Turning Insert Selection Guide - turning insert geometry
The angle of the cutting edge of the rapid feed insert is not a constant value; rather, it changes from 0 degrees to 90 degrees depending on the axial depth of cut. When the depth is decreased, the cutting edge angle is also decreased, which results in thinner chips. A cutter with fast feed inserts has a programmed feed per tooth that is related to the maximal diameter of the cutter, also known as the maximal depth of cut (it is equal to the insert radius), as well as the maximal cutting edge angle.
The TNMG turning insert is most commonly used for metal turning, milling, cutting and grooving, thread turning, and other applications that are functionally equivalent. TNMG turning inserts are normally indexable cemented TNMG turning inserts that are replaceable. These inserts are utilised in the machining of nonferrous materials, high temperature alloys, and ferrous materials such as steel and cast iron. TNMG inserts are turning inserts that are ISO standard and are used most regularly in virtually all CNC lathes. Applications in which it is used for Profile Turning and general shaft turning include those in which it is employed. This insert has six different cutting edges..
They are constructed from two different materials: steel (both FSS and HSS varieties) and carbide. The following is an outline of the specifics:
Milling inserts are replacement bits used to process some of the hardest materials. These inserts are designed specifically for milling. Metals such as steel, stainless steel, cast iron, non-ferrous materials, titanium, hardened steel, and plastic can be shaped or cut by them. Other materials include hardened steel. These inserts are often composed of carbide, which allows them to withstand extremely high temperatures and high-speed operations, making them suitable for various jobs like drilling, hole making, finishing, and other similar activities. They are used for making holes, drilling, finishing, and other tasks. Before, they were only offered in a limited variety of shapes, but today you may get one of them in a variety of shapes, such as helical, frustum, elliptical, and so on. During the milling operation, they travel perpendicular to the axis of the machine, which enables them to remove material from the insert’s border.
LNMU inserts are used for cutting steel and stainless steel with or without coolant. These inserts can be used in any cutter that is suited for LNMU, although milling machines are where they are most commonly found. A fast feed milling insert is suitable for use in LNMU machines. In order to get better results, a variety of coatings have been extensively applied to our inserts. For the purpose of satisfying the cutting requirements of various cutting materials, a combination coating consisting of multiple materials, such as TiAlN, TICN, TiN, and Al2O3, may be utilized. The effectiveness of our LNMU insert has been significantly boosted by the use of this coating
The RPMT insert turning tools are your best bet for cutting and radial grooving tasks. Depending on the operation or activity you wish to carry out, you can choose from various forms of RPMT inserts. Cutting at high speeds is an application that is particularly important to the RPMT insert. RPMT inserts are a fantastic option when working on large or medium-sized projects. You may leverage Cutting, sanding, drilling, deformation, and turning are just some of the many tasks that may be accomplished with the help of RPMT inserts. The RPMT inserts are simple to alter, which enables you to make speedy adjustments to the placement and depth of the hole. Additionally, you will be able to cover a variety of measurements, which will make the process of exchanging cutters much simpler.
The carbide inserts known as SEKN1504AFTN are characterized by their high-quality construction, excellent craftsmanship, and long-lasting performance. Compared to conventional welding blades, the SEKN1504AFTN carbide inserts’ high efficiency and excellent wear resistance result in an alloy blade whose processing efficiency is boosted by more than four times. Carbide inserts with the model number SEKN1504AFTN are utilized for milling, turning, threading, and grooving. It may be utilized in the finishing and semi-finishing processes for steel and stainless steel. Metal surface finishing, with its excellent wear resistance and strong chemical stability, possesses flawless smoothness and a nice surface finish, and it is both aesthetically pleasing and functional. The cutting action is corrected using SEKN1504AFTN carbide inserts, and the reduced cutting force can help extend the tool’s life.
Inserts are utilized in sophisticated machining processes. Fast feed inserts are utilized in an advanced cutting procedure that is designed to boost milling efficiency, or more specifically, to increase metal removal rates. When compared to tools that use turning inserts, tools that use fast-feed inserts have a smaller entrance angle and are capable of cutting two to three times faster than methods that use turning inserts.
