The Ultimate Online Fusion 360 CAD School - fusion 360 website
Cutting speedunit
As of 2018, the Federal Trade Commission (FTC) considers both lab-grown and mined diamonds to be real. The only difference between the two is the point of origin. Unlike mined diamonds, lab-grown diamonds such as CVD diamonds have a guaranteed origin. This means that you can prove that a CVD diamond is not a blood diamond and does not involve unethical production methods.
But an individual diamond, whether lab-grown or mined, is valued based on the 4Cs: carat, cut, clarity, and color. Because CVD diamonds are chemically and physically identical to mined diamonds, they are graded the same way.
To help understand these two concepts, let’s consider a simple analogy of a car moving at a linear speed of 60 km/h, with the wheels rotating at 500 rpm. The diameter of the wheel and its rotation make the car move on paved roads. But when you describe the speed of a vehicle, you explain it in kilometers per hour. Cutting speed can be compared to the linear speed of a car, which depends on the wheel’s diameter and the number of turns. It measures the linear distance the tool moves relative to the workpiece in a certain amount of time. Cutting speed is measured in millimeters per minute (mm/min), meters per minute (m/min), or feet per minute (ft/min).
What is cutting speedformula
CVD Diamonds are lab-grown diamonds made through a process called Chemical Vapor Deposition. This is one of two primary methods for creating lab-grown diamonds. CVD diamonds are produced in a laboratory setting without the negative environmental or human toll of mining.
The feeds for end mills used in vertical milling machines range from 001 to 002 feeds per tooth for very small diameter cutters on steel workpieces to 010 feeds per tooth for large cutters in aluminum workpieces. Since the cutting speed for mild steel is 90, the RPM for a high-speed 3/8″ double-round cutter is:
Spot drilling prevents the drill bit from overheating and breaking when drilling or tapping. It involves drilling through a portion of the part, then withdrawing the drill bit to remove the chips and allowing the piece to cool. A common practice is to turn the chuck a full turn and then back out a half turn. After each withdrawal of the drill or threader, remove as many chips as possible and oil the surface between the drill or threader and the workpiece.
As lab-grown diamonds have grown in popularity — due to their beauty, brilliance, and guaranteed origin — the term “CVD diamonds” has entered the conversation. CVD refers to a method for creating lab-grown diamonds. But this technical term and the diamond-making process it describes is often unfamiliar to shoppers ready to buy a diamond.
Feed per tooth is the amount of material that each tooth of the tool should remove as it rotates and moves toward the workpiece. As the workpiece moves toward the tool, each tooth of the tool moves equally, producing chips of equal thickness. The chip thickness or feed per blade and the number of teeth in the tool are the basis for determining the feed rate. The ideal cutting speed and feed rate are measured in inches per minute (IPM) and are calculated using the following formula:
The most prominent myth about CVD diamonds is that they are not worth anything because they are not as rare or unique as mined diamonds. This is largely false.
CVD diamonds are formed using the same process as mined diamonds, which means every CVD diamond is a unique, one-of-a-kind diamond. They do cost less because CVD diamonds are priced closer to their true value, with no middlemen markups. As such, they will have a lower resell value.
HPHT is more costly and less energy efficient than CVD. This is why most lab-grown diamonds are produced using HPHT. Although HPHT diamonds are free from the human and environmental toll of mining, CVD diamonds are the more sustainable choice. All VRAI created diamonds are produced through CVD.
CVD diamonds do not fade over time, just like mined diamonds do not fade over time. The brilliance and clarity that your CVD diamond has when purchased will always be there if you take proper care of it.
On the other hand, the feed rate can be compared to the rotation of a car’s wheels. It is simply the distance the tool travels during one revolution of the part. We measure it in inches per revolution (inch/rev) or millimeters per revolution (mm/rev). Still using the example of an automobile, a wheel rotating at higher revolutions may use more power and wear faster than a wheel rotating at lower revolutions. This wear is caused by friction and heat between the tire and the road surface. Similarly, spindle speed affects tool life, cutting temperature, and power consumption. Feed rate also affects tool life and energy consumption during machining, but their impact is usually neglected compared to cutting forces. Feed rate, on the other hand, has a greater impact on machining time and surface finish of the machined part. This is important because the choice of cutting parameters affects the product’s final quality. The course of the machining process is different when the cutting speed is low and when it is high. This is why the selection of machining parameters is so important.
Choosing a CVD diamond for your engagement ring or fine jewelry means that you’re celebrating your values alongside your love and personal style.
What is cutting speedin milling
Diamond simulants, or simulated diamonds, refer to gemstones that are used to look like diamonds. This includes moissanite, Herkimer diamonds and cubic zirconia. To the untrained eye, moissanite and cubic zirconia look like diamonds at first glance. But the chemical composition of simulated diamonds is different and inferior to CVD diamonds. Herkimer diamonds are actually a form of quartz crystal.
