What Happens To Your Body When You Cut Yourself? - cutting deeper
This video uses insert nuts with an outside diameter of around 8.5mm, smaller than those I am using in the video. The first hole should be 9mm in diameter for something like this. You can use softwoods as thin as 8mm if you need a tight-fitting. The manufacturer should always determine the pilot hole size. For drilling depths, drills are equipped with depth-stops. This is especially useful if you need to drill many holes at once.
Taps and dies are tools used to create screw threads, which is called threading. Many are cutting tools; others are forming tools. A tap is used to cut or form the female portion of the mating pair (e.g. a nut). A die is used to cut or form the male portion of the mating pair (e.g. a bolt). The process of cutting or forming threads using a tap is called tapping, whereas the process using a die is called threading.
With soft or average hardness materials, such as plastic, aluminum or mild steel, common practice is to use an intermediate (plug) tap to cut the threads. If the threads must extend to the bottom of a blind hole, the machinist uses an intermediate (plug) tap to cut threads until the point of the tap reaches bottom, and then switches to a bottoming tap to finish. The machinist must frequently eject chips to avoid jamming or breaking the tap. With hard materials, the machinist may start with a taper tap, whose less severe diameter transition reduces the torque required to cut threads. To threads to the bottom of a blind hole, the machinist follows the taper tap with an intermediate (plug) tap, and then a bottoming tap to finish.
Considering stopping your waste management service? Canceling with us is straightforward and hassle-free. We prioritize our customer's needs and ensure a ...
A tap cuts or forms a thread on the inside surface of a hole, creating a female surface that functions like a nut. The three taps in the image illustrate the basic types commonly used by most machinists:
1 shipments of Titan Manufacturing & Distributing Dba: Titan Brands Inc. with information about suppliers, customers, products purchased and sold, ...
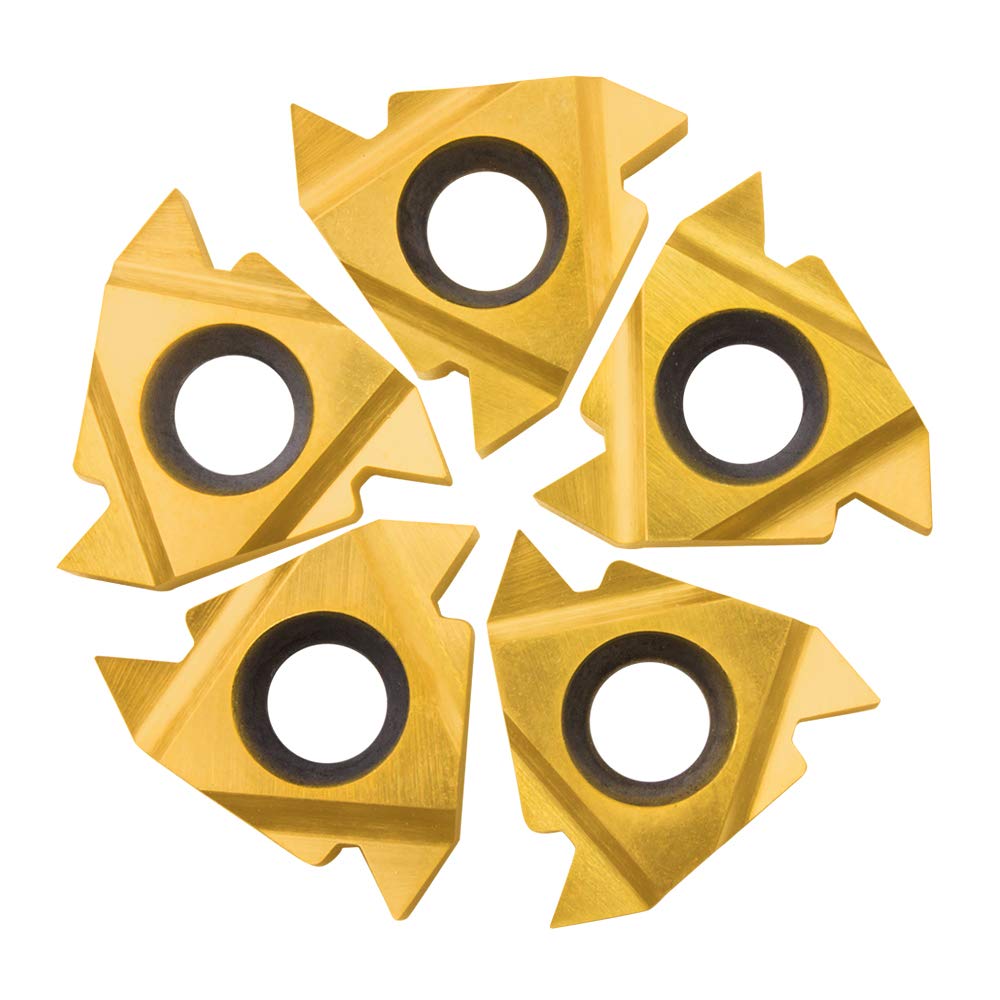

Unlike full profile inserts, multi-point inserts have more than one insert point (NT>1), similar to full profile inserts. If an insert consists of two points, the productivity is doubled. If an insert consists of three points, the productivity is tripled. As a result, the tool’s life is extended, productivity is increased, and costs are reduced since fewer passes are required. Because the cutting edge has a longer contact length, stable conditions are necessary due to the increased cutting forces. Besides being able to clear all the teeth, it also needs to have a sufficient gap behind the last thread for the insert to insert fully.