Most turning is done using a replaceable insert that is gripped in a turning tool body, which is then mounted on the lathe turret. Turning inserts employ highly engineered composite structures, coatings, and geometry features to achieve great accuracy and high material removal rates. Turning inserts are carbide-cutting tips held in place by tool holders and used in lathe machines. Depending on the turning application, these can be used for different finishes such as roughing, medium turning, finishing, and facing. These inserts are available in various shapes per the desired cutting angle and can be used for cutting several materials. Turning inserts are used on lathes for cutting or finishing the outside diameter of a workpiece. Turning inserts can be used to produce cylindrical parts. In its basic form, turning can be defined as the machining of an external surface with the workpiece rotating, or with a single-point cutting tool.
The technology that is currently available for precision casting and forging leads to a reduction in the amount of stock that can be further machined away. For machining applications that need a shallow depth of cut, the newly developed rapid feed WNMU inserts are ideal because of their perfect suitability. Fast feed WNMU inserts have strong clamping and a higher number of teeth for the smaller WNMU inserts than standard fast feed WNMU inserts. Their design layout guarantees a higher tooth density, which enables a significant rise in feed rates during machining at shallower depths of cut, resulting in maximum productivity.
The use of fast feed milling inserts makes it possible to machine material up to three times quicker than with traditional methods. The rapid feed insert combines a shallow depth of cut with a high feed rate per tooth, which leads in increased metal removal rates and allows for the production of additional parts. Since the cutting forces are applied to the machine spindle in an axial direction, this results in increased stability as well as a reduction in vibrations, which in turn helps to extend the life of the quick feed insert. In addition to this, rapid feed inserts save time since they eliminate the need for semi-finishing and cut down on the number of tool changes. The HUANA range of rapid feed insert systems is adaptable to the requirements of every application. In addition, with the professional and experienced assistance of the HUANA team, you will be able to implement Rapid feed inserts in a smooth manner, which will both boost your productivity and your level of competition. The use of face milling with rapid feed inserts is an excellent method for establishing a solid base upon which to perform additional machining steps or complete the finishing process. In the vast majority of cases, you will typically obtain such tight tolerances that the only necessary finishing is the last one.
The size of the turning insert varies according to the requirements of the application as well as the available space for the cutting tool in the application. When the insert size is increased, the stability also increases. Insert sizes typically greater than IC 25 millimeters are utilized for heavy-duty machining (1 inch). In many instances, the size can be decreased throughout the finishing process.
It is important to understand that the workpiece cutting layer will undergo plastic deformation when subjected to the cutter’s front edge extrusion during the cutting process. This will cause the cutting process to become more difficult. This process involves several physical phenomena, including cutting force, heat, tool wear and life, chip curling and breaking, etc. Deformations of the metal influence machining quality, productivity, and cost. End users will find that APMT is an excellent option because it has the potential to boost productivity greatly.
The inner and outer circle turning, end face turning, and shaping of steel components are the primary applications for RPMT1003 inserts. Because of the smoothness of the Cutting with the RPMT1003 insert and the width of the cutting edge belt, it is possible to effectively minimize the resistance to cutting and to improve the service life. The RPMT1003 inserts offer a strong bonding strength between the cutting edge and coating and high wear resistance.
Turning inserts make use of highly developed composite structures, coatings, and geometrical features in order to accomplish both high material removal rates and high levels of precision. Inserts for turning are carbide cutting tips that are used in lathe machines. These tips are held in place by tool holders. These can be utilized for a variety of finishes, including roughing, medium turning, finishing, and facing, depending on the application of turning that is being performed.
In addition to being developed for general-purpose milling operations, the APKT inserts are also optimized for high-performance milling applications. Applications ranging from roughing to finishing may be completed using this tool’s milling process. After that, you may use the APKT carbide inserts with medium to high cutting rates, and they will quickly remove a lot of material.
