Topsfield Town Library - topsfield library
The addition of stabilizing elements such as Ti, Nb (Cb), and Ta can also provide increased resistance to sensitization, especially for long-term exposures in the critical range in service. These stabilizing elements tend to form carbides that are more stable than chromium carbide in the temperature range of 2250 to 1450°F. So as the alloy cools from high temperatures, the carbon combines with the stabilizing elements and is unavailable for chromium carbide precipitation at the lower sensitizing temperature range of 950 to 1450 °F. Common stabilized austenitic grades include Type 321, 347, 20-Cb3, and 316Ti. Figure 4 summarizes the carbide precipitation reactions that occur in type 304 and 347 stainless steels.
DiamondToolcatalog
Three approaches have been used with the austenitic stainless steels to minimize to the effects of IGA. Material that has been sensitized can be solution annealed by heating to a temperature where the carbides dissolved and the chromium-depleted regions are eliminated. The carbon is then kept in solution by rapid cooling through the sensitizing temperature range. The recommended solution anneal temperature depends on the alloy and is typically done in the range of 1900 to 2150°F followed by rapid cooling.
Recommended for You ... Not exactly what you want? Post Sourcing Request. Hot Searches. Pipe EndSingle EndDouble EndTube EndHead ...
Diamond Tools app
Although intergranular attack of ferritic stainless steels is similar to that found in austenitic stainless steels, there are some important differences. Because the solubility of nitrogen is low in the ferritic crystal structure, the precipitates that cause sensitization in ferritic grades include both chromium carbides (Cr23C6) and chromium nitrides (Cr2N).
The chromium carbides tend to precipitate at the grain boundaries of austenitic stainless steels in the 950 to 1450°F temperature range. Any exposure or thermal excursion into this temperature range during metal manufacture, fabrication, or service could potentially sensitize the steel.
With the ferritic grades, sensitization occurs during cooling from higher temperatures (>1700 °F). At these high temperatures the carbides and nitrides are put into solution and during cooling they can precipitate at grain boundaries resulting in chromium depletion. The very high diffusion rates in the ferrite structure make it impossible to cool the steel fast enough to avoid precipitation of carbides and nitrides at grain boundaries. For this reason, most commercial ferritic grades avoid sensitization by restricting the level of C and N and requiring the addition of stabilizing elements such as Ti, Ta, or Nb.
DiamondTooland Horseshoe company

