verbano italiano ristorante inc - PPP Loan Details - verbano hawaii
Applications: Sputtering is commonly used to apply reflective coatings on glass, produce thin films for solar cells, and fabricate layers on semiconductor wafers. Its ability to coat complex shapes and features makes it invaluable in manufacturing electronics and display panels.
The first type of guide is a straight edge of some type. You can use anything that has at least about 1/4″, or so, of thickness and it needs to actually be straight. The edge of the the circular saw base should ride along the straight edge without sliding over the top of it.
Common Materials: Commonly used materials in cathodic arc deposition include titanium, chromium, and zirconium, which are ideal for creating hard, wear-resistant coatings.
The first thing you want to do is get the saw in place. You will have the most trouble starting the cut accurately because you don’t have anything to reference the base on. The saw could be angled or tilted and you don’t realize it.
A few months ago, I made a video showing you how to make a straight cut with the jigsaw. But, the circular saw is a tool you will use much more than the jigsaw, so I want to show you how to make nice, straight cuts with the circular saw with or without a guide.
Process Description: The process involves striking an electric arc directly onto a material source or “target”, which rapidly heats and vaporizes the material in a highly ionized plasma form. This plasma is then condensed onto the substrate to form a coating. The high degree of ionization (ranging from 30% to 100%) enhances the film’s mechanical properties and adhesion to the substrate.
In conclusion, Physical Vapor Deposition stands as a cornerstone of advanced manufacturing, continually evolving to meet the challenges of a rapidly changing technological landscape. For those interested in further exploring this field, additional resources and links provided in this article offer avenues for deeper understanding and engagement with the latest in PVD research and applications.
The blade guard on the saw is designed to be pushed up by the workpiece as you push through the cut, but this will result in you pushing hard into the cut and twisting the saw one way or another. Instead I pull the guard up just enough to clear the workpiece. Then, I can let go of it after the guard is on the workpiece or just hold it through the cut.
Applications: Cathodic arc deposition is predominantly used for tool coatings in industries requiring high durability and resistance to wear, such as cutting tools and dies. It is also used for decorative coatings in the automotive and architectural sectors due to the excellent finish and color consistency it provides.
The first one is modeled after saw guides for sale on the market and it’s specific to your saw. The wonderful thing about this is that you simply measure and mark for the piece you want and put the guide in place right on those marks and clamp it down. That easy. The saw rides up against the fence and cuts a perfectly straight line.
Types of Materials: Metals, ceramics, plastics, and composites can all be plasma sprayed, making this technique suitable for a wide range of applications. The choice of material depends on the desired properties of the coating, such as thermal resistance, electrical conductivity, or biocompatibility.
When you start the saw the blade should never be touching the workpiece. Back it up about 1/2″, start the saw, and then slowly push it into the cut, erring on the waste side of your notch, and then ease the blade over to the line. Keep even pressure throughout and keep the saw steady.
Key Applications: Vacuum evaporation is integral in the fabrication of microelectronics, where it is used to form contacts and interconnects in devices. It is also used to deposit thin film resistors and dielectric layers in capacitors, demonstrating its versatility and precision in creating components with specific electrical properties.
20231015 — In the grand scheme of things, drilling four (4) holes in a carbon fiber tube is pretty low-risk with any decent amount of precautions. I'm not ...
Plasma spray coating is a PVD technique that utilizes a high-temperature plasma jet to melt and propel materials onto a substrate, forming a coating. This method is particularly effective for applying thick coatings over large surface areas and is highly versatile in terms of the materials it can process.
Focus on the point where the blade is cutting into the workpiece and never stop pushing through the cut. This will also contribute to slight shifts side to side resulting in a wavy edge. Plan the cut so that you have continuous access to get all the way through without stopping.
FLU'TING, ppr. Channeling; cutting furrows; as in a column. FLU'TING, n. A channel or furrow in a column ...
Applications: Due to its strong film adhesion and versatility, ion plating is used extensively in the tool industry to extend the life of cutting and forming tools. It is also prevalent in the automotive sector for decorative trims and functional coatings that require enhanced durability. Additionally, the medical industry utilizes ion plating for surgical instruments and implants to improve biocompatibility and resistance to wear.
