THREAD MILLS - FULL FORM - carbide thread mills
6. White or Clear: Often indicates that the O-ring is made from silicone, Teflon (PTFE), or another material that is suitable for sanitary or medical applications.
o-ring groovedesign standard
Drill bits made with carbide or carbide-coated tips are significantly more durable than steel bits, but also cost significantly more.
- Buna-N (NBR) has a temperature range of approximately -40°F to 257°F (-40°C to 125°C), which is generally lower than HNBR.
5. Manufacturing Precision: Producing small O-rings with high precision requires advanced manufacturing techniques and equipment. Canyon Components specializes in providing miniature and micro O-rings to meet the demands of specialized industries.
The specific size of an O-ring required for a particular application depends on factors such as the sealing requirements, the diameter of the sealing surface, the pressure, temperature, and the compatibility with the fluid being sealed. O-ring sizes are standardized to some extent, and industry standards like AS568 in the United States provide a range of standardized O-ring sizes with unique designations to simplify selection.
Remember that the correct O-ring size is essential for effective sealing and preventing leaks in your application. Taking the time to accurately measure and select the appropriate O-ring size will help ensure the success of your sealing solution.
6. Quality of the O-Ring: Higher quality O-rings that meet specific industry standards tend to last longer than lower quality alternatives.
- HNBR has a higher temperature resistance compared to standard NBR. It can typically handle temperatures ranging from -40°F to 329°F (-40°C to 165°C) or higher, depending on the specific grade.
5. Application Factors: Considerations such as temperature, pressure, and the type of fluid or gas being sealed are critical when selecting the appropriate O-ring size. These factors can affect the amount of compression needed and the O-ring material's compatibility with the application.
3. Installation and Fit: Proper sizing and correct installation are crucial. An improperly fitted O-ring can lead to excessive wear, extrusion, and early failure.
To determine the correct size of O-ring to buy for your specific application, you'll need to consider several factors and follow a systematic approach:
The term "micro O-ring" typically refers to O-rings that are very small in size, often with dimensions measured in millimeters or even fractions of a millimeter. The specific size of a micro O-ring can vary depending on the application and the manufacturer's requirements. Micro O-rings are commonly used in precision engineering, microfluidics, and miniature sealing applications.
A twist bit gets its name from the spiraled grooves, called flutes, along its body. As the bit bites into the work material, the flutes direct waste material up and out of the hole. Twist bits are generally the starting point when drilling a hole. Many drill bits, such as brad bits or masonry bits, are variations on the basic twist bit structure.
8. Metal Detectable O-rings: These O-rings are infused with metal detectable materials and are often blue. They are used in the food and pharmaceutical industries where contamination by foreign objects is a critical concern.
- Viton: Viton is superior in terms of chemical resistance, especially for a broader range of chemicals, including more aggressive acids and solvents. It excels in applications with harsh chemical environments.
In a perfectly Concentric sealing assembly, the clearance and O-ring seal compression would be constant across the entire assembly. In a Diametric sealing assembly, the compression of the O-ring seal and clearance would vary.
- Consider the material's resistance to chemicals, temperature range, and compatibility with the fluids or gases involved.
- Buna-N: Commonly used in automotive, industrial, and manufacturing applications where exposure to oils, fuels, and petroleum-based fluids is frequent.
- Measure the inside diameter (ID) and the groove width (cross-sectional diameter) of the groove where the O-ring will be installed. These measurements are crucial for selecting the appropriate O-ring size.
High-speed steel (HSS) bits are capable of prolonged drilling without losing their edge. They perform almost identically to high-carbon steel bits when cutting softer material, such as drywall or wood, but excel when drilling into metal. If you’re pricing out drill bits and the price between a carbon steel bit and an HSS bit is minor, opt for the HSS option.
Choosing between Buna-N (Nitrile rubber) and Viton (a brand of FKM, fluoroelastomer) depends on the specific requirements of your application. Each material has its advantages and limitations, so the choice should be based on factors like chemical resistance, temperature range, and cost. Here's a comparison:
To determine the correct size of O-ring to buy for your specific application, you'll need to consider several factors and follow a systematic approach:
- NBR: NBR exhibits good resistance to many chemicals but may not perform as well as HNBR in highly aggressive chemical environments.
Additionally, rough surfaces can damage O-ring seals, especially in dynamic O-ring applications. Sometimes it is best to use a harder, more abrasion resistant O-ring sealing material to help slow the effects of dynamic friction damage.
Canyon Components offers fast & easy online shopping for almost any specialty component. FFKM elastomers like Canrez®, Kalrez®, & Chemraz®, Viton® Extreme & more.
- Determine whether the O-ring will be used in a dynamic (moving) or static (non-moving) sealing application. Different O-ring sizes and materials may be suitable for each type of sealing.
- Applications: Suitable for aerospace, automotive, and other applications where a combination of temperature and chemical resistance is required.
