TYPE F Adapters ( Male NPT x Male CAM ) - npt ontario
CNCGroovingInsert
Imaginary circle that touches all sides of an insert. Used to establish size. Measurements are in fractions of an inch and describe the diameter of the circle.
Workpiece is held in a chuck, mounted on a face plate or secured between centers and rotated while a cutting tool, normally a single-point tool, is fed into it along its periphery or across its end or face. Takes the form of straight turning (cutting along the periphery of the workpiece); taper turning (creating a taper); step turning (turning different-size diameters on the same work); chamfering (beveling an edge or shoulder); facing (cutting on an end); turning threads (usually external but can be internal); roughing (high-volume metal removal); and finishing (final light cuts). Performed on lathes, turning centers, chucking machines, automatic screw machines and similar machines.
Space provided behind the cutting edges to prevent rubbing. Sometimes called primary relief. Secondary relief provides additional space behind primary relief. Relief on end teeth is axial relief; relief on side teeth is peripheral relief.
The mathematical expression denoting one of several parameters that describe surface texture (same as average roughness Ra). Average roughness is the arithmetic average height deviation of the measured surface profile from the profile centerline. See surface texture.
Replaceable tool that clamps into a tool body, drill, mill or other cutter body designed to accommodate inserts. Most inserts are made of cemented carbide. Often they are coated with a hard material. Other insert materials are ceramic, cermet, polycrystalline cubic boron nitride and polycrystalline diamond. The insert is used until dull, then indexed, or turned, to expose a fresh cutting edge. When the entire insert is dull, it is usually discarded. Some inserts can be resharpened.
CNC turningtoolsnamelist
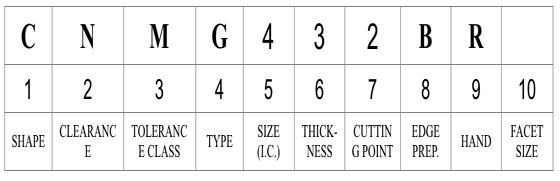
According to ANSI B212.4-2002 standard, identification of the indexable insert includes 10 positions denoted by a capital letter. Each position (from 1 to 10) defines a characteristic of the insert in the following order:
1. Shape2. Clearance3. Tolerance class4. Type5. Size6. Thickness7. Cutting-point configuration8. Edge preparation9. Hand10. Facet size
It will be a two-digit number carried to one decimal place when it is not a whole number: 1.2 – 5 ⁄ 32"; 1.5 – 3 ⁄ 16"; 1.8 – 7 ⁄ 32"; 2.5 – 5 ⁄ 16".
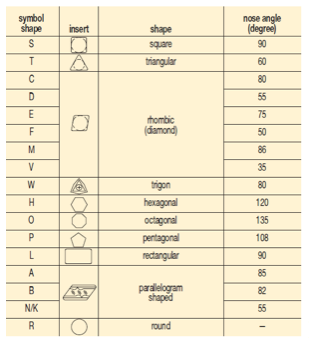
There are 16 standard shapes of indexable inserts, and each shape is identified by a capital letter as follows (Figure 1):
CNMGinsertfull form
Nine relief angle values have been described in ANSI B212.12-1991 standard. These angles are the difference from 90° measured in a plane normal to the cutting edge generated by the angle between the flank and top surface of the insert. Each relief angle is denoted by a capital letter as follows:
The sixth position is a significant one- or two-digit number indicating the number of sixteenths of an inch in the thickness of the insert. It is a one-digit number when the number of sixteenths of an inch in the thickness is a whole number: 1 – 1 ⁄ 16"; 2 – 1 ⁄ 8"; 3 – 3 ⁄ 16"; 4 – 1 ⁄ 4"; 5 – 5 ⁄ 16"; 6 – 3 ⁄ 8"; 7 – 7 ⁄ 16"; 8 – 1 ⁄ 2"; 9 – 9 ⁄ 16"; 10 – 5 ⁄ 8".
This makes a very accurate and smooth hole. This is typically for small holes (ie. less than 3/4" usually less than 1/2"). There are all kinds of reamers. The ...
There are 14 tolerance classes that control the indexability of the inserts. Each class is denoted by a capital letter. Letters for tolerances are A, B, C, D, E, F, G, H, J, K, L, M, U and N.
Explanation: Enter each code position to decode the specific insert characteristics according to ANSI B212.4-2002 standards.