Not all CVD diamonds are created equal. Many lab-grown diamonds are made in foundries that rely on fossil fuels for energy. Their carbon footprint can be as large as a traditional mine.
It takes one month for a rough CVD diamond to be fully formed. Once formed, a small slice of this diamond is cut off and placed back into the chamber to sustainably repeat the process.
All real diamonds, including CVD diamonds, are made of carbon and graded according to the 4Cs. Diamond simulants are not real diamonds. They are graded differently and of lesser value.
Thankfully, you don’t have to be a scientist to understand CVD diamonds. Read on to discover how CVD diamonds are made and why VRAI created CVD diamonds are right for you.
CVD diamonds are more affordable, real diamonds without the environmentally destructive consequences of diamond mining or potential human rights abuses. Not all lab-grown diamonds are sustainably created. But with a VRAI created CVD diamond you can trust that your diamond is free from human or environmental toll.
CVD diamonds and all lab-grown diamonds are real. They are physically identical to mined diamonds. The only difference between the two is the point of origin.

To determine the optimal cutting speed for a given machining project, the hardness of the workpiece and the tool’s strength must be considered. Hardness determines the material’s resistance to deformation caused by abrasion, dents, or scratches. Harder materials require special attention during machining, as they can easily shorten tool life. In general, the more complex the material, the lower the cutting speed should be. For example, materials such as titanium require lower cutting speeds than steel. The strength of the cutting tool plays an essential role in the allowable cutting speed for a Cutting operation. For example, high speeds can be used when machining tools from high-strength materials such as diamond and boron nitride, while high-speed steel tools require lower speeds.
What is cutting speedcalculator
HPHT diamonds use a thermodynamic process that involves placing a diamond seed into pure carbon, then exposing it to intense pressure and heat. The carbon attaches to the diamond seed in 14 different directions to form a rough diamond with a complex cuboctahedron shape.
The machine motion that causes the cutting tool to cut deep into or along the surface of the workpiece is called the feed rate. When cutting metal, feeds are usually measured in thousandths of an inch. Feed is represented slightly differently in different types of machines. Drilling machines with a motorized feed are designed to move the drill bit by a certain amount each time the spindle rotates. If the feed is set to 0.006″, the machine will move 0.006″ per spindle revolution. This is expressed in inches per revolution (IPR).
Computer numerical control (CNC) machining is one of the world’s most widely used techniques for manufacturing parts because of its high precision. One of the key reasons for its success is the relative motion between the CNC workpiece and the tool. We can classify these movements as cutting and feed movements and measure them with cutting and feed speeds. What is cutting speed, and how is it different from feed rate? How do these processing cutting parameters contribute to the success of a manufacturing project? This article will answer all these questions and more.
If you notice increasing dullness or cloudiness, and you didn’t damage the diamond, it most likely just needs to be cleaned.
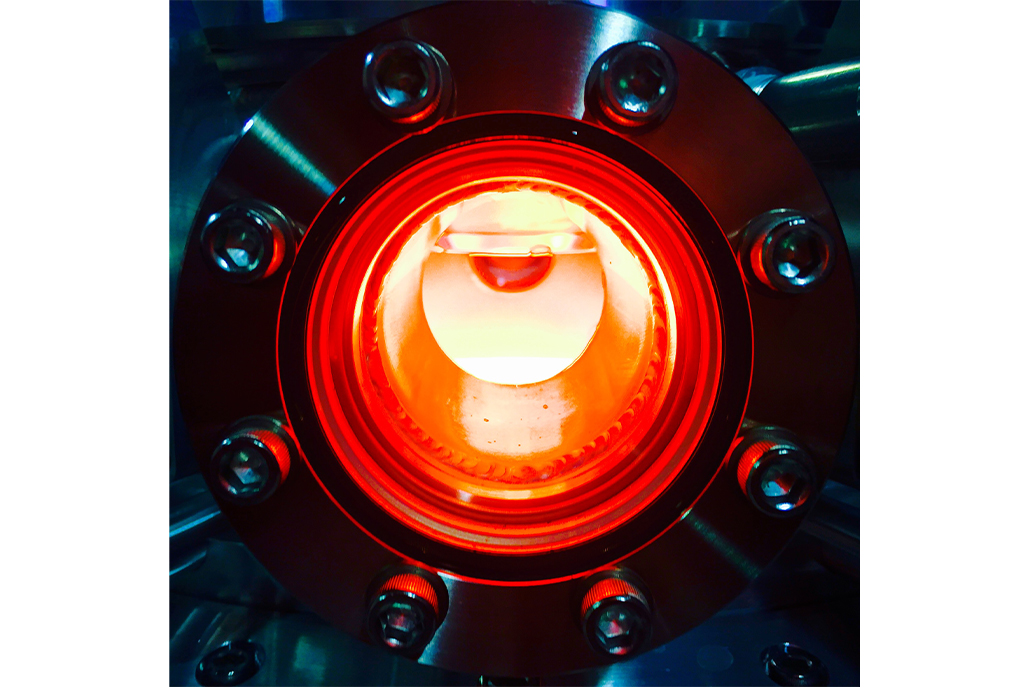
CVD diamonds are made by placing a small diamond slice in a vacuum chamber. This chamber converts carbon-heavy gasses into plasma. Through kinetics, the carbon atoms inside the chamber build on top of the diamond seed in a single vertical direction. The rough diamond then grows into a cleaner square shape.