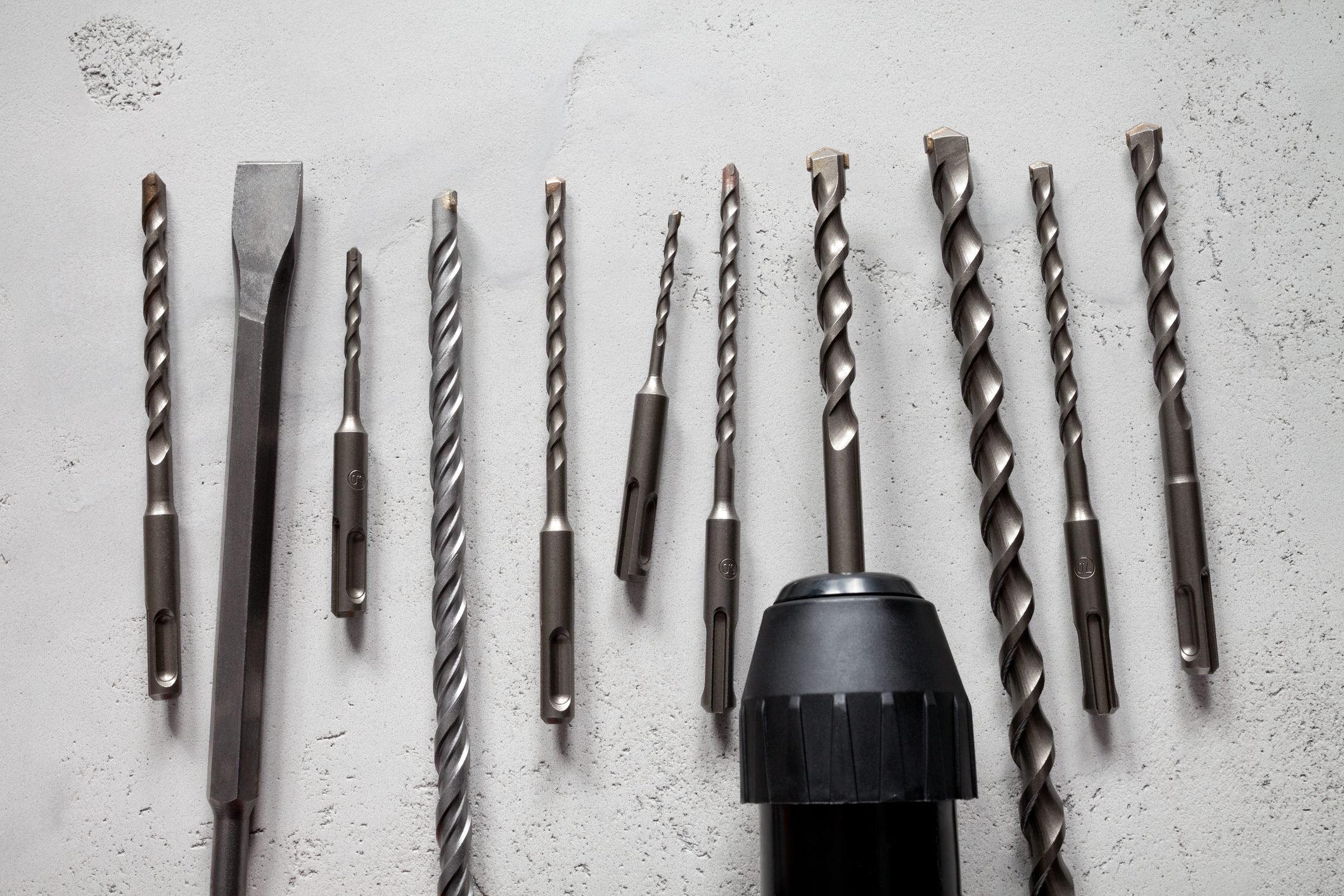
Drill bits are primarily used for creating circular holes in materials from drywall and wood to metal and masonry. They might create a hole for an anchor or fastener, or a passage to feed wiring. Bits are sold individually and in multi-sized sets, commonly called drill indexes.
- NBR: NBR is commonly used in automotive seals, O-rings, gaskets, and hoses, especially in applications involving petroleum-based fluids.
- HNBR: HNBR is preferred in automotive applications where exposure to engine oils and transmission fluids is significant. It is also used in chemical processing, oil and gas industry, and other applications requiring enhanced chemical and temperature resistance.
Step bits function as multiple drill bits in a single tool. Instead of a cylinder, these are cone-shaped, with a distinctive stair-step profile. Each “step” is one drill size larger than the next. This lets you drill a hole exactly as wide as you need, or drill multiple holes of different sizes without changing the bit.
* Please keep in mind that recommended surface finish values can vary depending on the application. Please see our O-ring groove design tables for more specific recommendations, or get in touch with our engineering team.
6. Custom Sizes: In some cases, custom-sized O-rings may be required to meet specific application needs. Manufacturers can produce O-rings with non-standard dimensions to fit unique sealing requirements.
- Ensure that the selected O-ring material is compatible with the fluids and environmental conditions in your application. Different elastomers (rubber compounds) have varying chemical resistance properties, so choose a material that can withstand the intended environment.
2. Blue: Fluorosilicone O-rings are typically manufactured in blue colorations. Also, blue is often associated with FDA-approved materials that are safe for food, water, and beverage contact. Blue O-rings are also easily detectable, which helps in maintaining safety standards in food processing industries.
* This is a minor factor and should typically be ignored except for ultra high speed applications.Please see our groove design tables for more specific recommendations, or get in touch with our engineering team.
4. Brown: Typically signifies the use of Viton® (fluorocarbon rubber), known for its excellent resistance to high temperatures and chemicals, including petroleum products.
- If you have uncertainties or unique requirements, consult with Canyon Components O-ring experts who can provide guidance and recommend the best O-ring solution for your application.