CNC insertmaterial
The fourth position is a capital letter denoting differences in design of insert, such as the existence of fixing holes, countersinks and special features on rake surfaces. There are 15 standard types in design as follows (Figure 3):
Point loads in the vicinity of tapered end cuts. Point loads that are applied in the vicinity of tapered end cuts are limited to certain magnitudes. If those ...
200982 — Inserts from Carmex, Valenite, Kennametal and others work well. I think the Carmex threading inserts are a good value in their uncoated grades.
In case of a facet, two letters are used. The first letter designates the facet angle: A – 45°; D – 60°; E – 75°; G – 87°; P – 90°; Z – Any other facet angle. The second letter designates the facet clearance angle:
Edmund Isakov, Ph.D., is a consultant, writer and frequent CTE contributor. He is the author of the books “Mechanical Properties of Work Materials” (Modern Machine Shop Publications, 2000); “Engineering Formulas for Metalcutting” (Industrial Press, 2004); “Cutting Data for Turning of Steel” (Industrial Press, 2009); the CD-ROM “International System of Units (SI)” (Industrial Press, 2012); and the software “Advanced Metalcutting Calculators” (Industrial Press, 2005). For more information, call (561) 369-4063 or visit www.edmundisakovphd.com.
Tolerances on dimensions (± from nominal) are denoted by letters A, B and T. Dimension A is the nominal inscribed circle (I.C.) of the insert. Dimension T is the thickness of the insert. For pentagon, triangle and trigon shapes, dimension B is the insert height, i.e., the distance between one side and the opposite corner (Figure 2).
Choose from our selection of collet chucks, CAT 40 taper end mill holders, carts for CNC tooling, and more. In stock and ready to ship.
On rectangular and parallelogram inserts, the width and length dimensions are used in place of the I.C. A two-digit number designates the sizes of these inserts. The first digit indicates the number of eighths of an inch in the width and the second digit indicates the number of fourths of an inch in the length of the insert.
Turninginserts types
It is a two-digit number carried to one decimal place when it is not a whole number: 1.2 – 5 ⁄ 64"; 1.5 – 3 ⁄ 32"; 2.5 – 5 ⁄ 32"; 3.5 – 7 ⁄ 32".
Due to the magazine’s space limitations, the authors provide the following tables showing most popular Kennametal’s indexable inserts only for general turning of steel, cast iron, and nonferrous alloys. These tables don’t cover all Kennametal chip breakers. (Figure 4 and Figure 5 also show Kennametal Inc. insert identification system and chip breaker identification system respectively.)
Highly Recommended: 6 local business owners recommend AZ Carbide. Visit this page to learn about the business and what locals in Cedar Springs have to say.
Jan 19, 2018 — The industry standard with regard to tail sizing for fine dovetailing in fine furniture, skinny pins and wider dovetails are the goal.
Angle of inclination between the face of the cutting tool and the workpiece. If the face of the tool lies in a plane through the axis of the workpiece, the tool is said to have a neutral, or zero, rake. If the inclination of the tool face makes the cutting edge more acute than when the rake angle is zero, the rake is positive. If the inclination of the tool face makes the cutting edge less acute or more blunt than when the rake angle is zero, the rake is negative.
Conditioning of the cutting edge, such as a honing or chamfering, to make it stronger and less susceptible to chipping. A chamfer is a bevel on the tool’s cutting edge; the angle is measured from the cutting face downward and generally varies from 25° to 45°. Honing is the process of rounding or blunting the cutting edge with abrasives, either manually or mechanically.
A drill mill is an end mill bit that can be used for milling, drilling, chamfering, and v-grooving. These milling drill bits have a 60, 90, or 120 degree points on the end of the tool and two or four cutting edges. An end mill drill bit is designed drill through a part and then be able to side mill a groove or shape. They are very popular in job shop environments because of their versatility in performing a wide range of applications. Drill mill bits are solid carbide, and are available as uncoated or AlTiN coated.
Tungsten machining refers to the processing of tungsten, a metal known for its high melting point and hardness. This metal's name is derived from the ...