2 days ago — Discover a wide range of wholesale wood saw machines, with a choice of harvey woodworking machines options and alternatives, ...
While modern nuts and bolts are routinely made of metal, this was not the case in earlier ages, when woodworking tools were employed to fashion very large wooden bolts and nuts for use in winches, windmills, watermills, and flour mills of the Middle Ages; the ease of cutting and replacing wooden parts was balanced by the need to resist large amounts of torque, and bear up against ever heavier loads of weight. As the loads grew even heavier, bigger and stronger bolts were needed to resist breakage. Some nuts and bolts were measured by the foot or yard. This development eventually led to a complete replacement of wood parts with metal parts of an identical measure. When a wooden part broke, it usually snapped, ripped, or tore. With the splinters having been sanded off, the remaining parts were reassembled, encased in a makeshift mold of clay, and molten metal poured into the mold, so that an identical replacement could be made on the spot.
Die nuts, also known as rethreading dies, are dies made for cleaning up damaged threads,[9] have no split for resizing and are made from a hexagonal bar so that a wrench may be used to turn them. The process of repairing damaged threads is referred to as "chasing." Rethreading dies cannot be used to cut new threads as they lack chip forming teeth.[10] However the external profile of a die does not strictly map to its function. Manufacturers of dies have produced models in a hex form which are intended for the creation of new threads.[11] These appear identical to solid dies in all aspects besides the external shape. Hexagonal thread cutting dies are used with a die stock with hexagonal holding features.
The biggest problem with simple hand-tapping is accurately aligning the tap with the hole so that they are coaxial—in other words, going in straight instead of on an angle. The operator must get this alignment close to ideal to produce good threads and not break the tap. The deeper the thread depth, the more pronounced the effect of the angular error. With a depth of 1 or 2 diameters, it matters little. With depths beyond 2 diameters, the error becomes too pronounced to ignore. Another fact about alignment is that the first thread cut or two establishes the direction that the rest of the threads will follow. You can't correct the angle after the first thread or two.
Thread tap canadian tire
A die cuts an external thread on cylindrical material, such as a rod, which creates a male threaded piece that functions like a bolt. Dies are generally made in two styles: solid and adjustable. An adjustable die may be adjusted either by an integrated screw or by a set of screws set in to the die holder (termed a "die stock"). Integral adjusting screws may be arranged to work axially, where the movement of the adjusting screw into a threaded hole in the die forces the slit section of the die open, or tangentially where a screw threaded in to one side of the slit bears against the opposite side of the slit. Dies without integrated screws are adjusted inside the die stock by radially-arranged screws. Two screws in the stock bear in to indentations on either side of the slit, tending to squeeze the slit closed, whilst a third screw with a tapered tip screws in to the slit forcing it open. Working these three screws against each other adjusts the die.
Flat geometry provides overall functionality; it can be used to work with a wide range of materials. A round cutting edge adds strength to the cutting edge.
There are several threaded inserts, each featuring a unique design, but they are all designed with female threading to support fasteners with male threading. A spiral design is a characteristic of circular threaded inserts, for example, and they are usually made of steel or bronze. The metal is coiled up in the appropriate size and shape to support the threaded fastener.