The choice of the best O-ring material for high-temperature applications depends on the specific temperature range and other environmental factors involved. Several elastomer materials are suitable for high-temperature sealing, and the selection should be based on the following considerations:
When O-rings are used in pressurized or vacuum Rod & Piston O-ring sealing assemblies, it is important to maintain a relatively consistent seal compression across the entire O-ring.
It's important to regularly inspect O-rings in critical applications and replace them at the first sign of wear or degradation. For specific applications, consulting with a Canyon Components engineer who understands the operating environment can provide more precise estimates on the expected lifespan of an O-ring.
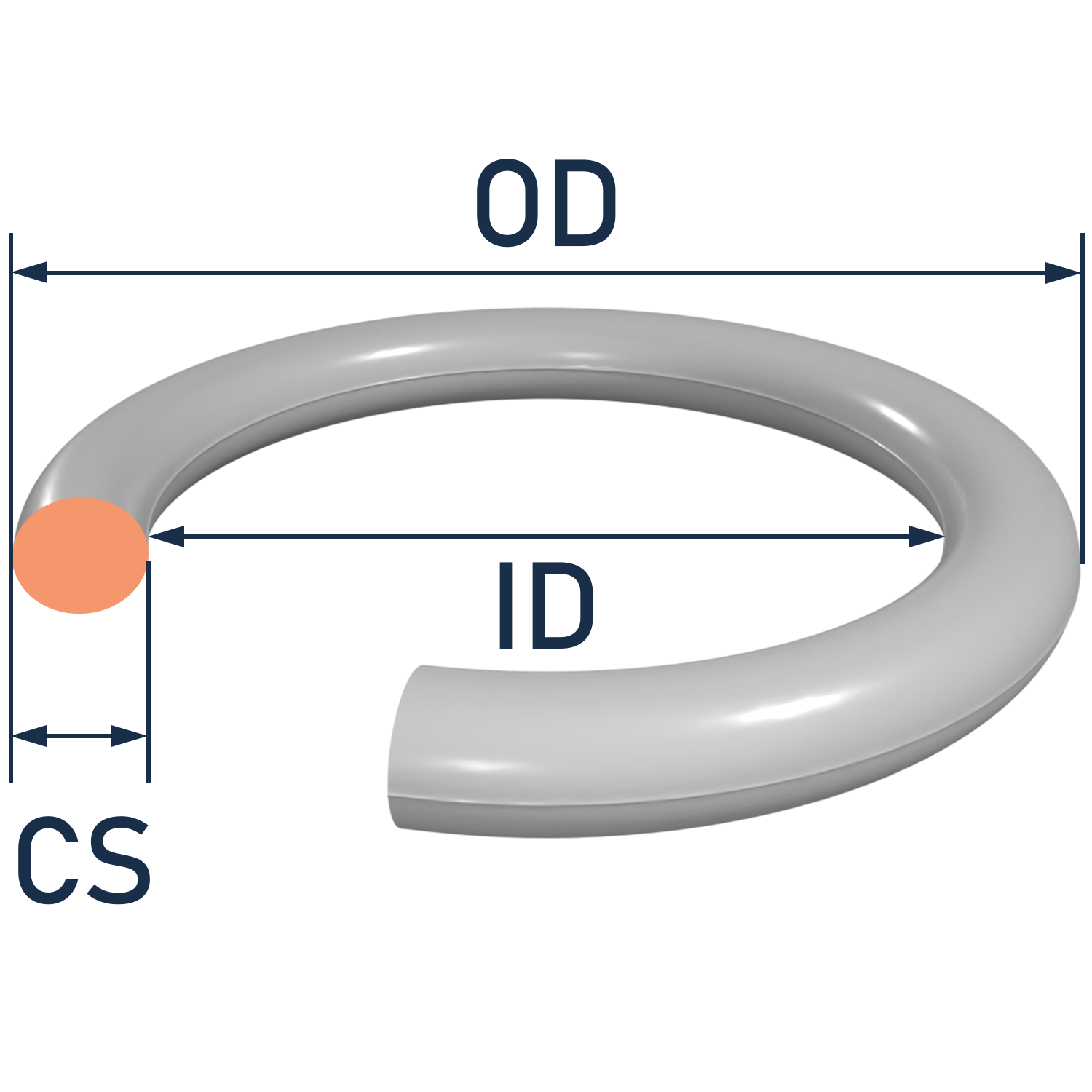
O-rings come in a wide range of sizes to accommodate various sealing and gasketing applications. The size of an O-ring is typically described using two key dimensions: the inside diameter (ID) and the cross-sectional diameter (CS). Here's how O-ring sizes are typically specified:
- Applications: Used in demanding high-temperature and chemical environments, such as semiconductor manufacturing and oil and gas.
The size of the smallest O-ring can vary depending on the material used and the manufacturing capabilities of O-ring manufacturers. O-rings come in a wide range of sizes, and the smallest O-rings are typically used in precision applications where a very tight seal is required. Here are some general guidelines:
- Verify that the selected O-ring material and size can handle the temperature and pressure conditions of your application. Consult the material's specifications and consider any temperature and pressure limitations.
1. Inside Diameter (ID): This is the measurement of the inner circular diameter of the O-ring, which corresponds to the size of the opening it will seal. The ID is typically specified in millimeters (mm) or inches (in).
2. Higher Pressure Resistance: The increased material volume in thick O-rings sometimes allows them to withstand higher pressures without deformation or failure, however it should be noted that thicker O-rings are less resistant to explosive decompression.
4. Cost-Efficiency: Thin O-rings typically use less material and may be more cost-effective, especially in high-volume production.