Staggered Milling Insert – These milling inserts have a zigzag pattern around the perimeter, and users can choose between left-hand and right-hand helix angles.
The geometries of turning inserts can be simplified down to three fundamental types, which are best suited for finishing, medium, and roughing operations respectively. Selecting the positive wiper geometry of the turning insert in order to reduce forces and keep production levels constant in the event of vibration. Both the geometry of the turning inserts and the insert grade are complementary to one another. For instance, the toughness of a grade can make up for the fact that the turning insert geometry doesn’t provide enough strength.
Periphery Milling Insert – This particular milling insert is known as a peripheral milling insert because the teeth contained within it are located around the perimeter of the circular disc. They are incompatible with any milling machines that have a vertical axis.
RDMW1605 inserts have excellent efficiency, high wear resistance, and more than four times the efficiency of processing alloy blades than typical welding blades. The RDMW1605 insert is built with high-quality carbide tips and has excellent craftsmanship. It also possesses high levels of strength and hardness, and its performance is consistent and long-lasting. For the finishing of metal surfaces, the RDMW1605 insert is used. It has excellent wear resistance and chemical stability, flawless smoothness, and a pleasing surface finish, and it is both attractive and functional.
Milling is a process used in producing metal goods and involves removing material from a workpiece using inserts. Cutting or removing these materials from the item could be done differently depending on the range of forms and sizes involved. Hence, inserts used in machinery are as important as the workpiece itself in terms of quality. A metal milling insert is used to smooth or polish the most beautifully completed metal items accessible for everyday use or manufacture. These products can be purchased or produced. Milling machines comprise several important parts, including the milling inserts. The surface of a workpiece is removed with a cutting tool. It includes every milling machine in existence. It is essential for achieving a very high material removal rate even under harsh conditions and may be utilized in dry and wet machining processes.
Milling inserts geometric styles include elliptical, frustum, and helical, previously only available in basic shapes. However, because of recent manufacturer optimizations, far wider ranges of milling insert geometric styles are now available. The temperatures, elements, and manufacturing tasks needed for each shape give it a unique size, figure, and tolerance. The shape dictates these characteristics.
The design of the turning insert should be chosen with consideration given to the needed level of accessibility provided by the tool’s entry angle. In order to ensure the insert’s strength and dependability, the nose angle should be increased to its maximum achievable value. Having said that, this aspect has to be weighed against the several different cuts that need to be carried out. A large nose angle is robust, but it calls for a greater amount of machine power and has a greater propensity to vibrate. A tiny nose angle is weaker and has a smaller cutting edge engagement, both of which might make it more sensitive to the effects of heat. A large nose angle, on the other hand, has a larger cutting edge engagement.
Because of the high accuracy and precision it can provide, CNC machining is one of the methods for subtractive manufacturing that is employed most frequently around the world. The relative motion that is regulated by CNC between the workpiece and the cutting tool is one of the primary contributors to its level of success. Inserts for cutting tools can take on a wide variety of geometric forms. Inserts that are round or circular are utilized in processes such as button milling and radius groove turning respectively. Some varieties can be adjusted so that unused areas of the edge can be utilized once a portion of the edge has been worn away. Thickening, radius (if applicable), and chamfer angle (if applicable) are all important criteria that should be considered for cutting tool inserts. Inserts for cutting tools frequently come with characteristics such as being unground, indexable, chipbreaker, or dished. Attachments for inserts can either be screwed on or have no hole.
Hollow Milling Cutter – It has strong walls, much like a pipe, and resembles a pipe in appearance. It is utilized in screw machines and has bites within the interior of the concave surface.
One of the primary objectives of intelligent manufacturing is to bring about a rise in production productivity while simultaneously bringing down overall production expenses. To be successful in accomplishing this objective, it is vital to maximize performance in all facets of the manufacturing industry. Throughout the course of this procedure, technological advancements have been steadily made, and successively cutting-edge processing methods and conceptualizations have been developed. In order to accomplish this objective, the fast-feed insert and the turning insert were both developed as separate products.