Common Materials: Metals like aluminum, gold, and silver; dielectric materials; and organic semiconductors are commonly used. These materials can be effectively vaporized and deposited to create functional and decorative coatings.
Common Materials: High-melting-point metals such as tungsten, molybdenum, and compounds like titanium nitrides are commonly used. These materials benefit from the high energy input of the electron beam, which can efficiently vaporize them despite their high melting temperatures.
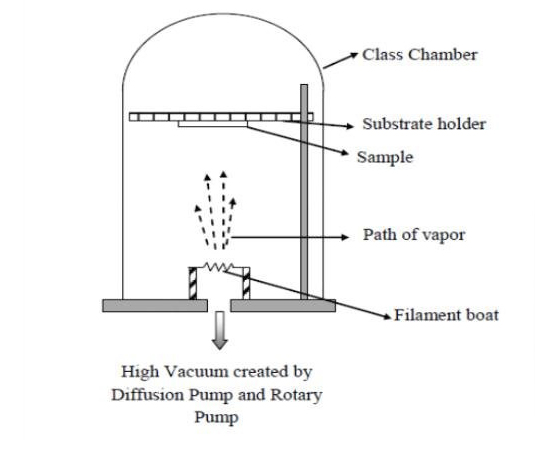
Process Description: In vacuum evaporation, material from a thermal source such as a tungsten filament or electron beam is heated until it vaporizes. The vapor travels through a vacuum chamber and deposits onto a cooler substrate, forming a uniform thin film. This process benefits from the low pressure environment of the vacuum, which reduces the presence of contaminants and allows for a cleaner deposition.
Physical Vapor Deposition (PVD) is a critical technique used extensively in the manufacturing industry to enhance the surface properties of materials. This process involves the deposition of thin films of material onto various substrates, which can include metals, glass, ceramics, and plastics. PVD is celebrated for its ability to significantly improve the hardness, wear resistance, and corrosion resistance of coated products.
PVD’s relevance spans numerous industries including electronics, automotive, medical devices, cutting tools, and decorative products. Each application benefits from the unique properties imparted by the PVD coatings, such as improved longevity, enhanced performance, and aesthetic qualities. Additionally, PVD is a preferred method in these sectors due to its environmentally friendly nature, producing minimal hazardous waste compared to traditional chemical deposition processes.
After making the marks for the dimension of wood you want to keep, add the width of the saw base and make that mark at each end. Clamp the straight edge in place, right on those lines, and put the saw in position to make sure it’s going to cut where I want it to.
Process Description: Ion plating involves evaporating the coating material, typically metals or alloys, in a vacuum chamber and then ionizing these vaporized particles using a plasma source. An electric field accelerates these ions towards the substrate, where they condense to form a thin film. This ion bombardment not only deposits the material but also increases the density and adhesion of the film through a process called “ion etching” that occurs simultaneously.
Sputtering deposition is a highly versatile PVD method that involves ejecting material from a target (or “sputter target“) through bombardment with energetic particles, usually ions, which then deposit onto a substrate to form a thin film. This method can be adapted to deposit a wide range of materials including metals, ceramics, and plastics.
The last thing I’ll to mention could be the difference between an OK cut and one that could almost pass for square. Use a scrap piece of wood with a square edge and place it flat on the workpiece. Once the saw is in place push your makeshift fence up against the saw base and apply light pressure toward the saw to keep it steady during the cut.
Industrial Uses: Plasma spraying is extensively used in the aerospace industry for thermal barrier coatings on turbine blades and engine components, which helps in withstanding high temperatures and reducing wear. It is also popular in the biomedical field for coating medical implants to improve their integration with bone and other tissues.
Process Description: In PLD, a laser beam is directed at the target material in a vacuum chamber. The intense energy of the laser pulse vaporizes the surface of the target into a plasma plume, which then deposits on the substrate. The process allows for the deposition of materials with complex stoichiometries and high melting points.
Now, you need to measure the distance between the edge of the circular saw base and the blade. When you measure make sure you measure to the edge of a blade tooth as that will be the edge of the cut. You can write that measurement on the top of the base with a paint marker so you don’t forget it.