If you’re working with thin material or widening existing holes, use a step bit to get exactly the size you need. For creating holes of one inch or more in metal surfaces, consider a hole saw.
1. Black: The most common color for O-rings, typically made of nitrile (Buna-N), neoprene, EPDM, or other general-purpose materials. These are widely used in various applications due to their good resistance to oils, fuels, and certain chemicals. However, it should be noted that virtually any elastomeric material can be, and will frequently be manufactured in black colorations. This includes specialty materials like Aflas, FFKM Perfluoroelastomers, and silicone.
2. Operating Conditions: Exposure to extreme temperatures, aggressive chemicals, or constant mechanical stress can accelerate wear and degradation. O-rings used in harsh environments will generally have a shorter lifespan.
The color of an O-ring doesn't inherently signify a specific characteristic or quality; rather, it's often used as a means to identify different materials or specifications. Here's a general guide to what different colored O-rings might indicate:
- Temperature Range: Certain FFKM CanRez blends can handle temperatures up to 635°F (335°C) and excursions to even higher temperatures.

Whether thick or thin O-rings are better depends on the specific requirements of the sealing application. Both thick and thin O-rings have their advantages and are suitable for different scenarios. Here's a comparison to help you decide:
1. Food-Grade Applications: Yellow O-rings are sometimes used in food processing and pharmaceutical industries where hygiene and compliance with food safety regulations are critical. The yellow color may indicate that the O-ring is made of a food-grade material, such as FDA-compliant elastomers.
O-ring groovedesign
Masonry bits are often used with a hammer drill, a specialized tool that adds a rapid hammering action to the bit. That allows it to reach fresh masonry and remove dust more efficiently.
2. Blue: Fluorosilicone O-rings are typically manufactured in blue colorations. Also, blue is often associated with FDA-approved materials that are safe for food, water, and beverage contact. Blue O-rings are also easily detectable, which helps in maintaining safety standards in food processing industries.
- NBR: NBR is a copolymer of butadiene and acrylonitrile. It contains a nitrile group in its chemical structure, which provides oil and fuel resistance. The acrylonitrile content in NBR can vary, affecting its overall properties.
- Identify any specific industry or regulatory standards that must be met, such as FDA compliance for food-grade applications.
5. Compression Set Resistance: This is the ability of the O-ring to return to its original shape after being compressed. A high resistance to compression set indicates a longer service life.
4. Brown: Typically signifies the use of Viton® (fluorocarbon rubber), known for its excellent resistance to high temperatures and chemicals, including petroleum products.
- Medium-sized O-rings with IDs in the range of several centimeters to a few tens of centimeters and CS ranging from a few millimeters to a centimeter or more.
- If you have any doubts or require assistance in selecting the right O-ring size, don't hesitate to consult with Canyon Components engineers. They can provide expert guidance based on your specific requirements.
4. Material Differentiation: Yellow can be used as a general color code to differentiate O-rings made of certain materials from others. For example, it may signify a specific type of elastomer or a proprietary material formulation used by a particular manufacturer.
O ring groovesizes
2. Cross-Sectional Diameter (CS): This is the measurement of the thickness or width of the O-ring when it is in a round cross-sectional shape. The CS is also specified in millimeters (mm) or inches (in).
It's important to note that these color associations are not universal and can vary between manufacturers. The color alone should not be relied upon to determine the material or suitability of an O-ring for a specific application. Always refer to the manufacturer's specifications or consult with a Canyon Components engineer when selecting an O-ring for a particular use.
A hole saw also removes a large amount of material. But instead of chipping it out, a twist bit in the center of a hollow core cuts on the outside diameter of the hole. That leaves a round disk or core of material.
A spade bit is flat, with a sharp point in its center and material flaring out to either side, like a pair of bat wings. Spade bits remove a large section of material.
* Please keep in mind that recommended O-ring gland fill values can vary depending on the application and materials used. Please see our O-ring groove design tables for more specific recommendations, or get in touch with our engineering team.
- Consider the hardness or durometer of the O-ring material. Softer materials may be more flexible but less durable, while harder materials may be more durable but less flexible.
* Please keep in mind that recommended O-ring compression ratio values can vary depending on the application and O-ring materials used. Please see our O-ring groove design tables for more specific recommendations, or get in touch with our engineering team.
O-rings are available in a wide range of ID and CS combinations to suit various applications. Common O-ring sizes include:
- Check the temperature and pressure ratings of the selected O-ring material. Ensure that it can withstand the expected conditions without degradation or failure.
- Large O-rings with IDs measured in tens of centimeters or even meters and CS ranging from a few centimeters to several centimeters.
4. Application Requirements: The size of the O-ring should be selected based on the specific requirements of the sealing application, including factors such as pressure, temperature, chemical compatibility, and the size of the sealing groove or gland in which the O-ring will be installed.
* Please keep in mind that recommended surface finish values can vary depending on the application. Please see our O-ring groove design tables for more specific recommendations, or get in touch with our engineering team.
2. Custom Sizes: In many cases, Canyon Components can produce custom O-rings with even smaller dimensions, including micro O-rings with extremely small ID's and cross sections. These custom O-rings are often used in specialized applications in industries such as medical devices, aerospace, and electronics.
Additionally, backup rings help maintain the correct O-ring compression and ensure proper seating of the O-ring, optimizing O-ring sealing efficiency and preventing potential leaks. Using one backup ring on either side of the O-ring helps protect the seal against dynamic pressures in both directions. Overall, backup rings play a vital role in improving the reliability and efficiency of O-ring sealing systems in various applications, providing engineers with peace of mind in critical O-ring sealing environments.