In softer woods and plywood, thread-in inserts are a good choice because their coarse outside threads ease the cutting process. You can then screw the insert into place by drilling a hole the right size for its body. White oak and maple are hardwoods, so drilling a hole slightly larger than the outside thread diameter and epoxying in the insert is recommended. If the insert is close to the edge of the part and screwing it in might split it, make sure to drill a hole slightly larger than the outside thread diameter. It would be best if you covered the end of the insert with epoxy to protect the threads inside.
Threading bitfor steel
Solid dies cut a nominal thread form and depth, whose accuracy is subject to the precision the die was made with, and the effects of wear. Adjustable dies can be slightly compressed or expanded to provide some compensation for wear, or to achieve different classes of thread fit (class A, B and more rarely, C). Adjustable taps also exist but are not common. These have a tip that is split through the flutes and an axial screw which forces the cutting edges slightly apart.
There is no V-profile insert attached to the thread crests. Using the same diameter screw and nut is imperative before threading any screw or nut. This can be accomplished by turning the outer diameter of the screw to the same diameter as the inner diameter of the nut. Furthermore, it is possible to use the same insert for multiple pitches as long as the thread profile angle (60° or 55°) and radius are the same. As a result, the nose radius of the insert is smaller to cover the range of pitches, therefore reducing the tool life and creating Burrs on the tool.
Threading bithome depot
Metalworking taps and dies were often made by their users during the 18th and 19th centuries (especially if the user was skilled in tool making), using such tools as lathes and files for the shaping, and the smithy for hardening and tempering. Thus builders of, for example, locomotives, firearms, or textile machinery were likely to make their own taps and dies. During the 19th century the machining industries evolved greatly, and the practice of buying taps and dies from suppliers specializing in them gradually supplanted most such in-house work. Joseph Clement was one such early vendor of taps and dies, starting in 1828.[1] With the introduction of more advanced milling practice in the 1860s and 1870s, tasks such as cutting a tap's flutes with a hand file became a thing of the past. In the early 20th century, thread-grinding practice went through significant evolution, further advancing the state of the art (and applied science) of cutting screw threads, including those of taps and dies.

Inserts with threads on both the outside and the inside of the carbide threading insert are called externally threaded inserts. Generally, the inserts are threaded into a pre-tapped hole, or, in the case of some carbide threading inserts, the inserts can tap their own thread into a drilled or molded hole. Various types of anchorages are then used, including nylon locking elements, as well as other means.
One of the leading K-12 education companies, Solution Tree offers professional development, online courses, and education books for teachers.
Both tools can be used to clean up a thread, which is called chasing. However, using an ordinary tap or die to clean threads generally removes some material, which results in looser, weaker threads. Because of this, machinists generally clean threads with special taps and dies—called chasers—made for that purpose. Chasers are made of softer materials and don't cut new threads. However they still fit tighter than actual fasteners, and are fluted like regular taps and dies so debris can escape. Car mechanics, for example, use chasers on spark plug threads, to remove corrosion and carbon build-up.
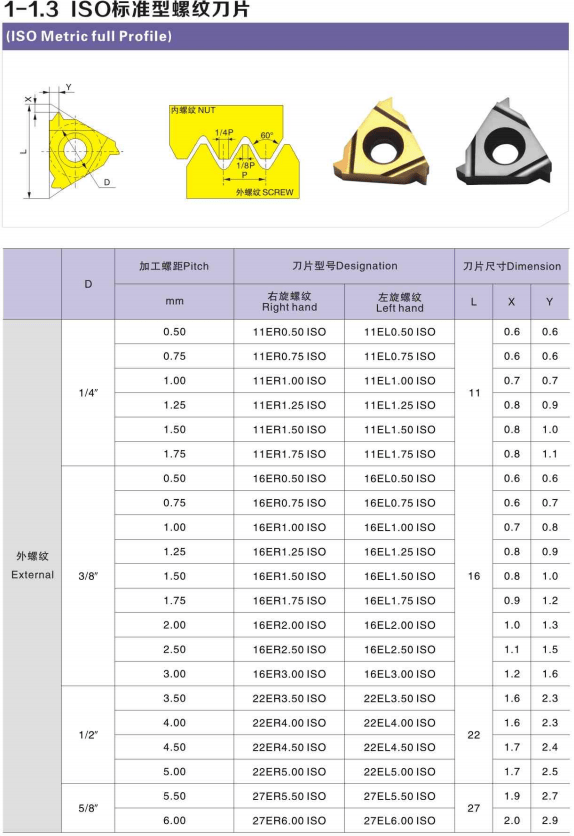
Some of the most common or standard angles for turning inserts include 55, 60, and 90. There could be some variation in these, but they are most frequently used. In addition, some common models of threading inserts include 16ER AG55, 16IR AG55, GC1125, GC1135, GC1025, 16er ag60 insert, 11er a60, 11ir a60 inserts, 16Ir ag60 insert and CB7015.