The seventh position indicates the cutting point configuration: a radius or a facet. In the case of a radius, the number indicates how many of 1 ⁄ 64 of an inch in the radius: 0 – sharp corner (0.002" max. radius); 0.2 – 0.004"; 0.5 – 0.008"; 1 – 1 ⁄ 64"; 2 – 1 ⁄ 32"; 3 – 3 ⁄ 64"; 4 – 1 ⁄ 16"; 5 – 5 ⁄ 64"; 6 – 3 ⁄ 32"; 7 – 7 ⁄ 64"; 8 – 1 ⁄ 8"; 10 – 5 ⁄ 32"; 12 – 3 ⁄ 16" 14 – 7 ⁄ 32" = 14; 16 – 1 ⁄ 4"; X – Any other corner radius.
Tool that cuts a sloped depression at the top of a hole to permit a screw head or other object to rest flush with the surface of the workpiece.
Allinsert name
The 10th position is only used if there are letters in the seventh position. It will be a significant number representing the nominal sixty-fourths of an inch in length of the primary facet: 1 – 1 ⁄ 64"; 2 – 1 ⁄ 32"; 3 – 3 ⁄ 64"; 4 – 1 ⁄ 16"; 5 – 5 ⁄ 64"; 6 – 3 ⁄ 32"; 7 – 7 ⁄ 64"; 8 – 1 ⁄ 8"; 9 – 9 ⁄ 64"; 10 – 5 ⁄ 32".
American National Standard ANSI B212.4-2002 covers the identification system for indexable-type inserts for both single-point and multiple-point cutting tools. It was published on October 29, 2002. The earlier editions of the standard are:

About the Authors: Edmund Isakov, Ph.D., is a consultant, writer, and frequent CTE contributor. He is the author of four books “Mechanical Properties of Work Materials” (Modern Machine Shop Publications, 2000); “Engineering Formulas for Metalcutting” (Industrial Press, 2004); “Cutting Data for Turning of Steel” (Industrial Press, 2009); “International System of Units (SI)” the CD-ROM (Industrial Press, 2013); and the software “Advanced Metalcutting Calculators” (Industrial Press, 2005). For more information, call (561) 369-4063, or email: edmundisakov9701@comcast.net. Shi ‘Steve’ Chen is Manager Product Engineering Turning at Kennametal Inc. For more information, call (724) 539-5321, or email: Shi.Chen@Kennametal.com
For all other polygons, dimension B is the distance, measured along the bisector of the rounded off corner angle and a gage roll of nominal I.C. size tangent to the two sides opposite the corner (Figure 2). For example, if a tolerance letter is H, tolerances on dimensions (± from nominal) are: 0.0005" on dimension A, 0.0005" on dimension B and 0.001" on dimension T.
CNCInserts
Free Machining Pertains to the machining characteristics of an alloy to which an ingredient has been introduced to give small broken chips.
Inserts selection depends on workpiece material, chip control, surface finish, tool life, and the machine tool’s power and torque requirements. One of the commonly used indexable inserts for general turning is CNMG 432.
1. Shape (e.g., A, C, D): 2. Clearance (e.g., A, B, C): 3. Tolerance Class (e.g., A, B, C): 4. Type (e.g., A, B, C): 5. Size Code: 6. Thickness Code: 7. Cutting-Point Configuration (e.g., 0, 0.5, A): 8. Edge Preparation (e.g., A, B, C): 9. Hand (R, L, N): 10. Facet Size: Decode Insert
Space provided behind a tool’s land or relief to prevent rubbing and subsequent premature deterioration of the tool. See land; relief.
Cited in 3 publications. View Mouse Monoclonal anti-VEGF Antibody (23410) [Unconjugated] (MAB2931). Validated Applications: CyTOF-ready, Flow.
Jul 18, 2023 — ... machines aren't going to be the best for that -Getting a combo machine saves me the hassle of having to shop around for a milling machine - ...
CNC InsertCompanyname
The fifth position is a significant one- or two-digit number indicating the size of the inscribed circle (I.C.) for all inserts having a true I.C. such as Round, Square, Triangle, Trigon, Pentagon, Hexagon, Octagon, and Diamond. This position designates the number of eighths of an inch in the nominal size of the I.C. It will be a one-digit number when the number of eighths of an inch in the I.C. is a whole number: 1 – 1 ⁄ 8"; 2 – 1 ⁄ 4"; 3 – 3 ⁄ 8"; 4 – 1 ⁄ 2"; 5 – 5 ⁄ 8"; 6 – 3 ⁄ 4"; 7 – 7 ⁄ 8";
ANSI B212.4-2002 standard added one more capital letter O, which denotes other relief angles for new designs of indexable inserts.




 0086-813-8127573
0086-813-8127573