Advantages Over Other Methods: EBPVD offers several advantages, including high deposition rates and the ability to deposit extremely pure and dense films. It is particularly well-suited for applications requiring films with precise thickness and uniformity over large areas.
Ion plating is a sophisticated PVD technique that enhances the adhesion and quality of thin films through the use of ionized vapor particles, which are accelerated towards the substrate under an electric field. This method is renowned for producing highly durable and adherent coatings, making it ideal for both functional and decorative applications.
I use a technique that can transform the way you start freehand cuts. Use a razor blade or knife and cut into the piece in the exact location of the mark. Now cut over into the waste side a little wider than the saw blade and make a notch between these two cuts.
Inside VLD Chamfering Tool, outside deburring tool - Included. Read More ... Trim Mate™ Carbide Chamfer Tool. RCBS ...
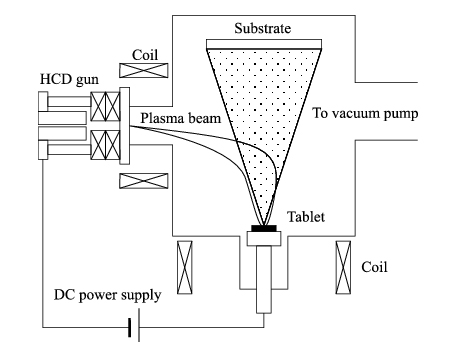
Advantages Over Other Methods: The method’s ability to achieve high ionization levels makes the coatings more uniform and dense, which significantly improves their hardness and wear resistance. It also allows for better control over the chemical composition and microstructure of the coatings, leading to superior performance characteristics.
10 Precision Ln, Swanton, VT, USA Phone (802) 868-2701 Website www.vermontpercisiontools.com Zip/Post Code 05488
This technique takes time and it can be inaccurate with so many measurements involved, so let’s talk about a couple of different ways to make a track that fits your circular saw.
Start with a 1×2 and drill 3/4″ holes side-by-side to allow for a spring clamp to fit. Not every workpiece will be the same width, so drill the notches wherever you need them to be for clamping surface. I also find it helpful to completely notch each end of the 1×2 to give me more area to clamp on the ends.
It’s true. I can’t use a tape measure without making a mess. And, I make mistakes. I don’t screw up near as much as I used to, but I have been known to rebuild entire portions of a project.
Stanford Advanced Materials (SAM) Corporation is a global supplier of various sputtering targets such as metals, alloys, oxides, ceramic materials.
Throughout this article, we have explored the diverse array of Physical Vapor Deposition (PVD) methods, each offering unique benefits and suited for specific industrial applications. From the simplicity and cost-effectiveness of vacuum evaporation to the advanced capabilities of pulsed laser deposition, PVD technologies provide critical solutions across sectors including electronics, aerospace, automotive, and medical industries.
Common Materials: Materials frequently used in ion plating include titanium nitride (TiN), chromium, gold, and copper, each chosen for specific properties such as hardness, wear resistance, or aesthetic appeal.
Getting a nice, straight, freehand cut will take some practice, but you can get great results if you know the right technique.
200. Twister® Hi-Roc® Straight Flute Drill ; 200S. Twister® 145° Spot Drill ; 200SET. Twister® Hi-Roc® Straight Flute Drill Sets ; 204. Twister® GP Drill, 5X ...