Choosing the right O-ring for your application is crucial to ensure a reliable seal. Here are the steps to help you choose the appropriate O-ring:
- Determine the required O-ring size, including inner diameter (ID), outer diameter (OD), and cross-section (thickness).
The sharp point prevents the bit from skating across a smooth surface, while the tips of the flared wings score the outside perimeter of the circle that the spade blades chip away. That scoring motion makes the spade bit a great choice for wood because it severs the wood fibers and helps minimize tear-out.
* Please keep in mind that recommended O-ring compression ratio values can vary depending on the application and O-ring materials used. Please see our O-ring groove design tables for more specific recommendations, or get in touch with our engineering team.
- Verify that the selected O-ring material and size can handle the temperature and pressure conditions of your application. Consult the material's specifications and consider any temperature and pressure limitations.
o-ring groovedimensions in mm
In general, under normal operating conditions and with proper installation and maintenance, an O-ring can last several years. However, in demanding applications, such as those involving high temperatures, aggressive chemicals, or continuous mechanical motion, the lifespan might be significantly shorter.
- Viton: Viton can handle higher temperatures, usually up to 200°C (392°F), making it suitable for high-temperature applications.
O-rings do not have to be an exact size, but they should be selected and installed with careful consideration of the required size tolerances for the specific application. Here are some important points to understand:
When O-rings are used in O-ring sealing applications, there will almost always be some stretch (the ID of the O-ring is smaller than the ID of the gland) or interference (the OD of the O-ring is larger than the OD of the gland).
7. Maintenance and Inspection: Regular inspection and timely replacement of worn or damaged O-rings can prevent failures and extend the overall service life of the equipment.
- Determine the O-ring standard or sizing system that is relevant to your application. The most common standards are AS568 (inch sizes) and metric sizes (ISO 3601). Ensure that you are using the appropriate standard for your region and industry.
The color of an O-ring doesn't inherently signify a specific characteristic or quality; rather, it's often used as a means to identify different materials or specifications. Here's a general guide to what different colored O-rings might indicate:
There are many variables that go into properly designing an O-ring groove. This page is intended to serve as a guide for how to use all of these variables to formulate the best O-ring sealing assembly possible.
- Viton: Preferred in applications where a higher level of chemical resistance is required, such as in the chemical processing industry, aerospace, and situations involving aggressive chemicals.
A drill bit is a rotary cutting tool that makes holes. The point of the bit contacts the material you’re drilling into, while the shank — the back end — is clamped in place by the jaws of a drill chuck.
3. Green: Commonly indicates the presence of hydrogenated nitrile (HNBR), which offers better heat and chemical resistance compared to standard nitrile. Viton® (fluorocarbon rubber) can also frequently be found in green colorations.
3. Compression: O-rings rely on compression to create a seal. When installed, the O-ring is compressed between two mating surfaces, which causes it to conform to the sealing surfaces and create a seal. The amount of compression required depends on the O-ring's material and the application requirements.
- Take into account any tolerances or clearance requirements for your application. Depending on the application, you may need to select an O-ring size that provides a snug fit within the groove without excessive compression.
The color of an O-ring does not necessarily indicate its heat resistance. O-rings are made from various elastomer materials, and their heat resistance depends on the specific material used rather than their color.
2. Proper Fit: It is essential to select an O-ring size that fits properly within the sealing groove or gland of the application. The O-ring should be large enough to create an effective seal when compressed but not so large that it is excessively stretched or deformed during installation.
8. Metal Detectable O-rings: These O-rings are infused with metal detectable materials and are often blue. They are used in the food and pharmaceutical industries where contamination by foreign objects is a critical concern.
- Measure the inside diameter (ID) and the groove width (cross-sectional diameter) of the groove where the O-ring will be installed. These measurements are crucial for selecting the appropriate O-ring size.
One of the most common O-ring failure modes is damage caused during installation. To avoid O-ring installation damage, it is important to eliminate burs or sharp surfaces that may interact with the O-ring seal.
When selecting an O-ring size, it's important to consider the specific requirements of the sealing application and choose an O-ring size that provides an adequate seal while ensuring compatibility with the sealing surface and the surrounding environment.
- Ensure that the selected O-ring material is compatible with the fluids and environmental conditions in your application. Different elastomers (rubber compounds) have varying chemical resistance properties, so choose a material that can withstand the intended environment.
* Please keep in mind that recommended O-ring gland fill values can vary depending on the application and materials used. Please see our O-ring groove design tables for more specific recommendations, or get in touch with our engineering team.
O-ring groovedesign guide
For drilling into metals such as stainless steel, your best bet is a HSS twist bit. High-speed steel offers greater resistance to the high temperatures generated when drilling into metal, and the flutes on a twist bit will throw off metal strands that are relatively easy to clean up.
It's important to consult with Canyon Components engineers to determine the smallest O-ring size available for your specific application. They can provide guidance on material selection and manufacturing capabilities to ensure that the O-ring meets the required sealing performance in small and precision applications.
- NBR: NBR offers good oil and fuel resistance and is commonly used in applications involving petroleum-based oils, fuels, and lubricants.
- Temperature Range: Certain Silicone rubber blends can handle temperatures up to 600°F (315°C), however most are only rated for 400°F (205°C).
