Working Principle of Milling Machine - cutting milling machine
These design rules were developed for structures subject to fatigue such as bridges and crane supporting structures, and it is acknowledged that their use for buildings where fatigue plays a minor role is extremely safe-sided.

BS EN 10025[1] sets mandatory limits for CEV for all structural steel products covered, and it is a simple task for those controlling welding to ensure that welding procedure specifications used are qualified for the appropriate steel grade, and CEV.
The term “quasi-static” would cover such structures – in reality that there may be some limited cycling of load, but that would not normally be considered – the design approach is to consider all loads as static. The key to the new approach is the formula to express the crack growth under 20,000 cycles. Experts at the University of Aachen (who were involved with the development of the Eurocode) provided this all-important expression.
Minimizing the sulphur level can enhance ductility , and toughness can be improved by the addition of nickel. The chemical composition for each steel specification is therefore carefully balanced and tested during its production to ensure that the appropriate properties are achieved.

Jul 3, 2019 — As you already mentioned, the solid carbide drill bits will easily drill through hardened steel, but they are brittle. You can anneal the ...
Freemachining steel
The various product standards specify minimum values of impact energy for different sub-grades of each strength grade. For non-alloy structural steels the main designations of the subgrades are JR, J0, J2 and K2. For fine grain steels and quenched and tempered steels (which are generally tougher, with higher impact energy) different designations are used. A summary of the toughness designations is given in the table below.
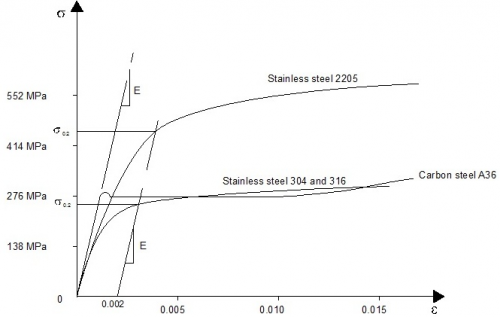
Grades of stainless steel are designated by a numerical 'steel number' (such as 1.4401 for a typical austenitic steel) rather than the 'S' designation system for carbon steels. The stress-strain relationship does not have the clear distinction of a yield point and stainless steel 'yield' strengths for stainless steel are generally quoted in terms of a proof strength defined for a particular offset permanent strain (conventionally the 0.2% strain).
Yield strength is the most common property that the designer will need as it is the basis used for most of the rules given in design codes . In European Standards for structural carbon steels (including weathering steel ), the primary designation relates to the yield strength, e.g. S355 steel is a structural steel with a specified minimum yield strength of 355 N/mm².
Machiningmaterials chart
The process for Quenched and Tempered steel starts with a normalized material at 900°C. It is rapidly cooled or 'quenched' to produce steel with high strength and hardness, but low toughness. The toughness is restored by reheating it to 600°C, maintaining the temperature for a specific time, and then allowing it to cool naturally (Tempering). Quenched and tempered steels have a 'Q' designation.
Order Fullerton Tool 4-Flute - 30° Helix - 3200 GP End Mills, TIALN, RH Spiral, Ball, Standard, 1/16, 30719 at Zoro.com. Great prices & free shipping on ...
Machining steelgrades
The susceptibility to embrittlement also depends on the alloying elements principally, but not exclusively, the carbon content. This susceptibility can be expressed as the 'Carbon Equivalent Value' (CEV), and the various product standards for carbon steels standard give expressions for determining this value.
This is the best bolt-on performance improvement available for any L76/98 including LS2/LS3. The package delivers exhilarating yet totally affordable supercharger performance, representing exceptional value and reliability. The increase in usable torque is outstanding, while maintaining (and consistently improving) fuel economy.
Fuel Economy remains the same (if not better) on average due to the increased torque available from the engine, with returns of under 12 liters per 100km easily achievable. More power is developed down lower in the engine rev range meaning the engine does not have to rev as hard to produce the same level of power. This is most noticeable when towing up a hill ‘ the gearbox does not have to downshift as often as more torque is available through the mid range.
Stainless steel is a highly corrosion-resistant material that can be used structurally, particularly where a high-quality surface finish is required. Suitable grades for exposure in typical environments are given below.
The most common means of providing corrosion protection to construction steel is by painting or galvanizing. The type and degree of coating protection required depends on the degree of exposure, location, design life, etc. In many cases, under internal dry situations no corrosion protection coatings are required other than appropriate fire protection. Detailed information on the corrosion protection of structural steel is available.
Apr 20, 2023 — The end mills specialize in deep axial trochoidal and high-speed machining applications and are offered in various lengths of cut.
Most commonmachining steel
BS EN 1993-1-3[5] tabulates values of basic yield strength fyb and ultimate tensile strength fu that are to be used as characteristic values in design.
Beststeelformachiningand welding
The effect of heat treatment is best explained by reference to the various production process routes that can be used in steel manufacturing, the principal ones being:
Mechanical working takes place as the steel is being rolled or formed. The more steel is rolled, the stronger it becomes. This effect is apparent in the material standards, which tend to specify reducing levels of yield strength with increasing material thickness.