Hardwoods, softwoods, and plywood all work well with press-in inserts because of their barbed exteriors. The well should be drilled so that the body of the insert will fit inside the hole. You can clamp the insert into place or tap it with a hammer and a block of wood. The drilling hole needs to be deep enough so that the epoxy engages only the tips of the insert barbs. This is especially important for applications where the clamping action tends to pull the inserts out of the wood, such as knobs on a drill-press fence extension.
DrillBit
Apr 24, 2021 — It's OK with a 1/16th" bit or the 1mm & 2mm. The smaller bits don't complete the hole before the chuck hits the wood. I have tried to find a ...
In just the same way that replacing threaded inserts is a straightforward process, removing them is equally straightforward. If you wish to see how to do this, please see below.
Nov 2, 2011 — It uses a dedicated router to punch butterfly-shaped dovetail keyway openings; then a matching polymer dovetail key is inserted to created a strong joint, ...
Once you know all the necessary details regarding threading inserts, you will now be able to use threading inserts in CNC threading more efficiently. It is important to remember all the steps mentioned above to give the best shot of Inserting the threads.
Whatever the thread pitch, profile or material, we can provide you with the solutions you need. The threading tools and inserts we offer help you produce quality threads for interiors and exteriors.
When threading is necessary for your application, precise and consistent threading is paramount. Huana Tools offers an exclusive selection of high-performance threading inserts that will ensure 100% accurate threading every time. Huana Tools threading inserts are made of tungsten carbide for both standard and custom threading applications. Our threading experts are also ready to help you improve the threading of your products.
Additionally, some inserts feature a nut wrapped around female threading that belongs to this kind of product; when a fastener is driven into the cage nuts, the tops of the nuts feature “wings” that dig into the object when the fasteners are driven into them.
These are suitable for sticky, work-hardening materials such as low-carbon steel, stainless steel, non-ferrous materials, and superalloys, to name a few. Their cutting edge is sharp, resulting in a high level of surface finish and low cutting forces.
Among threading inserts, some have a single cutting surface, while others have multiple surfaces which can be used to continue threading when a tooth wears out. Several dimensions determine the number of sides and angles of the threading insert.
To help with this alignment task, several kinds of jigs and fixtures can be used to provide the correct geometry (i.e., accurate coaxiality with the hole) without having to use freehand skill to approximate it:
Thread Maker Tool
Full profile inserts are the most popular inserts. With this tool, the crest of the thread can be cut completely, as well as the thread’s profile.
where T D {\displaystyle TD} is the tap drill size, M D {\displaystyle MD} is the major diameter of the tap (e.g., 3⁄8 in for a 3⁄8-16 tap), and 1 / N {\displaystyle 1/N} is the thread pitch (1⁄16 inch in the case of a 3⁄8-16 tap). For a 3⁄8-16 tap, the above formula would produce 5⁄16, which is the correct tap drill diameter. The above formula ultimately results in an approximate 75% thread.
Whether manual or automatic, the processing of tapping begins with forming (usually by drilling) and slightly countersinking a hole to a diameter somewhat smaller than the tap's major diameter. The correct hole diameter is listed on a drill and tap size chart, a standard reference in many machine shops. The proper diameter for the drill is called the tap drill size. Without a tap drill chart, you can compute the correct tap drill diameter with:
Tapping may either be achieved by a hand tapping by using a set of taps (first tap, second tap & final (finish) tap) or using a machine to do the tapping, such as a lathe, radial drilling machine, bench type drill machine, pillar type drill machine, vertical milling machines, HMCs, VMCs. Machine tapping is faster, and generally more accurate because human error is eliminated. Final tapping is achieved with single tap.
During the 19th and 20th centuries, thread standardization was evolving simultaneously with the techniques of thread generation, including taps and dies.
The use of a suitable lubricant is essential with most tapping and threading operations. Recommended lubricants for some common materials are as follows:
TapBit
Choose from our selection of carbide ball end mills, including over 950 products in a wide range of styles and sizes. In stock and ready to ship.
The work piece (blank) to be threaded, which is usually slightly smaller in diameter than the die's major diameter, is given a slight taper (chamfer) at the end that is to be threaded. This chamfer helps center the die on the blank and reduces the force required to start the thread cutting.[8] Once the die has started, it self-feeds. Periodic reversal of the die is often required to break the chip and prevent crowding.