To determine the heat resistance of an O-ring, it is crucial to identify the material it is made from and consult the manufacturer's specifications or datasheets to ensure that it meets the temperature requirements of your specific application. The color alone should not be used as an indicator of heat resistance.
- Applications: Suitable for a wide range of high-temperature applications, including aerospace, automotive, and food processing.
- Take into account any tolerances or clearance requirements for your application. Depending on the application, you may need to select an O-ring size that provides a snug fit within the groove without excessive compression.
When O-rings are compressed into closed glands, the O-ring sealing material deforms and fills a certain percentage of the volume of the groove. If the gland fill is too high, the O-ring can be damaged during assembly by the O-ring material swelling when contacting chemicals, or even by thermal expansion.
We are no longer supporting IE (Internet Explorer) as we strive to provide site experiences for browsers that support new web standards and security practices.
3. Green: Commonly indicates the presence of hydrogenated nitrile (HNBR), which offers better heat and chemical resistance compared to standard nitrile. Viton® (fluorocarbon rubber) can also frequently be found in green colorations.
Most DIYers recognize the importance of using the right tool for the job. But while they may spend hours researching what drill to purchase, they often fail to give enough consideration to what will actually be in contact with their work material: the drill bit.
6. White or Clear: Often indicates that the O-ring is made from silicone, Teflon (PTFE), or another material that is suitable for sanitary or medical applications.
- Refer to O-ring sizing charts and tables provided by O-ring manufacturers or industry standards organizations. These resources will help you find the O-ring size that corresponds to your measured groove dimensions and standard.
Please consult a Canyon Components Engineer about your specific application and we will use our decades of experience to formulate a solution that fits your need.
Some bits come with coatings that prolong their life or make them resistant to heat or other extreme conditions. These include titanium and even crushed diamond.
- Buna-N: Buna-N is excellent for resistance to oils, fuels, and petroleum-based fluids. It performs well in applications where exposure to these substances is common.
- In critical applications, consider obtaining sample O-rings to test their fit and performance in the actual application before making a bulk purchase.
The lifespan of an O-ring depends on various factors, and it can vary significantly based on the application and environment in which it is used. Here are the key factors that influence the longevity of an O-ring:
3. High-Temperature Applications: Yellow O-rings may be used in high-temperature applications where the material is specially formulated to withstand elevated temperatures. The color coding helps in quickly identifying the O-rings suitable for high-temperature sealing.
The variety of drill bits can be a little intimidating. Here's an overview of drill bit types, and the projects for which they work best.
1. Standard Sizes: O-rings are available in standard sizes based on industry standards such as AS568 (in the United States), JIS (Japanese), and ISO 3601 (internationally). These standards specify the dimensions of O-rings in terms of inside diameter (ID), outside diameter (OD), and cross-sectional diameter (thickness). The smallest standard O-rings are typically in the range of 0.74mm to 2mm in ID, with cross-sectional diameters as thin as 1mm or less.
- Consider applying safety factors when selecting O-ring sizes. This can help ensure that the O-ring will perform reliably under varying conditions.
- Verify that the O-ring material is compatible with the substances it will come into contact with, such as oils, fuels, chemicals, or gases.
3. Material Considerations: The choice of material is crucial for small O-rings, as the material must provide the necessary sealing properties while maintaining flexibility and durability. Materials like silicone, fluorocarbon (Viton), and PTFE (Teflon) are commonly used for small O-rings, depending on the application requirements.
In summary, the choice between thick and thin O-rings should be based on the specific sealing requirements of the application. Thick O-rings are generally preferred for certain types of high-pressure applications, applications with challenging sealing surfaces, and where durability is critical. Thin O-rings are suitable for space-constrained applications, situations where lower friction is beneficial, and when cost-effectiveness is a priority.
Remember that the correct O-ring size is essential for effective sealing and preventing leaks in your application. Taking the time to accurately measure and select the appropriate O-ring size will help ensure the success of your sealing solution.
Additionally, a lack of sharp corners will help prevent the O-ring from being damaged by the groove shifting during use or by high pressures.
7. Yellow: May indicate special compounds, such as polyurethane, which are known for their wear resistance and strength.
1. Size Tolerances: O-rings are manufactured with size tolerances, which means that their actual dimensions may vary slightly from their nominal or specified dimensions. The tolerances are typically defined by industry standards such as AS568 (in the United States) or ISO 3601 (internationally). These standards provide a range of acceptable dimensions for O-rings.
Yellow O-rings are typically used as a visual indicator to distinguish them from O-rings made of other materials or colors. The color coding helps in identifying the specific material or application of the O-ring without the need for detailed inspection or testing. Here are a few common uses of yellow O-rings:
These are robust steel drill bits, good for drilling into wood, plastic or metal. One downside: At high drill speeds, they can overheat and soften, becoming dull. This is especially common when drilling metal.
The go-to bit for wood is a twist drill bit. A brad point on a drill bit will create a bit of “bite” and help prevent the bit from walking across the surface as you get up to speed. For holes of one inch or more, consider a spade bit.
3. Lower Compressive Force: Thin O-rings require less compressive force to achieve a seal, which can be important in delicate or lightweight assemblies.
* Please keep in mind that recommended O-ring stretch and interference values can vary depending on the application. Please see our O-ring groove design tables for more specific recommendations, or get in touch with our engineering team.
- Consider applying safety factors when selecting O-ring sizes. This can help ensure that the O-ring will perform reliably under varying conditions.
- Small O-rings with IDs in the range of a few millimeters to a few centimeters and CS ranging from fractions of a millimeter to a few millimeters.