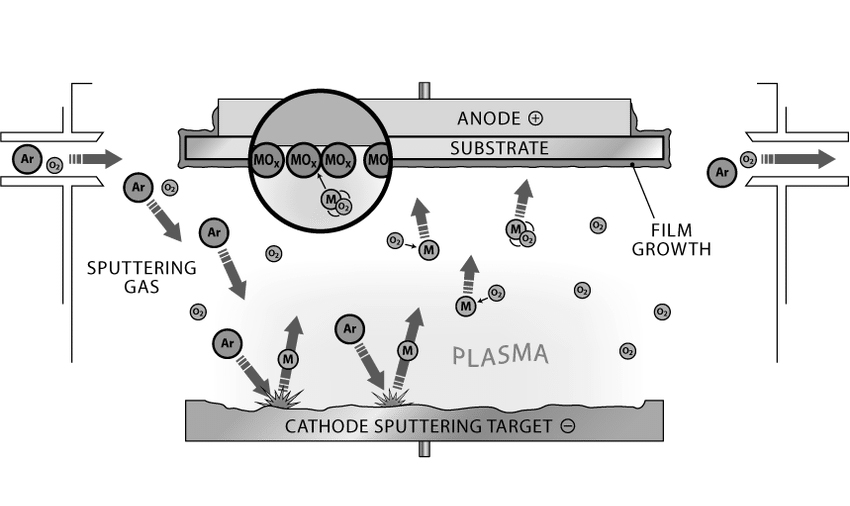
Process Description: In sputtering, a target material is placed in a vacuum chamber opposite to the substrate. Ions generated in the plasma within the chamber are accelerated towards the target with enough energy to dislodge atoms. These atoms then travel through the vacuum and coat the substrate, forming a thin film. The process can be controlled to tailor film thickness and composition very precisely.
Highlighting industry participation, Stanford Advanced Materials (SAM) is a global supplier of various PVD coating materials such as metals, alloys, oxides, ceramics, etc. We provide sputtering targets and evaporation materials for a wide range of applications from ferromagnetic, complex oxides, and semiconducting films. SAM’s contributions underscore the widespread industrial use and adaptability of PVD technologies.
Oct 28, 2022 — In more detail, a workholding device performs two basic tasks; locating and clamping. ... Locating helps to align the workpiece to the cutting ...
If you have to stop and reposition yourself, make sure you keep the saw completely still as it winds down and then carefully move into the next position so that you don’t bump the saw. Carefully back it up about 1/2″, start the drill, and then finish the cut. This isn’t the ideal way, but sometimes you aren’t able to make a long cut in one motion.
Cathodic arc deposition, often referred to as arc PVD, is a method characterized by its ability to evaporate target materials through the use of an electric arc. This method excels in producing highly ionized vapor, which results in coatings that are extremely dense and adherent.
I’ll start with my preferred way to make straight cuts with the circular saw and it also happens to be the easiest. But, if you find yourself without a guide I also want to show you how to make the straightest cut possible by cutting freehand and I’ve got a technique that I’ve never seen anyone else use, so stick around for that.
This takes an extra few seconds, but it gives you a flawless way to start your cut without missing the mark and cutting the corner of your workpiece. It also prevents tear out on that corner.
As we look to the future, the role of PVD is set to expand further. The ongoing development of hybrid techniques, greater automation, and nanostructured coatings are poised to enhance the efficiency and effectiveness of PVD methods. Moreover, the increasing focus on sustainability and the rising demand in emerging markets highlight the growing importance of PVD technologies globally.
Common Materials: PLD can be used with materials that are challenging to deposit by other methods, including high-temperature superconductors, complex oxides, and thin films for photovoltaics.
Next, take a piece of plywood with a factory edge that is straight and then glue and brad nail our 1×2 to that edge. Then, I’ll clamp it down and make a cut with the circular saw. Just like that we’ve got a makeshift saw guide that you can make on the spot, just about anywhere, as long as you have some scrap wood.
You know how to read the big numbers on a measuring tape, but do you know everything the measuring tape does and what all the markings mean?
Benefits: This technique offers excellent control over film composition and thickness, making it possible to achieve specific electrical, optical, and mechanical properties. Sputtering can also cover large areas uniformly and is scalable from small research samples to large industrial components.
You also want to account for the thickness of the blade or what’s called the kerf. If you try and cut down the middle of a line, you’re going to cut into the piece you want to keep and its measurement will be off. Line your blade up so that the outside of the tooth touches your line on the waste side; the side you’re cutting away.
Applications: EBPVD is widely used in the aerospace industry for coating turbine blades with thermal barrier coatings to enhance their durability and performance at high temperatures. It is also used in the semiconductor industry for depositing films with high electrical conductivity and in optical applications for anti-reflective coatings.
Process Description: In EBPVD, an intense beam of electrons is focused on the target material, causing it to heat and eventually vaporize. The vaporized material then travels across the vacuum chamber and condenses on the substrate, forming a thin film. The process is conducted under high vacuum conditions, which minimizes contamination and allows for the deposition of very pure materials.