Although in general machine tapping is more accurate, tapping operations have traditionally been very tricky to execute due to frequent tap breakage and inconsistent quality of tapping.
This type of geometry is used for materials that are long in the chips. The product can also be used as a byproduct to strengthen stainless steel, alloyed steel, and non-ferrous metals. A machining geometry optimized for chip-forming to maximize the efficiency and precision of the process. The use of this geometry is not recommended for radial infeed operations.
To overcome these problems, special tool holders are required to minimize the chances of tap breakage during tapping. These are usually classified as conventional tool holders and CNC tool holders.
G02 and G03 Circular Motion are modes for the CNC Machine. G02 ... Circular Interpolation Motion CW3 of 4 draggables. X0, Y24 of 4 draggables ...
The largest tap and die company to exist in the United States was Greenfield Tap & Die (GTD) of Greenfield, Massachusetts. GTD was so vital to the Allied war effort from 1940–1945 that anti-aircraft guns were placed around its campus in anticipation of possible Axis air attack[citation needed]. The GTD brand is now a part of Widia Products Group.
The term internal thread refers to a thread found on nuts or tapped holes, while the term external thread refers to one found on bolts, studs, or screws. The axial thread form is the name given to orientated threads that are oriented axially. There are three parts to a thread profile. These are the crest, the root, and the flanks.
Double-lead taps and insert taps need different speeds and feeds, and different starting hole diameters than other taps.
Threading bitfor metal
It can be challenging to fit the screw into the hole. Some screws include a hex socket built into the head. You can use flat blade screwdrivers with the slot. You can prevent the machine screw from moving by using the one you plan to use in the final fitting and attaching a locking nut. Once the insert nut is fully driven home, it can be finished with an impact driver. You can remove the machine screw by removing the nut with a small spanner. In addition to threaded inserts with heads.
where T D {\displaystyle TD} is the tap drill size, M D {\displaystyle MD} is the major diameter of the tap (e.g., 10 mm for a M10×1.5 tap), and pitch is the pitch of the thread (1.5 mm in the case of a standard M10 tap) and so the correct drill size is 8.5 mm. This works for both fine and coarse pitches, and also produces an approximate 75% thread.
In terms of threading, externally threaded inserts are those with threads on the exterior, as their name implies. The threads have been internalized, but the external threads are also present. In this regard, I would like to know what this external threading is for. It is much easier to drive them into predrilled holes if they feature external threading since they can easily be driven into them.
Tapping case studies with typical examples of tapping operations in various environments are shown on source machinetoolaid.com [1]
Thread tapping tool
For a stronger thread, it ensures the bottom, top, and depth of the thread are all in the right places. Also, regardless of the thread profile, this will help eliminate any deburring. Due to the larger nose radius, fewer passes are needed compared to a V-profile insert. In addition, it allows you to thread more efficiently. For this reason, it is necessary to have a separate insert for each pitch and profile.
A comprehensive reference for US tap and drill bit sizes can be found in the chart provided by Albany County Fasteners. This chart includes detailed specifications for machine screw size, threads per inch, major and minor diameters, and appropriate drill sizes for different materials.
Oct 1, 2014 — A two-digit number designates the sizes of these inserts. ... Replaceable tool that clamps into a tool body, drill, mill or other cutter body ...
The GlobalSpec SpecSearch database provides information about many different types of threading inserts. Most are described according to shape.
The inserts have an external thread that resembles a coarse wood screw thread and an inside thread that resembles a fine machine screw thread. You can effectively use machine screws in wood with them, as they are useful for any item that will require the screw to be removed later. The threads of conventional wood screws are damaged when you remove them from the wood. If the line completely disappears from a wood screw hole, the screw will no longer be able to be fitted into that hole. Threaded inserts allow threaded machine screws, which is a more convenient method to accomplish this task.
Inserts with threads are an excellent choice for reinforcing threads on bolts and studs when they are frequently installed and removed. Choosing the right threaded inserts when working with weaker materials can provide a strong, durable solution.
For thread turning, one of the most important considerations in choosing the correct insert geometry. Geometry affects many aspects of the tool life, such as chip control, insert wear, thread quality, and tool life in general.
Kadimi manufactures Special Form Flat Thread Rolling dies for specific needs and supplying in India and worldwide to automotive industrial applications in ...




 0086-813-8127573
0086-813-8127573