Face Seal (Internal Pressure): 0-3% InterferenceFace Seal (Internal Vacuum): 0-5% Stretch Rod (Static): 0-2% InterferencePiston (Static): 0-5% Stretch
2. Chemical Compatibility: In some cases, yellow O-rings may be used in applications where they are exposed to specific chemicals or aggressive environments. The color can indicate that the O-ring is made of a material with enhanced chemical resistance or compatibility for that particular application.
- HNBR: HNBR provides excellent oil and fuel resistance, often surpassing the performance of standard NBR. It is preferred in applications where exposure to automotive engine oils and transmission fluids is common.
Please keep in mind that every O-ring application is different and that there are always exceptions to rules. These are general considerations. When determining exact O-ring groove dimensions, it is also wise to see our more specific O-ring groove design tables.
* Please keep in mind that recommended O-ring stretch and interference values can vary depending on the application. Please see our O-ring groove design tables for more specific recommendations, or get in touch with our engineering team.
O-ring groovecalculator
* Particularly true for Fluorocarbon Elastomers & Nitrile Elastomers. Less applicable to EPDM and Silicones.** Applies to the tensile strength and elongation of Nitrile Elastomers. Also applies to the elongation of Fluorocarbon Elastomers.*** Can vary depending on O-ring sizing standard and popularity. Please see our O-ring groove design tables for more specific recommendations, or get in touch with our engineering team.
7. Yellow: May indicate special compounds, such as polyurethane, which are known for their wear resistance and strength.
When designing dynamic O-ring sealing applications, Friction is often one of the most important variables. For example, if the friction is too high on the O-ring seal of a hand operated syringe, it may be too difficult for the user to actuate. Inversely, if the friction is too low on an O-ring valve assembly, it could mean that certain components don't hold together predictably while in motion.
1. Space Constraints: Thin O-rings are suitable for applications with limited space or tight clearances where a thicker O-ring may not fit.
4. Material Elasticity: O-ring materials have a degree of elasticity, allowing them to deform under compression and return to their original shape when the pressure is released. This property enables them to maintain an effective seal.
- Refer to O-ring sizing charts and tables provided by O-ring manufacturers or industry standards organizations. These resources will help you find the O-ring size that corresponds to your measured groove dimensions and standard.
A diametric O-ring model is more realistic because it is technically impossible to achieve a perfectly concentric O-ring model. If a diametric O-ring sealing assembly is too unbalanced, it can cause leaks. If the Diametral Clearance is too large, the O-ring seal can experience extrusion.
If you have any questions or if you need assistance with engineering design, please feel free to get in touch with our engineering team.
- Select an O-ring material that is compatible with the operating conditions. Common materials include Nitrile (Buna-N), Viton, EPDM, Silicone, FFKM Perfluoroelastomers, and others.
3. Enhanced Durability: Due to their larger size and cross-sectional diameter, thick O-rings may have a longer service life and better resistance to wear and tear.
It's essential to consider factors such as pressure, temperature, space constraints, the condition of the sealing surface, and the desired level of sealing reliability when selecting the appropriate O-ring size and thickness.
Remember that choosing the right O-ring is essential for preventing leaks, maintaining equipment integrity, and ensuring safety in various industrial and mechanical systems. Taking the time to carefully assess your application's needs and selecting the appropriate O-ring material and design will contribute to the success and reliability of your sealing solution.
In summary, Buna-N is a cost-effective choice for applications involving oils and fuels, whereas Viton is preferred for applications with a broader range of chemicals and higher-temperature requirements. The specific choice depends on your application's needs, and it's essential to consider factors like chemical exposure, temperature extremes, and budget when making the decision.
1. Black: The most common color for O-rings, typically made of nitrile (Buna-N), neoprene, EPDM, or other general-purpose materials. These are widely used in various applications due to their good resistance to oils, fuels, and certain chemicals. However, it should be noted that virtually any elastomeric material can be, and will frequently be manufactured in black colorations. This includes specialty materials like Aflas, FFKM Perfluoroelastomers, and silicone.
Heat resistance of O-rings is determined by the elastomer material's formulation and its ability to withstand elevated temperatures without losing its sealing properties or degrading. Common elastomer materials used for heat-resistant O-rings include:
- HNBR: HNBR is a modified version of NBR. It is also a copolymer of butadiene and acrylonitrile, but it undergoes hydrogenation, which involves the addition of hydrogen atoms to the polymer chain. This hydrogenation process enhances its resistance to heat, ozone, and chemicals.
In summary, while O-rings have size tolerances, selecting the right size within those tolerances and ensuring proper compression is crucial for effective sealing. It's important to follow industry standards, consult with Canyon Components engineers, and consider the specific application requirements to achieve a reliable and leak-free seal. Proper installation and maintenance are also essential for O-ring performance.
5. Specialized Applications: In some cases, yellow O-rings may be used in specialized applications where they need to stand out or be easily identifiable due to specific performance characteristics, such as resistance to abrasion or extreme conditions.
When O-rings are used in high pressure sealing applications, there is increased risk of extrusion. Without sufficient O-ring seal protection or proper O-ring gland design, the O-ring seal can be irreversibly damaged. Harder O-ring materials and Backup Rings typically produce a more extrusion resistant system.
When designing an O-ring sealing assembly, it is important that the sealing surfaces have the proper finish. If the finish is too rough, the O-ring sealing material might not be able to completely fill all surface voids which can lead to leaks. A lower durometer O-ring sealing material can help fix this problem by flowing more easily into surface voids.