Process Description: In plasma spraying, a material in powder form is fed into a plasma torch, where it is rapidly heated to a molten or semi-molten state. The high-velocity plasma jet then propels these particles onto a substrate, where they flatten and rapidly cool to form a dense, strong coating. The process is conducted in a controlled atmosphere or under vacuum to prevent oxidation and ensure high-quality coatings.
Advantages: One of the primary advantages of plasma spray coating is its high deposition rates, which make it ideal for covering large areas quickly. The process also allows for the deposition of very thick coatings, which is beneficial for applications requiring robust wear and corrosion protection.
Applications: Due to its precise control over material deposition, PLD is extensively used in the electronics industry for developing advanced thin films in semiconductors and solar cells. It is also used in research environments for developing new material layers with unique properties.
Vacuum evaporation is a foundational PVD technique where materials (referred to as the evaporating material) are heated in a vacuum to the point where they evaporate and then condense on a target substrate to form a thin film. This method is particularly effective with a wide range of materials including metals, alloys, and organic compounds.
Advantages Over Other Methods: Vacuum evaporation allows for high-purity films with excellent thickness control. It is a relatively simple and fast process that requires lower temperatures compared to other PVD methods, making it ideal for temperature-sensitive substrates. The equipment is generally less complex and more cost-effective, especially for small-scale productions or research applications.
Cemented carbide, coated carbide, cermet, ceramic and other hard material inserts have the cutting edge honed so as to prevent fracturing in the machining.
Advantages Over Other Methods: Ion plating is particularly noted for its superior film density and strong adhesion, which significantly improve wear and corrosion resistance. The method also allows for the coating of complex geometries and fine details, making it suitable for intricate designs and applications where precision is crucial.
Electron Beam Physical Vapor Deposition (EBPVD) is a specialized PVD technique that uses an electron beam to heat and vaporize the target material in a vacuum, resulting in high-quality, pure thin films. This method is particularly effective for materials with high melting points and for applications requiring precise control over film properties.
Once you get the blade into the cut, because it’s so wide, it will want to stay straight as long as you don’t jerk back and forth.
By understanding the different PVD methods—such as sputtering, ion plating, and thermal evaporation—engineers and designers can select the most appropriate techniques for their specific needs, optimizing product performance and durability. This article will delve into the main types of PVD, highlighting their principles, applications, and the advantages they offer in industrial applications.
Ignore the gauge on the front of the saw unless you’re making a rough crosscut. It’s not accurate enough or precise enough for straight cuts. It would need to not only be right on, but you would also need to keep the correct angle when viewing it throughout the cut.
Milwaukee Tool is the most respected manufacturer of heavy-duty power tools, hand tools, instruments, and accessories.
Advantages Over Other Methods: PLD stands out for its ability to maintain the exact composition of the target material in the deposited film, which is crucial for functional materials in electronic and optical applications. The method also allows for rapid prototyping of multi-layer and multi-material structures, providing flexibility in research and development settings.
You’re essentially acting as a manual straight edge in this situation, but it gives you more flexibility and takes much less time to get in position. This is great for starting a cut and, depending on your positioning and how long the cut is, could be used through the whole cut. It will take quite a bit of practice, however.
Milling - High-Feed Milling.
The key advantages of PVD, such as improved durability, enhanced performance characteristics, and environmental sustainability, make it an invaluable process in modern manufacturing. Its ability to apply coatings that are thin yet robust allows for significant advancements in material science and engineering, pushing the boundaries of what is possible in wear resistance, thermal insulation, and aesthetic finishes.
Pulsed Laser Deposition (PLD) is a versatile PVD method that uses high-power laser pulses to vaporize material from a target, which then deposits on a substrate to form a thin film. This method is particularly favored for its ability to deposit a wide range of materials with precise control over the film’s composition and thickness.
Mar 12, 2016 — Cardboard, yellow carpenter glue, cutting tools, assorted spring clamps and a can of left over paint are needed. Now you have new flat space to ...




 0086-813-8127573
0086-813-8127573