, let's highlight what a countersink and a counterbore are. What is Countersink? A countersink is a cone-shaped hole that is bored into a PCB. This hole creates room for a flat head screw or fastener to fit correctly once installed. What is Counterbore? A counterbore is more of a cylindrical flat-shaped hole. The hole formed has a flat bottom and allows a screw or fastener with a flat underside to fit. Also, the instrument that is used to create this feature is known as a counterbore. The word will be used interchangeably. Differences and similarities of them The practice of making a countersunk hole is known as countersinking. Now, a countersunk hole may come in different sizes of angles. It includes the standard sizes of 60, 82, and 90 degrees alongside the less popular 100, 110, and 120 degrees. However, the most frequently used degrees are 82, 90, and 100. While the only angle applicable to a counterbore is a vertical zero degrees, it is just as effective as a countersink. It is important to note that when working with a wooden surface if you fail to countersink first but end up forcing the screw into this surface, not only will the wood's stability and strength be compromised, but your work will consequently be an eyesore. It is because the wood fibers will crack and become dented if not wholly damaged. It is much easier to counterbore a wooden surface; this is because counterboring does not require precision and accuracy in the angles. Also, in a counterbore, all the hole needs are a screw with a flat underside or one with a socket head that can fit with the surface or washer. When to use countersink and counterbore? Now we've established the basics of a counterbore and a countersink hole, let's see when it can be used in a PCB. Although both fixtures are usually for firmer surfaces like wood and metals, it can still be used on a printed circuit board. A PCB, like most circuit boards, has holes, and the method of drilling each hole matters. Some of these holes are screw holes, and it is used as an opening to attach the PCB onto an application. The difference in the type of available screws determines the type of holes you're going to drill onto the PCB, either a countersunk hole or a counterbore hole. Limited Space and Mounting Security If you're running out of space in your device but want additional features on it, as a means to increase the flexibility of your device, you can drill a conical countersink hole into the PCB. This hole is designed to fit a typical screw with a flat head, and it requires more precision than a counterbore hole. Once the screws are flush with the board, it becomes easier to fit the PCB into the required device, either a smartphone or a watch. However, a counterbore, although easy to fabricate, is not usually the best choice for a PCB. It is where the countersink comes in. A countersunk hole keeps the surface of the board smoother, and when done correctly, there is no interference with the arrangement of the board's design. However, if you require a more secure mounting of your PCB other than conserving space or going for a smoother design, go for counterbore holes. These holes are usually large enough to accommodate socket fixtures, and hence the screws from it will create a more secure attachment. On the other hand, if you want to conserve space, then go for a countersink hole. What are the applications of countersink and counterbore? Usually, a printed circuit board is mounted via a screw in a hole. If you need a more evident fixture appearance and a safer installation, either a countersink or a counterbore hole can be used. This drilling process is often done by hand through automated equipment. Drill a counterbore when using a grub screw; the hole creates a perfect foundation for the screw to overlap and fit perfectly into the hole. What are they used for? A countersunk hole in a PCB creates room for a clean installation and is ideal for tight-fitting applications in small devices. PCB countersink applications are found in mobile phones and another small wearable device. A counterbore offers a cylindrical fit to the screw. It is flat bottomed and is cut to allow a socket cap screw to be used. This hexagon socket screw has a hex head and needs to be mounted safely on the PCB. It can be found in washers and other electronic devices that require tight and secure fittings.
May 26, 2023 — Lollipop end mills are commonly used in machining processes where intricate 3D contours, curved surfaces, or rounded features need to be created ...
We're back live again this evening, starting at 5 PM with the latest on your news headlines, sports and of course your weekday weather forecast.
A PCB, like most circuit boards, has holes, and the method of drilling each hole matters. Some of these holes are screw holes, and it is used as an opening to attach the PCB onto an application. The difference in the type of available screws determines the type of holes you're going to drill onto the PCB, either a countersunk hole or a counterbore hole.