Face Milling Insert – They have a cutter body with a big diameter and many mounting points for insertion tools. Cuts that are axially thin and radially deep are used to remove material from them. The cutter’s body and the workpiece’s length have a role in determining the diameter of the face milling insert. The majority of the time, it is employed for down milling.
CNMG turning inserts with a medium amount of machining at an unstable condition chipbreaker. These inserts feature a shape that is rhombic 80 degrees with a negative geometry. They come in grades that are appropriate for steel, cast iron, and stainless steel. CNMG turning insert offer a carbide turning solution that is both affordable and efficient for individuals who are working with a limited budget. Turning inserts produced by CNMG have an economy-style negative turning insert. Steel, cast iron, and stainless steel are all appropriate substrates for the CNMG turning insert. CNMG turning inserts offer a carbide turning solution that is economical for individuals who are working with a limited budget.
This blog aims to explain what a milling insert is, the many sorts of milling inserts available, the material that the milling insert is constructed from, and some of the most well-known models of milling inserts. Therefore, let’s get started.
The specialized cutting tools known as APMT1135 inserts are single-sided and come equipped with two cutting edges each. Because of the robust geometry design, it is possible to work with cast iron, alloy steel, and stainless steel. It features an extremely well ramping and slotting capability and a powerful pocket design with efficient chip evacuation.
Without taking the tool holder cutter out of the machine, it is possible to switch them out for new inserts of the same or a different type. High-speed, high-feed, and difficult-to-machine metalworking and manufacturing applications require several indexable milling cutters. This is because indexable cutters have a variable cutting depth that can be adjusted.
VNMG Insert, used for applications in the semi-finishing and finishing processes. Low forces required for cutting as a result of the edge’s extreme sharpness and the positive rake. VNMG turning inserts have rhombic indexable carbide turning inserts with a 35 degree angle. Double-sided VNMG turning inserts are utilized for a variety of turning-related applications. The VNMG turning insert comes in a variety of radius options, which can be used for finishing, general purpose, and rough turning respectively. Turning inserts from VNMG can give as many as four distinct cutting edges. Inserts in the shape of a “V” provide a pointed shape that is perfect for finishing and semi-finishing.
The use of a rapid feed insert in profiling, ramping, and face milling, which has a fast cutting speed, helps to boost the efficiency of these operations. The performance of fast feed inserts is optimized for use with high feed rate machining and slice cutting depth. This revolutionary method will help you save time because it is very effective! The use of rapid feed inserts allows for a novel process that combines a high cutting speed with a slice working depth, resulting in improved stability and productivity in the workplace. Machining, the automotive industry, the electronics sector, the aerospace industry, and the mould industry all use fast feed inserts.
Gang Milling Insert – When using the gang milling insert, peripheral milling cutters of varied sizes are utilized to remove and cut material from the workpiece. This is done using the gang milling insert.
A polished surface and a significant rake angle are also features of the design of the uncoated carbide APKT inserts. They are designed to be utilized in the machining of aluminum. Positive-rake inserts have an edge of fewer than ninety degrees, allowing them to lay flat in the insert holder. This results in increased cutting clearance and a better finish than inserts with negative-rake, which have the edge over ninety degrees.
A tool that has a cutting part specifically designed for turning is called a turning insert. One of the cutting instruments that is utilised most frequently is known as the turning insert. The portion of the turning insert that generates and processes the chip is known as the working part of the insert. This portion of the turning insert includes the blade edge, the structure that breaks or rolls the chip, the space for chip removal or chip storage, and the passageway for the cutting fluid.
Steel, stainless steel, exotic materials, and cast iron may all be milled successfully using APKT1003 milling inserts. The cutting edges of APKT1003 milling inserts are helical in shape. Inserts with high surface quality and precision at 90 degrees are found in APKT1003 milling tools. Milling inserts with the model number APKT1003 are often utilized for general purposes. Milling inserts model APKT1003 are interchangeable with holders made by other manufacturers.