The alloying elements also produce a different response when the material is subjected to heat treatments involving cooling at a prescribed rate from a particular peak temperature. The manufacturing process may involve combinations of heat treatment and mechanical working that are of critical importance to the performance of the steel.
The substantial increase in Power and Torque is due to the positive displacement Magnuson Mp90 supercharger that gives you Maximum boost from off idle all the way to the redline. This makes it perfect for towing or four wheel driving when you need low down torque. With just 5.5psi of pressure, power gains of over 45% can be safely achieved on an internally stock engine. (BOOST UPGRADE AVAILABLE).
Ductility is a measure of the degree to which a material can strain or elongate between the onset of yield and eventual fracture under tensile loading as demonstrated in the figure below. The designer relies on ductility for a number of aspects of design, including redistribution of stress at the ultimate limit state, bolt group design, reduced risk of fatigue crack propagation and in the fabrication processes of welding, bending and straightening. The various standards for the grades of steel in the above table insist on a minimum value for ductility so the design assumptions are valid and if these are specified correctly the designer can be assured of their adequate performance.
After having designed the world first Supercharger kit back in 2005 when the Hilux was first released, Bullet Cars has recently introduced the new intercooled Mp90 Supercharger kit as an aftermarket option. The Magnuson Intercooled Supercharger is the basis of this new kit with Bullet modifications to simplify installation to any 4.0 litre V6 Hilux.
The main and basic difference between up milling and down milling is the direction of rotation of cutter to the feed. The milling operation is used to facing of ...
Milling Feed. The feed (milling machine feed) can be defined as the distance in inches per minute that the work moves into the cutter. On the ...
SCI publication P419 presents modified steel thickness limits which may be used in buildings where fatigue is not a design consideration. These new limits have been derived using exactly the same approach behind the Eurocode design rules, but crucially reduce the crack growth due to fatigue. The word “reduce” is used, since to assume no growth at all would be to eliminate the effect of fatigue altogether. Some fatigue (20,000 cycles) is allowed for based on indicative guidance from a DIN Standard.
Steel machining propertieschart
Form B Center Drills have both 60° and 120° tips.ISO, NFE 66051-B, DIN 333-B, JIS-1.
Best mildsteelformachining
A further important property is that of corrosion prevention. Although special corrosion resistant steels are available these are not normally used in building construction. The exception to this is weathering steel .
Stainless steels are generally much tougher than carbon steels; minimum values are specified in BS EN 10088-4[15]. BS EN 1993-1-4[6] states that austenitic and duplex steels are adequately tough and not susceptible to brittle fracture for service temperatures down to -40°C.
Get the 904862 Vacuum Pump Premium Durable High Performance online at Jumia Kenya and other Generic Headlight Wipers & Accessories on Jumia at the best ...
There is a wide range of steel grades for strip steels suitable for cold forming. Minimum values of yield strength and tensile strength are specified in the relevant product standard BS EN 10346[4].
The stress-strain behaviour of stainless steels differs from that of carbon steels in a number of respects. The most important difference is in the shape of the stress-strain curve. While carbon steel typically exhibits linear elastic behaviour up to the yield stress and a plateau before strain hardening is encountered, stainless steel has a more rounded response with no well-defined yield stress. Therefore, stainless steel 'yield' strengths are generally defined for a particular offset permanent strain (conventionally the 0.2% strain), as indicated in the figure on the right which shows typical experimental stress-strain curves for common austenitic and duplex stainless steels. The curves shown are representative of the range of material likely to be supplied and should not be used in design.
The selection of an appropriate sub-grade, to provide adequate toughness in design situations is given in BS EN 1993‑1‑10[12] and its associated UK NA[13]. The rules relate the exposure temperature, stress level etc, to a 'limiting thickness' for each sub-grade of steel. PD 6695-1-10[14] contains useful look-up tables and guidance on selection of an appropriate sub-grade is given in ED007.
BS EN 1993-1-4[6] tabulates nominal (characteristic) values of yield strength fy and ultimate minimum tensile strength fu for steels to BS EN 10088-1[7] for use in design.
The mechanical properties apply to hot rolled plate. For cold rolled and hot rolled strip, the specified strengths are 10-17% higher.
Quenching involves cooling a product rapidly by immersion directly into water or oil. It is frequently used in conjunction with tempering which is a second stage heat treatment to temperatures below the austenitizing range. The effect of tempering is to soften previously hardened structures and make them tougher and more ductile.
All structural steels are essentially weldable. However, welding involves locally melting the steel, which subsequently cools. The cooling can be quite fast because the surrounding material, e.g. the beam, offers a large 'heat sink' and the weld (and the heat introduced) is usually relatively small. This can lead to hardening of the 'heat affected zone' (HAZ) and to reduced toughness. The greater the thickness of material, the greater the reduction of toughness.