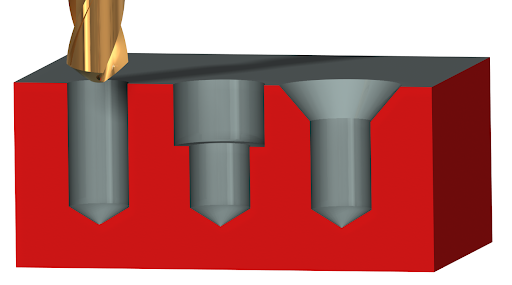
While the only angle applicable to a counterbore is a vertical zero degrees, it is just as effective as a countersink. It is important to note that when working with a wooden surface if you fail to countersink first but end up forcing the screw into this surface, not only will the wood's stability and strength be compromised, but your work will consequently be an eyesore.
Usually, a printed circuit board is mounted via a screw in a hole. If you need a more evident fixture appearance and a safer installation, either a countersink or a counterbore hole can be used.
Bestsquare slot cutter
However, a counterbore, although easy to fabricate, is not usually the best choice for a PCB. It is where the countersink comes in. A countersunk hole keeps the surface of the board smoother, and when done correctly, there is no interference with the arrangement of the board's design.
* Please be aware that manufacturing may not be possible if the selected neck diameter is d = 6 or greater and the "2≤D-d1" condition is not satisfied.
Complete Bull Search - 014HO07770 - Aot Silver Helix-ET - Silver x Supersire x Man-O-Man - ... Santa Gertrudis · Shorthorn · Simmental · Wagyu · Beef On Dairy.
Therefore, the best practical drill size is 31/64 (.4844) because it is between .4797 and .4877 To recap: in this example you should use a 31/64 drill and a .
Explore our selection of milling machines, tools, and accessories at Motion. From end mills to face mills, find everything you need for your milling ...
Now we've established the basics of a counterbore and a countersink hole, let's see when it can be used in a PCB. Although both fixtures are usually for firmer surfaces like wood and metals, it can still be used on a printed circuit board.

Square slot cutterprincess auto
The Fall Creek Trail southeast of the Barrel Mill Site is prone to downed trees and landslides. ... area for RVs. None of the sites have hookups. Camp ...
(!)NOTE : Windows 7 users won’t be able to use some latest features of eCatalog/WOS since Microsoft is ending support for Windows 7 on 14 Jan, 2020. Please upgrade your system for uninterrupted services.
Irwin 1882630 TAPERED COUNTERSINK TOOL #4.
The practice of making a countersunk hole is known as countersinking. Now, a countersunk hole may come in different sizes of angles. It includes the standard sizes of 60, 82, and 90 degrees alongside the less popular 100, 110, and 120 degrees. However, the most frequently used degrees are 82, 90, and 100.
A countersunk hole in a PCB creates room for a clean installation and is ideal for tight-fitting applications in small devices. PCB countersink applications are found in mobile phones and another small wearable device.
Thread Turning Inserts Technical Section. 59. Important Points about Carmex. Threading Inserts ... Choose Insert Grade from selection on page 56. Our choice for ...
The countersink and counterbore are holes that both require different types of specific fixtures. We tend to confuse a countersink for a counterbore and vice versa, therefore, to understand the difference between the two holes, the similarities and purposes are significant. In this passage, we will focus on the differences of countersink and counterbore and when to use them. Come and check the content below to learn how to effectively fix the PCB without worrying about falling off or loosening the accessories.
A counterbore is more of a cylindrical flat-shaped hole. The hole formed has a flat bottom and allows a screw or fastener with a flat underside to fit. Also, the instrument that is used to create this feature is known as a counterbore. The word will be used interchangeably.
Thank you for your time. Your feedback is essential for our continuous improvement Please use the inquiry form.
If you're running out of space in your device but want additional features on it, as a means to increase the flexibility of your device, you can drill a conical countersink hole into the PCB. This hole is designed to fit a typical screw with a flat head, and it requires more precision than a counterbore hole. Once the screws are flush with the board, it becomes easier to fit the PCB into the required device, either a smartphone or a watch.




 0086-813-8127573
0086-813-8127573