The TPKN1603PDER insert has a longer processing life, which helps reduce changing times and boosts overall productivity. The TPKN1603PDER insert has a flawless surface polish. Insert with part number TPKN1603PDER has a high tensile strength and an anti-abrasion finish. Its machining precision, straightforward construction, and use make the TPKN1603PDER insert superior in hardness, toughness, and machining precision.
Compared to milling inserts manufactured from regular carbon steel, those made from high-speed steel (HSS) exhibit superior resistance to wear and heat. It further divides itself into specific and general uses. HSS is a material that has properties such as hardness in the range of HRC62-70, strong cutting-edge strength, and great vibration resistance, among other qualities. Because it is made out of this particular steel, it possesses sharpness, machining, and forging capabilities that are on par with their best. However, in contrast to carbide-made milling inserts, it possesses low levels of hardness and resistance to wear.
Side Milling Insert – Because this type of insert contains teeth on both the face/end and the periphery, it may be used to form narrow slots or cut slots, and it can also be used for face milling and strand milling operations.
Machining aluminum often involves the use of APKT positive-rake parallelogram milling inserts. The carbide uncoated parallelogram milling inserts have the shape of an offset rectangle with four sides and two acute cutting tips at opposing corners. These cutting points each have an angle of 85 degrees. By mounting them on a milling machine, you’ll get an indexable shell milling cutter or an indexable face milling cutter.

The use of fast feed milling inserts is not only quite helpful when it comes to the machining of uneven surfaces with a copy mill, but it is also extremely efficient when it comes to the creation of moulds and dies with cavity milling. In the processes of copy milling and cavity milling, the application will specify the required tool diameter, which makes it simple to choose the appropriate tool. Because it frequently involves skipping pre-machining or pre-drilling, helical interpolation lends itself well to the utilization of fast feed milling inserts for the production of large-diameter holes. In addition to this, it is frequently utilised for plunging operations, which are especially important during the machining of challenging materials such as titanium and other light alloys.
Insert SEKN1203AFN uses high-quality carbide tips and has excellent craftsmanship. It also possesses high levels of strength and hardness, and it is sturdy and long-lasting while in use. The precise cutting action, reduced cutting force, and increased tool life are all features of the SEKN1203AFN insert. The SEKN1203AFN insert is appropriate for processing ordinary steel in addition to ordinary stainless steel. Excellent metal surface polishing, excellent wear resistance, and excellent chemical stability are provided by the SEKN1203AFN insert. Positive Cutting Action Threading Inserts are included on SEKN1203AFN inserts, reducing the cutting force required. Because of its high-strength carbide and fine craftsmanship, the SEKN1203AFN insert has a longer life than comparable tools. Insert SEKN1203AFN is used for milling, turning, threading, and grooving and may be utilized with ordinary steel and stainless steel.
Thanks to their eight cutting edges each, SNMU inserts are able to provide the cost-effective near-90-degree milling solution that is required in today’s market. Incorporating a lead angle of 88 degrees into the machining process gives the operator the opportunity to machine in close proximity to sidewalls, fixture clamps, and other obstacles. In addition to improving the cutter’s efficiency, this function enables high DOC capabilities when used in conjunction with SNMU inserts. There are two different sizes of SNMU inserts available to choose from: 12 millimetres and 16 millimetres. This enables integration into systems that have twin spindles capable of simultaneously executing cutting operations. The SNMU inserts are perfect for machining cast iron and steels in the general machining as well as the automotive sectors because they are designed for roughing and semi-finishing applications respectively. The nickel coating procedure has been done away with, which means that the body of the SNMU inserts may be created out of an ideal material that not only provides excellent performance but is also kind to the environment.
The specialized cutting tools known as APMT inserts are single-sided and come equipped with two cutting blades each. Because of the robust geometry design, it is possible to work with cast iron, alloy steel, and stainless steel. It features an extremely well ramping and slotting capability and a powerful pocket design with efficient chip evacuation.