What is cutting speedand spindlespeed
The naked eye cannot tell the difference between a CVD diamond and mined diamond. Most trained gemologists cannot tell the difference between a polished mined diamond and a polished CVD lab-grown diamond without using advanced technology.
All VRAI created diamonds are made through the CVD process. VRAI is committed to being truly sustainable from start to finish, which is why we use CVD instead of HPHT.
Cutting speedvs feed rate
What is cutting speedof steel
Threading guides are an integral part of creating usable straight threads. The threader is already refined and centered when using a lathe or milling machine. Be careful when setting threaders by hand because a 90° threader guide is much more accurate than the human eye. It is very important to use oil when drilling and tapping. It keeps the drill bit from squeaking, the cut is smoother, chips are removed, and the drill and material do not overheat.
Chip thinning is a manufacturing defect that occurs when machining a workpiece with a cutting width of less than half the tool diameter. This reduces chip load (the amount of material removed during one revolution of the cutting tool), resulting in longer lead times. One way to reduce the impact of thinner chips is to machine the workpiece at high feed rates. This helps increase productivity and tool life. Now that you understand the difference between feed rate and Cutting speed, you will agree that these two machining parameters are essential in CNC machining. However, even if you choose the ideal cutting speed and feed rate, the success of your project depends on the shop you work with. Chipping affects the appropriate depth of cut.
Both lab-grown and mined diamond prices are driven by the market. Like all goods, their price varies depending on supply and demand.
After determining the SFM for a given material and tool, the spindle speed can be calculated, as this value depends on the cutting speed and tool diameter:
All lab-grown diamonds are not CVD diamonds. There are two methods for producing lab-grown diamonds: chemical vapor deposition (CVD) or high pressure, high temperature (HPHT).
Tool feed can be defined as the distance in inches per minute that the work moves into the cutter. On milling machines, the feed rate is independent of the spindle speed. This is great for faster feed rates and for larger, slow-moving tools.
Both methods are based on the same growth process as mined diamonds. All lab-grown diamonds form first as carbon atoms under high temperature and immense pressure, then bond together to grow a crystalline lattice structure. Once fully formed, diamonds are cut and polished to reveal their brilliance.
Due to high demand, and inflated diamond prices, mined diamonds cost more and have a higher resell value than CVD diamonds. However, that doesn’t mean that CVD diamonds aren’t valuable.
VRAI goes above and beyond to protect the future of this planet, our only home. VRAI created diamonds are Carbon Neutral Certified. Our diamonds are grown in the world’s first carbon neutral foundry. We convert greenhouse gas into VRAI created diamonds using 100% hydropower from America’s Columbia River.
Lab-grown diamonds also require less labor and fewer resources to produce. This is why CVD diamonds cost less than mined diamonds.
What is cutting speedin lathe
There are several prominent myths about CVD diamonds, mostly due to the long-standing and false belief that lab-grown diamonds are not real.
Most CVD diamonds are less expensive than mined diamonds. This has nothing to do with their value. The price is based on fewer middlemen and less demand. CVD diamonds (such as VRAI created diamonds) pass through fewer hands than mined diamonds. No mining companies, cartels, or third-party diamond dealers had to be paid to create and set the lab-grown diamond into jewelry.
The hardness of the Cutting tool material also has a big impact on the recommended cutting speed. The harder the drill bit, the higher the cutting speed. The softer the drill bit, the slower the recommended cutting speed.

Explore our full inventory of lab-grown diamonds online or at a VRAI showroom. VRAI created diamonds are the only Carbon Neutral Certified diamonds in the world, grown in our zero-emission foundry using 100% renewable energy. Unmatched in quality and sustainability, shop our full collection of expertly crafted VRAI created diamond jewelry, engagement, and wedding rings.
CVD diamonds are lab-grown diamonds. Lab-grown diamonds are real diamonds. They have the same chemical composition and formation process as mined diamonds. They are graded and tested exactly the same as mined diamonds.




 0086-813-8127573
0086-813-8127573