The product standards also specify the permitted range of values for the ultimate tensile strength (UTS). The minimum UTS is relevant to some aspects of design.
Ohio ZIP code map and Ohio ZIP code list. View all zip codes in OH or use ... 45235. Standard. Cincinnati. Hamilton County. Area Code 513 · 45236. Standard.
The UK National Annex to BS EN 1993-1-1[2] allows the minimum yield value for the particular thickness to be used as the nominal (characteristic) yield strength fy and the minimum tensile strength fu to be used as the nominal (characteristic) ultimate strength.
For hot rolled carbon steels, the number quoted in the designation is the value of yield strength for material up to 16 mm thick. Designers should note that yield strength reduces with increasing plate or section thickness (thinner material is worked more than thick material and working increases the strength). For the two most common grades of steel used in UK, the specified minimum yield strengths and the minimum tensile strength are shown in table below for steels to BS EN 10025-2[1] .
Steelmachinability chart
The strengths of commonly used structural stainless steels range from 170 to 450 N/mm². Austenitic steels have a lower yield strength than commonly used carbon steels; duplex steels have a higher yield strength than common carbon steels. For both austenitic and duplex stainless steels, the ratio of ultimate strength to yield strength is greater than for carbon steels.
Weathering steel is a high strength low alloy steel that resists corrosion by forming an adherent protective rust 'patina', that inhibits further corrosion. No protective coating is needed. It is extensively used in the UK for bridges and has been used externally on some buildings. It is also used for architectural features and sculptural structures such as the Angel of the North.
Materials suitable for a higher class may be used for lower classes but might not be cost effective. Materials within brackets might be considered if some moderate corrosion is acceptable. Accumulation of corrosive pollutants and chlorides will be higher in sheltered locations; hence it might be necessary to choose a recommended grade from the next higher corrosion class.
Thermomechanically rolled steel utilises a particular chemistry of the steel to permit a lower rolling finish temperature of around 700°C. Greater force is required to roll the steel at these lower temperatures, and the properties are retained unless reheated above 650°C. Thermomechanically rolled steel has an 'M' designation.
Steel cools as it is rolled, with a typical rolling finish temperature of around 750°C. Steel that is then allowed to cool naturally is termed 'as-rolled' material. Normalizing takes place when as-rolled material is heated back up to approximately 900°C, and held at that temperature for a specific time, before being allowed to cool naturally. This process refines the grain size and improves the mechanical properties, specifically toughness. Normalized-rolled is a process where the temperature is above 900°C after rolling is completed. This has a similar effect on the properties as normalizing, but it eliminates the extra process of reheating the material. Normalized and normalized-rolled steels have an 'N' designation.
Automatically calculate speed and feed for your Dapra double-sided button / face milling platform program.
The use of high tensile steel can reduce the volume of steel needed but the steel needs to be tough at operating temperatures, and it should also exhibit sufficient ductility to withstand any ductile crack propagation. Therefore, higher strength steels require improved toughness and ductility, which can be achieved only with low carbon clean steels and by maximizing grain refinement. The implementation of the thermomechanical rolling process (TMR) is an efficient way to achieve this.
The properties of structural steel result from both its chemical composition and its method of manufacture , including processing during fabrication. Product standards define the limits for composition, quality and performance and these limits are used or presumed by structural designers. This article reviews the principal properties that are of interest to the designer and indicates the relevant standards for particular products. Specification of steelwork is covered in a separate article.
... cutting tools, and cast iron ductile cast iron machining cutting tools ... Introduction of Metal additive manufacturing work processing · View Exhibition ...
Whether you are out in the hot desert exploring or working the vehicle hard in low range on a sandy beach, the high efficiency Water to Air Intercooler located internally within the manifold stabilises air intake temperatures to deliver safe, consistent power across a broad range of temperatures.
For design, the mechanical properties are derived from minimum values specified in the relevant product standard. Weldability is determined by the chemical content of the alloy, which is governed by limits in the product standard. Durability depends on the particular alloy type - ordinary carbon steel, weathering steel or stainless steel .
Steel derives its mechanical properties from a combination of chemical composition, heat treatment and manufacturing processes. While the major constituent of steel is iron, the addition of very small quantities of other elements can have a marked effect upon the properties of the steel. The strength of steel can be increased by the addition of alloys such as manganese, niobium and vanadium. However, these alloy additions can also adversely affect other properties, such as ductility, toughness and weldability .
It is in the nature of all materials to contain some imperfections. In steel these imperfections take the form of very small cracks. If the steel is insufficiently tough, the 'crack' can propagate rapidly, without plastic deformation and result in a 'brittle fracture'. The risk of brittle fracture increases with thickness, tensile stress, stress raisers and at colder temperatures. The toughness of steel and its ability to resist brittle fracture are dependent on a number of factors that should be considered at the specification stage. A convenient measure of toughness is the Charpy V-notch impact test - see image on the right. This test measures the impact energy required to break a small notched specimen, at a specified temperature, by a single impact blow from a pendulum.




 0086-813-8127573
0086-813-8127573