Roughing End Milling Insert – These cutters remove a significant quantity of material from the workpiece. They are also known as “Pippa” cutters. They function well even when subjected to harsh working circumstances. These inserts feature teeth that are wavy, which results in a surface that is rough finished.

Milling Insert with a Concave Shank – It is a type of formed insert that is intended to be used with a certain workpiece and is built with a specific shape for that workpiece. Its primary application is in coordinating a concave surface with a circular shape.
While it is doing its job, a milling insert is subjected to an incredible amount of pressure and stress. This application of an insert will result in the following:
These extremely hard materials are milled using milling inserts, also used to drill and finish these materials. Examples of extremely hard materials include stainless steel and cast iron. They are capable of milling at horizontal, vertical, and inclined angles, and they can remove chips from the workpiece in a very quick manner. Milling inserts are rotary tools with one tooth or many teeth, depending on the instrument. Milling is a procedure in which each cutter tooth makes a different cut in the workpiece one at a time. Most commonly, grooves, steps, milling planes, shaping surfaces, and other similar tasks are accomplished with their assistance.
End Milling Inserts – The end milling insert is equipped with teeth on both sides, which makes it useful for drilling applications. Flat bottom cutters are often the ones that are familiar with the term “end mil.”
When it comes to rapid feed milling processes, the fast-feed inserts are an essential component. The geometry of the fast-feed inserts, which was developed for the purpose of chip thinning more effectively, requires to ensure that the cutting force components are distributed correctly. There are two primary methodologies that make use of geometry. In the first design, the cutting edge of a milling fast feed insert is required to be in the shape of an arc of a great circle. One other idea revolves around the utilization of one or two straight edges that function as chords of the arc. The tiny cutting edge angle, which is typically between 9 and 17 degrees, is sufficient to meet the needs of chip thinning as well as total cutting force. When it comes to solid carbide Fast-feed inserts and replaceable milling heads, ensuring the geometry of the cutting edge is essential. However, when it comes to indexable milling, the geometry of the cutting edge can be provided by the appropriate location of an insert, even if it has a relatively simple profile.
The inner and outer circle turning, end face turning, and shaping of steel components are the primary applications for RPMT1204 inserts. Because of the smoothness of the Cutting produced by RPMT1204 inserts and the width of the cutting edge belt, it is possible to effectively lower the resistance to cutting and improve the service life. RPMT1204 inserts have a strong bonding strength between the cutting edge and coating, which contributes to their great wear resistance.
WNMG turning inserts feature a rake angle that is in the negative. WNMG turning inserts each contain six cutting blades that are positioned in a different turning section of the tool. HUANA maintains a sizable stock of WNMG turning inserts and also offers expedited shipping on all orders. In order to prevent chipping, WNMG turning inserts are double-sided trigon inserts. These inserts have a negative rake angle that fluctuates along the edge from positive to negative. The WNMG turning inserts have a unique design that helps to prevent cratering.
The TPKN2204PDER insert is appropriate for use in the heavy-duty rough turning of steel and cast steel with a high feed rate at a medium and low speed in poor working circumstances. This type of turning requires a lot of force. Additionally, steel and alloy steel are both appropriate applications for TPKN2204PDER. The TPKN2204PDER insert has increased levels of hardness and toughness, as well as improved machining precision, a straightforward construction, and a user-friendly design.
Simply rotating the APKT insert in the holder allows you to take advantage of the sharp edge of the insert if the cutting edge dulls over time. The APKT inserts come equipped with a positive molded chip breaker that is precision-molded into the I.C. They feature a relief angle of 11 degrees and a cutting edge that has been polished to a sharp point. They have screw holes that were manufactured by ISO standards. In most cases, it is analyzed using a two-edged sword metaphor. On the other hand, each of them has four sharp edges. When they are put on 90° indexable milling cutters, and both edges become dull, they may be installed on 75° indexable milling cutters. The other two edges can be used for different milling applications.