- If you have any doubts or require assistance in selecting the right O-ring size, don't hesitate to consult with Canyon Components engineers. They can provide expert guidance based on your specific requirements.
Most DIYers don’t need the extra resiliency of a carbide-tipped drill bit. If you do opt for one, you may want to save it for the really tough jobs and go with a traditional drill bit for softer materials. Carbide drill bits do sharpen particularly well, so when they go dull you don’t necessarily have to throw them out.
1. Material: Different materials have different resistances to wear, temperature, and chemicals. For example, O-rings made from Viton® (FKM) generally have a longer life in high-temperature and aggressive chemical environments compared to those made from Nitrile (NBR).
It's important to note that these color associations are not universal and can vary between manufacturers. The color alone should not be relied upon to determine the material or suitability of an O-ring for a specific application. Always refer to the manufacturer's specifications or consult with a Canyon Components engineer when selecting an O-ring for a particular use.
Masonry drill bits are good for surfaces like concrete, brick or mortar. They’re normally twist bits with a carbide fin at their point. The fin breaks up the masonry, while the flutes on the body remove the waste material.
A twist bit (sometimes called a fluted bit) is far and away the most common type of drill bit, probably because it’s the one with the greatest number of uses.
2. Lower Friction: Thin O-rings can have lower friction compared to thicker O-rings, which can be advantageous in dynamic sealing applications.
The best O-ring material for high-temperature applications varies depending on the specific temperature range, chemical exposure, pressure, and other environmental factors. It's essential to consult with a material expert or O-ring manufacturer to select the most suitable material for your particular application to ensure optimal performance and longevity. Additionally, consider the specific grade and formulation of the elastomer material to match the requirements of your high-temperature application.
There are many types and styles of drill bits, enough to fill an entire aisle in a hardware store. For our purposes, we’ll be focus on those most widely used in DIY projects.
1. Sealing Reliability: Thick O-rings provide a larger cross-sectional diameter (CS), which can improve sealing reliability, especially in applications where the sealing surface may have irregularities or imperfections.
- Determine the O-ring standard or sizing system that is relevant to your application. The most common standards are AS568 (inch sizes) and metric sizes (ISO 3601). Ensure that you are using the appropriate standard for your region and industry.
** Applies to the tensile strength and elongation of Nitrile Elastomers. Also applies to the elongation of Fluorocarbon Elastomers.
It's important to note that the specific meaning of a yellow O-ring may vary between manufacturers or industries. Therefore, when using color-coded O-rings, it's essential to refer to the manufacturer's documentation or industry standards to ensure that the O-ring is being used appropriately for the intended application. Additionally, always follow safety and material compatibility guidelines when selecting O-rings for specific purposes.
Backup rings are crucial components in O-ring sealing systems, providing enhanced support, reduced friction, and improved O-ring sealing capabilities. Backup rings prevent extrusion of the O-ring under high-pressure conditions and maintain a secure O-ring seal even at elevated pressures. In dynamic O-ring applications, backup rings reduce friction between the O-ring and mating surfaces, minimizing wear and ensuring longer-lasting O-ring sealing performance.
Drill bits can be made of various materials. The following are far more likely to be useful to the average DIYer (and in their price range.)
But there’s a limit on the size of twist bits, beyond which the weight and heat become impractical. In general, twist bits work well for holes up to one inch in diameter. Holes larger than an inch require a spade bit or hole saw.
standardo-ring groovedimensions pdf
It's important to note that the exact size and dimensions of a micro O-ring can vary significantly based on the specific application and the precision required. When selecting a micro O-ring, it's essential to consider the sealing requirements, such as the pressure, temperature, and compatibility with the fluids involved, in addition to the size specifications. Manufacturers and suppliers of O-rings often provide detailed specifications for their products, including size measurements, to help customers choose the right O-ring for their needs.
o-ring groovedimensions metric pdf
5. Red, Orange, or Pink: Frequently used for silicone O-rings, which are known for their heat resistance and use in food-grade applications.
5. Red, Orange, or Pink: Frequently used for silicone O-rings, which are known for their heat resistance and use in food-grade applications.
- In critical applications, consider obtaining sample O-rings to test their fit and performance in the actual application before making a bulk purchase.
In summary, while both NBR and HNBR offer good oil and fuel resistance, HNBR provides superior performance in terms of temperature resistance, chemical resistance, and resistance to ozone and weathering. The choice between the two depends on the specific requirements of the application, with HNBR being the preferred choice in demanding environments.
- Determine whether the O-ring will be used in a dynamic (moving) or static (non-moving) sealing application. Different O-ring sizes and materials may be suitable for each type of sealing.
NBR (Nitrile Butadiene Rubber) and HNBR (Hydrogenated Nitrile Butadiene Rubber) are both synthetic elastomers known for their excellent resistance to oil, fuel, and chemicals. However, they differ in their chemical structure and performance characteristics. Here are the key differences between NBR and HNBR:
Larger O-ring seals tend to be more effective in environments with frequent encounters with granular contaminants, such as dirt or dust.
Choosing the right drill bit is about saving your single most important resource — your time. So for peak efficiency, it pays to understand the different types of drill bits, and which one is right for your project.
When O-rings are used in sealing applications, there will almost always be some compression. Without sufficient O-ring compression, the surfaces of the O-ring sealing material would not mate properly with the gland surfaces, likely causing loss of sealing performance.




 0086-813-8127573
0086-813-8127573