Touch the end mill to the top of the part and check the offset with a rule from either side. When it appea
In practical application, the loss of cross section thickness and the introduction of cracks can have severe consequences for applications like pressure containment.
Like other common materials, metals have a visible grain structure when they are viewed under magnification. Rapid corrosive attack of immediately adjacent grain boundaries with little or no attack of the grains is called Intergranular Corrosion.
DiamondToolSUPPLY
Surgical Instruments | Hone Tools & Accessories | Form Wheels | Broach & Hob Wheels | Grit Size Chart Bottom Grinding Mandrels 1 | Jig/ID Grinding Mandrels 2 | Jig/ID Grinding Mandrels Borazon Bonded Mandrels | Home | Email
May 23, 2012 — 016 times the drill diameter per flute. Both flutes is about 3% of the tools diameter. Now... Multiply that by the rpm = feed rate in inches per ...
Oct 26, 2017 — You can measure runout by spinning the part while an indicator gage takes readings across the pertinent surface — either a cross section to ...
With the stabilized grades, standard solution annealing treatments generally do not tie up all the available carbon. So when the stabilized grades in the solution-annealed condition have long time exposures to the sensitizing temperature range (1450 to 950 °F), chromium carbide precipitation and sensitization can occur. Stabilizing heat treatments can be used to more effectively tie up carbon by completing the precipitation reactions. These treatments consist of holding the alloy for several hours in the 1500 to 1600°F temperature range.
Common practices such as welding, stress relief, and hot forming can expose the steel to the sensitizing temperature range. The formation of chromium carbides is readily reversed by a solution anneal heat treatment. The test methods outlined in ASTM A262 have been developed to detect susceptibility to intergranular attack in austenitic stainless steels.
Diamond Tools Pottery
If sensitization has occurred in a ferritic stainless steel, the condition can be “healed” by back diffusing chromium into the depleted regions. “Healing” can be achieved by holding the material at 1100 – 1200 °F for several hours. The test methods outlined in ASTM A763 have been developed to detect susceptibility to intergranular attack in ferritic stainless steels.
Dec 14, 2017 — here's how i setup mine, Back chamfering is a little bit of a work around in fusion, I use contour as my toolpath, select that chamfer I want, ...
Milwaukee Tool is the most respected manufacturer of heavy-duty power tools, hand tools, instruments, and accessories.
20211018 — Mills can machine cylindrical features but if the part is purely cylindrical, then a lathe is a better, more precise option. More complex ...
Melting Point. 2000º C. Magnetic Properties. Slightly Magnetic. Coefficient of Friction. Tungsten Carbide on Tungsten. Carbide without Lubricant. 0.25. Material ...
Diamondtoolminecraft
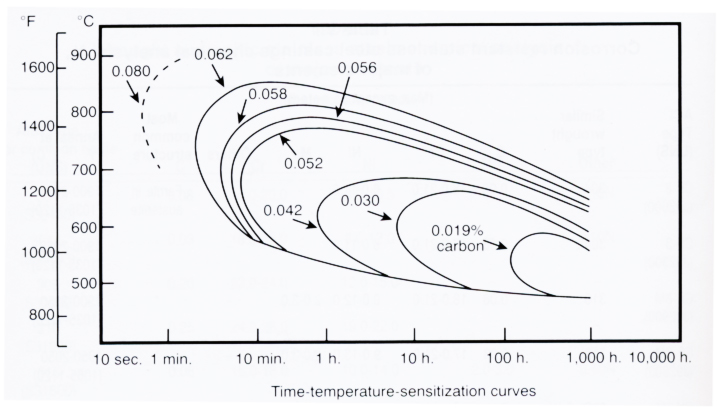
The time and temperature required to produce susceptibility to intergranular attack (IGA) is dependent on alloy composition, particularly the carbon content. Figure 3 shows the time-temperature-sensitization curves for Type 304 alloys with varying amounts of carbon content.
Buy Masonry Drill Bit, Extra Length, 3/8 x 6-In. -120816 from Walmart Canada. Shop for more Drill Bits & Accessories available online at Walmart.ca.
DiamondToolWhite Cap
With austenitic stainless steels, intergranular attack is usually the result of chromium carbide precipitation (Cr23C6) at grain boundaries, which produces a narrow zone of chromium depletion at the grain boundary. This condition is termed sensitization and it is shown schematically Figure 2. Sensitization involves the precipitation of chromium carbides at grain boundaries, which results in a narrow zone of chromium depletion at the grain boundary.
To our customers, we are committed to providing solutions to their problems by providing professional excellence; consistent, high-quality precision craftsmanship: quality assurance programs to support the operation; delivery when promised; personal attention and integrity; and customer service equal to or beyond expectations. We will maintain a manageable number of selected high performance suppliers and sub-contractors who are committed to providing the quality, level of pricing and service that will support and sustain the reputation of DTM. in the market niche served.
DiamondToolrental

Resistance to IGA can also be achieved by reducing the carbon content to below 0.030% level. As shown in Figure 3, lower carbon contents move the nose of the time-temperature-sensitization curve to longer times. The low carbon grades such as Types 304L, 316L, and 317L have been designed to resist sensitization during typical welding operations, but they do not resist sensitization by long term exposure in the critical temperature range in service. The higher alloyed, more corrosion resistant stainless steels such as the 904L and 6Mo alloys have very low carbon contents and susceptibility to IGA is typically not a concern.
Diamond Tool Manufacturing is a full service Diamond and CBN electroplated tooling manufacturer with CNC machining and grinding capabilities. DTM is fully staffed with technicians trained to aid you in improving your processes through the use of superabrasive tooling.
Because the chromium is the primary alloying element that makes stainless steel corrosion resistant, the chromium-depleted regions are susceptible to preferential corrosion attack. It is believed that this occurs because the chromium content immediately adjacent to the carbide may be below that required for the stainless steel alloy. If the carbides form a continuous network on the grain boundary, then corrosion can produce a separation or gap at the boundary and possible grain dropping or loss.
Details. Create a uniform chamfer on the edge of any work piece to add character while retaining crisp geometric lines. Chamfer size easily adjusts by changing ...
Rapid attack at the grain boundaries can result in grains “dropping” or falling out of the metal surface resulting in the disintegration of the steel. Figure 1 shows the appearance of a surface where this is occurring. In practical application, the loss of cross section thickness and the introduction of cracks can have severe consequences for applications like pressure containment.
Mission Statement: Continue long term growth in the business of precision machining and superabrasive-pIating by providing exceptional quality workmanship, superior value, and highly personalized solutions to completely satisfy customer desires and needs through a balanced commitment of excellence to our customers, our suppliers, and our employees. Commitment: Our commitment and vision begin with our employees and the belief that they are the foundation of our company. Through ingraining them with the values and work ethics. We can maintain a staff of hard working, loyal, committed employees who enjoy the freedom to earn a comfortable standard of living for themselves and their families and have fun doing it. We will provide an excellent working environment where employees are treated as family, fairly and with respect and where they have the earning potential proportional to personal performance. We will ensure that recruiting and hiring practices pursue personnel only with the same work ethic.




 0086-813-8127573
0086-813-8127573