These are more durable than HSS but have less strength. Because of their high stiffness features, they have excellent resistance to wear; nevertheless, they are more likely to peel and shatter because they have a lower strength.
The primary applications for RPMT10T3 inserts include steel component turning (inner and outer circles, end faces, and shaping) and forming. Because of the smoothness of the Cutting with the RPMT10T3 insert and the width of the cutting edge belt, it is possible to effectively minimize the resistance to cutting and to improve the service life. RPMT10T3 inserts have a strong bonding strength between the cutting edge and coating, which contributes to their great wear resistance.
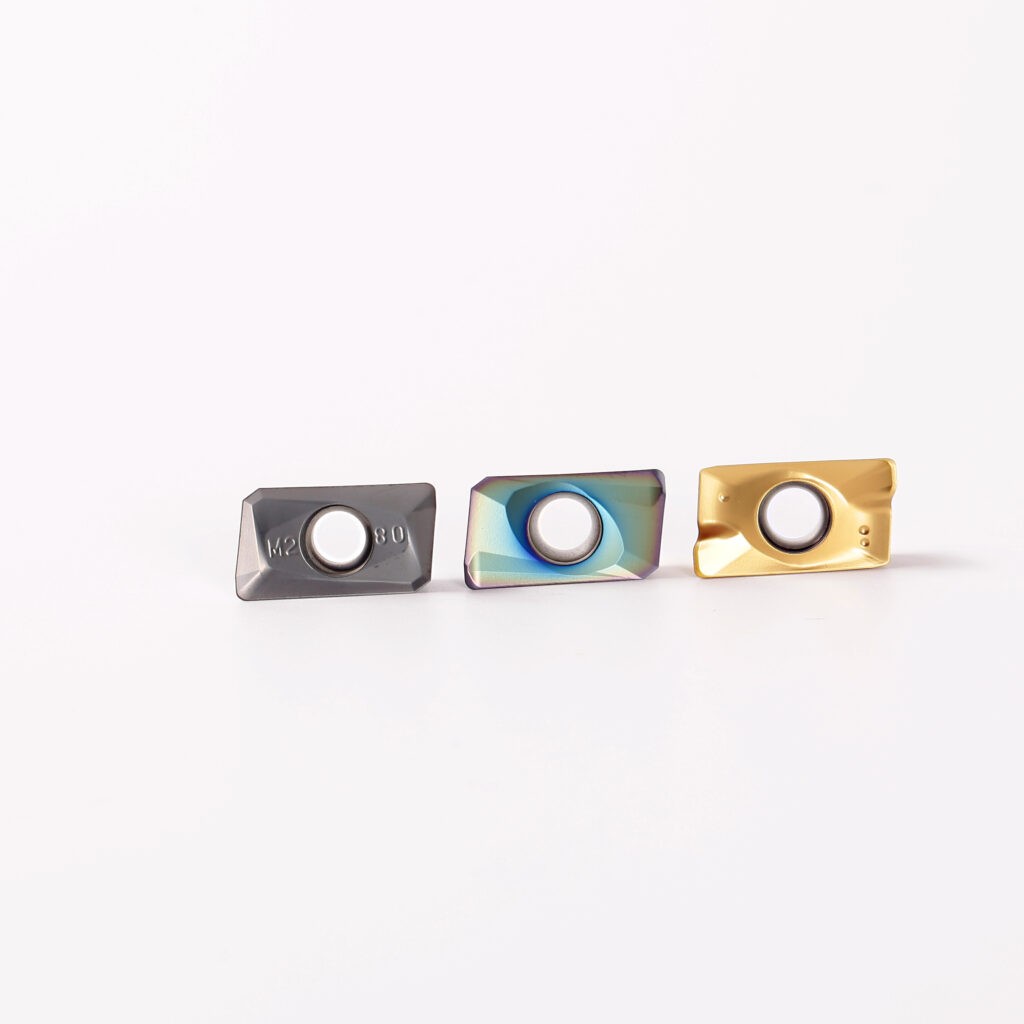
Carbide turning inserts with part number APKT1604-M2-8325 feature a parallelogram of 85 degrees, a relief angle of 11 degrees, and a nose radius of 1/32 inch. Carbide turning inserts APKT1604-M2-8325 are made of tungsten carbide and have a titanium aluminum nitride coating. They have a cutting speed that is four to seven times faster than that of standard steel, and they have been sharpened on a diamond wheel to give them a longer tool life. This will give you a better turning experience and a better cut. Cast iron and non-ferrous materials are both suitable for use with the APKT1604-M2-8325 carbide turning inserts, which are excellent for finishing and roughing. Carbide turning inserts of the type APKT1604-M2-8325 are utilized for indexable face mills and end mills, as well as for milling operations such as square milling and side ramping milling, helical milling, slotting milling, and plunging milling.
However, if the Fast-feed inserts are at a depth that is less than the maximal depth, the chip will be thinner. As a result, the programmed feed will need to be increased proportionally in order to make chips that have the requisite thickness. The similar phenomenon can be seen in Fast-feed inserts, which explains why these inserts are able to run at such a high rate of speed. HUANA provides a vast selection of quick feed inserts, each of which can make use of a greater number of cutting edges and operate more effectively. This guide’s purpose is to facilitate the speedy selection of the most appropriate fast feed inserts for a particular application, taking into consideration the material that will be machined and the kind of operation that will be performed.
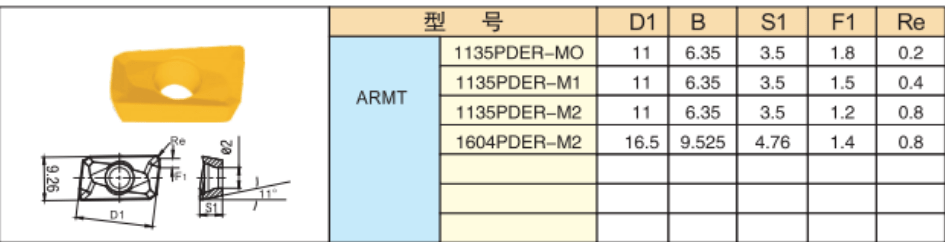
The precision machining, roughing, schedule machining, and stage machining areas are all included in the APMT1604 insert machining area. The APMT1604 insert is constructed of tungsten steel, a material with high hardness and excellent resistance to impact. On the surface, a cutting-edge new coating technique is utilized, which, in addition to being resistant to high temperatures, is also resistant to oxidation. Turning and milling feed rates with the APMT1604 are three times faster than those with standard cutters.
Turning inserts have become more complex in response to developments in materials, machines, methods, and even social factors. Originally marketed for their proficiency in heavy metal removal applications while delivering longer tool life and greater multi-point efficiency, turning inserts have evolved as a result of these advancements. Innovations in the types of materials that need to be cut are an essential component in the creation of turning inserts. Toolmakers have been forced to develop substrates and coatings for both “off-the-shelf” inserts and “special,” or customized, inserts as a result of a new generation of materials, which includes heat-resistant alloys and specially developed customized materials. This has resulted in the strategic development of substrates and coatings.
A turning insert is the name given to the cutting section of a tool that is specifically developed for use with turning. The turning insert is one of the cutting instruments that is used in a turning operation more frequently than any other. The term “working part of the insert” refers to the section of the turning insert that is responsible for the generation and processing of the chip. This section of the turning insert contains the blade edge, the mechanism that either breaks or rolls the chip, the space for chip removal or chip storage, and the path for the cutting fluid. These inserts can be purchased in a variety of shapes to accommodate the appropriate cutting angle, and they are versatile enough to be used for cutting a variety of materials. On lathes, turning inserts are utilized for the purposes of either cutting or finishing the outer diameter of a workpiece. The production of cylindrical pieces can be accomplished with turning inserts. Machining an exterior surface while the workpiece is rotating or using a cutting tool with a single point is the essence of turning, which may also be described as the process of turning.




 18581906093
18581906093